|
Involuntary Treatment
Involuntary treatment or mandatory treatment refers to medical treatment undertaken without the consent of the person being treated. Involuntary treatment is permitted by law in some countries when overseen by the judiciary through court orders; other countries defer directly to the medical opinions of doctors. Some countries have general legislation allowing for any treatment deemed necessary if an individual is unable to consent to a treatment due to a perceived lack of Mental capacity in England and Wales, capacity, other legislation may specifically deal with involuntary psychiatric treatment of individuals who have been diagnosed with a mental disorder. Psychiatric treatment normally happens in a psychiatric hospital after some form of involuntary commitment, though individuals may be compelled to undergo treatment outside of hospitals via outpatient commitment. The diagnosis of mental disorders can be carried out by some form clinical practitioner, or in some cases law en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Right To Die
The right to die is a concept rooted in the belief that individuals have the Self-ownership, autonomy to make fundamental decisions about their own lives, including the choice to Suicide, end them or undergo voluntary euthanasia, central to the broader notion of Health freedom movement, health freedom. This Rights, right is often associated with cases involving Terminal illness, terminal illnesses or incurable pain, where assisted suicide provides an option for individuals to exercise control over their suffering and dignity. The debate surrounding the right to die frequently centers on the question of whether this decision should rest solely with the individual or involve Government, external authorities, highlighting broader tensions between Civil liberties, personal freedom and societal or legal restrictions. Religious views on suicide, Religious views on the matter vary significantly, with some traditions such as Hinduism (''Prayopavesa'') and Jainism (''Santhara'') permitti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aktion T4
(German, ) was a campaign of Homicide#By state actors, mass murder by involuntary euthanasia which targeted Disability, people with disabilities and the mentally ill in Nazi Germany. The term was first used in post-WWII, war trials against doctors who had been involved in the killings. The name T4 is an abbreviation of 4, a street address of the Chancellery department set up in early 1940, in the Berlin borough of Tiergarten, Berlin, Tiergarten, which recruited and paid personnel associated with Aktion T4. Certain German physicians were authorised to select patients "deemed incurably sick, after most critical medical examination" and then administer to them a "mercy death" (). In October 1939, Adolf Hitler signed a "euthanasia note", backdated to 1 September 1939, which authorised his physician Karl Brandt and ''Reichsleiter'' Philipp Bouhler to begin the killing. The killings took place from September 1939 until the end of World War II in Europe in 1945. Between 275,00 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hippocratic Corpus
The Hippocratic Corpus (Latin: ''Corpus Hippocraticum''), or Hippocratic Collection, is a collection of around 60 early Ancient Greek medical works strongly associated with the physician Hippocrates and his teachings. The Hippocratic Corpus covers many diverse aspects of medicine, from Hippocrates' medical theories to what he devised to be ethical means of medical practice, to addressing various illnesses. Even though it is considered a singular corpus that represents Hippocratic medicine, they vary (sometimes significantly) in content, age, style, methods, and views practiced; therefore, authorship is largely unknown. The ancient commentaries on this corpus, from writers such as Attalion and Oribasius, are myriad. Hippocrates began Western society's development of medicine, through a delicate blending of the art of healing and scientific observations. What Hippocrates was sharing from within his collection of works was not only how to identify symptoms of disease and proper di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ovary
The ovary () is a gonad in the female reproductive system that produces ova; when released, an ovum travels through the fallopian tube/ oviduct into the uterus. There is an ovary on the left and the right side of the body. The ovaries are endocrine glands, secreting various hormones that play a role in the menstrual cycle and fertility. The ovary progresses through many stages beginning in the prenatal period through menopause. Structure Each ovary is whitish in color and located alongside the lateral wall of the uterus in a region called the ovarian fossa. The ovarian fossa is the region that is bounded by the external iliac artery and in front of the ureter and the internal iliac artery. This area is about 4 cm x 3 cm x 2 cm in size.Daftary, Shirish; Chakravarti, Sudip (2011). Manual of Obstetrics, 3rd Edition. Elsevier. pp. 1-16. . The ovaries are surrounded by a capsule, and have an outer cortex and an inner medulla. The capsule is of dense connect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
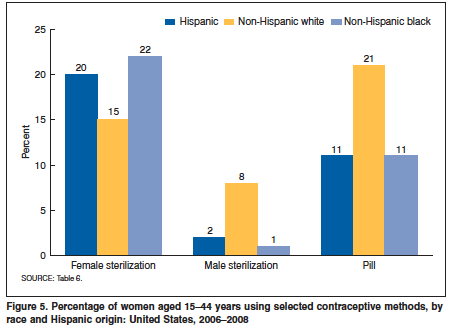
Sterilization (medicine)
Sterilization (American and British English spelling differences, also spelled sterilisation) is any of several medical methods of permanent birth control that intentionally leaves a person unable to Human reproduction, reproduce. Sterilization methods include both surgical and non-surgical options for both males and females. Sterilization procedures are intended to be permanent; reversal is generally difficult. There are multiple ways of having sterilization done, but the two that are used most frequently are tubal ligation for women and vasectomy for men. There are many different ways tubal sterilization can be accomplished. It is extremely effective, and in the United States, surgical complications are low. With that being said, tubal sterilization is still a method that involves surgery, so there is still a danger. Women who choose tubal sterilization may have a higher risk of serious side effects, more than a man has with vasectomies. Pregnancy, Pregnancies after tubal steri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transgender
A transgender (often shortened to trans) person has a gender identity different from that typically associated with the sex they were sex assignment, assigned at birth. The opposite of ''transgender'' is ''cisgender'', which describes persons whose gender identity matches their assigned sex. Often, transgender people desire medical assistance to Gender transition, medically transition from one sex to another; those who do may identify as transsexual.. "The term ''transsexual'' was introduced by Cauldwell (1949) and popularized by Harry Benjamin (1966) [...]. The term ''transgender'' was coined by John Oliven (1965) and popularized by various transgender people who pioneered the concept and practice of transgenderism. It is sometimes said that Virginia Prince (1976) popularized the term, but history shows that many transgender people advocated the use of this term much more than Prince." Referencing .. "The use of terminology by transsexual individuals to self-identify varies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 – 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher and theoretical biologist. He was highly influential in the development of theoretical computer science, providing a formalisation of the concepts of algorithm and computation with the Turing machine, which can be considered a model of a general-purpose computer. Turing is widely considered to be the father of theoretical computer science. Born in London, Turing was raised in southern England. He graduated from University of Cambridge, King's College, Cambridge, and in 1938, earned a doctorate degree from Princeton University. During World War II, Turing worked for the Government Code and Cypher School at Bletchley Park, Britain's codebreaking centre that produced Ultra (cryptography), Ultra intelligence. He led Hut 8, the section responsible for German naval cryptanalysis. Turing devised techniques for speeding the breaking of Germ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Castration
Chemical castration is castration via anaphrodisiac drugs, whether to reduce libido and sexual activity, management of cancer, to treat cancer, or otherwise. Unlike orchiectomy, surgical castration, where the gonads are removed through an incision in the body,"Can Castration Be a Solution for Sex Offenders? Man Who Mutilated Himself in Jail Thinks So, but Debate on Its Effectiveness Continues in Va., Elsewhere" by Candace Rondeaux for the Washington Post, July 5, 2006 chemical castration does not remove organs and is not a form of Human sterilization (surgical procedure), sterilization. Chemical castration is general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schutzstaffel
The ''Schutzstaffel'' (; ; SS; also stylised with SS runes as ''ᛋᛋ'') was a major paramilitary organisation under Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party in Nazi Germany, and later throughout German-occupied Europe during World War II. It began with a small guard unit known as the ''Saal-Schutz'' ("Hall Security") made up of party volunteers to provide security for party meetings in Munich. In 1925, Heinrich Himmler joined the unit, which had by then been reformed and given its final name. Under his direction (1929–1945) it grew from a small paramilitary formation during the Weimar Republic to one of the most powerful organisations in Nazi Germany. From the time of the Nazi Party's rise to power until the regime's collapse in 1945, the SS was the foremost agency of security, mass surveillance, and state terrorism within Germany and German-occupied Europe. The two main constituent groups were the '' Allgemeine SS'' (General SS) and ''Waffen-SS'' (Armed SS). The ''Allgemeine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Action 14f13
Action 14f13, also called '' Sonderbehandlung'' (special treatment) 14f13 and Aktion 14f13, was a campaign by Nazi Germany to murder Nazi concentration camp prisoners. As part of the campaign, also called ''invalid'' or ''prisoner euthanasia'', the sick, the elderly and those prisoners who were no longer deemed fit for work were separated from the rest of the prisoners during a selection process, after which they were murdered. The Nazi campaign was in operation from 1941 to 1944 and later covered other groups of concentration camp prisoners. Background In spring 1941, ''Reichsführer-SS'' Heinrich Himmler met with ''Reichsleiter'' Philipp Bouhler, head of the Hitler Chancellery, to discuss his desire to relieve concentration camps of ''excess ballast'', sick prisoners and those no longer able to work. Bouhler was Hitler's agent for implementation of ''Aktion T4'', the ''euthanasia'' program for the mentally ill, disabled and inmates of hospitals and nursing homes deemed unworth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Holocaust
The Holocaust (), known in Hebrew language, Hebrew as the (), was the genocide of History of the Jews in Europe, European Jews during World War II. From 1941 to 1945, Nazi Germany and Collaboration with Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy, its collaborators systematically murdered some six million Jews across German-occupied Europe, around two-thirds of Europe's Jewish population. The murders were carried out primarily through mass shootings and poison gas in extermination camps, chiefly Auschwitz concentration camp#Auschwitz II-Birkenau, Auschwitz-Birkenau, Treblinka extermination camp, Treblinka, Belzec extermination camp, Belzec, Sobibor extermination camp, Sobibor, and Chełmno extermination camp, Chełmno in Occupation of Poland (1939–1945), occupied Poland. Separate Nazi persecutions killed a similar or larger number of non-Jewish civilians and prisoners of war (POWs); the term ''Holocaust'' is sometimes used to include the murder and persecution of Victims of Nazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auschwitz Concentration Camp
Auschwitz, or Oświęcim, was a complex of over 40 Nazi concentration camps, concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in Polish areas annexed by Nazi Germany, occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It consisted of #Auschwitz I, Auschwitz I, the main camp (''Stammlager'') in Oświęcim; #Auschwitz II-Birkenau, Auschwitz II-Birkenau, a concentration and extermination camp with gas chambers, #Auschwitz III, Auschwitz III-Monowitz, a Arbeitslager, labour camp for the chemical conglomerate IG Farben, and List of subcamps of Auschwitz, dozens of subcamps. The camps became a major site of the Nazis' final solution, Final Solution to the Jewish question. After Germany Causes of World War II#Invasion of Poland, initiated World War II by Invasion of Poland, invading Poland in September 1939, the ''Schutzstaffel'' (SS) converted Auschwitz I, an army barracks, into a prisoner-of-war camp. The initial transpo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |