|
Inuinnaqtun Language
Inuinnaqtun (, ; natively meaning 'like the real human beings/peoples') is an Inuit language. It is spoken in the central Canadian Arctic. It is related very closely to Inuktitut, and some scholars, such as Richard Condon, believe that Inuinnaqtun is more appropriately classified as a dialect of Inuktitut. The government of Nunavut recognises Inuinnaqtun as an official language in addition to Inuktitut, and together sometimes referred to as Inuktut.''Official Languages Act'', S.Nu. 2008, c. 10 s. 3(1) wit s. 1(2). It is spoken in the |
Nunavut
Nunavut is the largest and northernmost Provinces and territories of Canada#Territories, territory of Canada. It was separated officially from the Northwest Territories on April 1, 1999, via the ''Nunavut Act'' and the Nunavut Land Claims Agreement, ''Nunavut Land Claims Agreement Act'', which provided this territory to the Inuit for self-government. The boundaries had been drawn in 1993. The creation of Nunavut resulted in the territorial evolution of Canada, first major change to Canada's political map in half a century since the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Newfoundland (now Newfoundland and Labrador) was admitted in 1949. Nunavut comprises a major portion of Northern Canada and most of the Arctic Archipelago. Its vast territory makes it the list of the largest country subdivisions by area, fifth-largest country subdivision in the world, as well as North America's second-largest (after Greenland). The capital Iqaluit (formerly "Frobisher Bay"), on Baffin Island in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inuktut
Inuktut is the collective name for the Inuit languages. It is used by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami, the Inuit Circumpolar Council, and the Government of Nunavut throughout Inuit Nunaat and Inuit Nunangat. Usage Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami (ITK) says "Inuktut is the language of Inuit spoken across Inuit Nunangat." According to ITK, it encompasses Inuvialuktun, Inuinnaqtun, Inuktitut, and Inuttut. The Inuit Circumpolar Council (ICC) indicates that in Canada Inuktut includes Inuvialuktun, Inuinnaqtun, and Inuktitut. The Government of Nunavut says that Inuktut encompasses the Inuit languages of Nunavut. The term is often used specifically to refer to the Inuit languages of Nunavut: Inuinnaqtun, spoken in Cambridge Bay and Kugluktuk Kugluktuk (, ; Inuktitut syllabics: ; ), known as Coppermine until 1 January 1996, is a hamlet at the mouth of the Coppermine River in the Kitikmeot Region of Nunavut, Canada, on Coronation Gulf, southwest of Victoria Island. It is Nunavut's ..., and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Utkuhiksalik
Utkuhiksalik, also known as Utkuhikhalik, Utkuhikhaliq, Utkuhiksalingmiutitut, Utkuhiksalingmiutut,Briggs, J. L. (1970), Never in anger. Portrait of an Eskimo family. Harvard University Press. Utkuhiksalingmiut Inuktitut, Utku,, or the Gjoa Haven dialect, is a sub-dialect of Natsilingmiutut (''Nattili┼ŗmiut'') dialect of Inuvialuktun (Western Canadian Inuit or Inuktitut) language once spoken in the Utkuhiksalik (ßÉģßæ”ßæ»ßō»ßÆāßō┤ßōĢßÆā Chantrey Inlet) area of Nunavut, and now spoken mainly by elders in Uqsuqtuuq (or Uq┼Īuqtuuq ßÉģߢģßō▒ߢģßææߢģ Gjoa Haven) and Qamani'tuaq (ߢāßƬßōéŌĆøßæÉßÉŖߢģ Baker Lake) on mainland Canada. It is generally written in Inuktitut syllabics. The traditional territory of the Utkuhiksalingmiut / Utkuhikhalingmiut / Ukkusiksalingmiut / Utkusiksalinmiut / Ukkuhikhalinmiut (meaning "the people of the place where there is soapstone" or "people who have cooking pots") people lay between Chantrey Inlet and Franklin Lake. They made their pots (''utkuhi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Natsilingmiutut
Natchilingmiutut (ßōćßæ”ßĢĀßōĢߢĢßÆźßÉģßæÉßæ”), Netsilik , Natsilik, Nattilik, Netsilingmiut, Natsilingmiutut, Nattilingmiutut, or Nattili┼ŗmiutut is an Inuit language variety spoken in western Nunavut, Canada, by Netsilik Inuit. ( 'people from Natchilik') came from 'seal' + postbase 'place with something' + postbase 'inhabitants of'. Classification * There are three main dialect divisions of Natsilingmiutut dialect: ** Natsilik subdialect, or Natsilik/Netsilik proper ** Arviligjuaq subdialect ** Illuiliq subdialect Special letters Natsilik dialect has the special letters: , used by some Nattili┼ŗmiut speakers. New encodings in Unicode were proposed for the Inuktitut syllabics Inuktitut syllabics (, or , ) is an abugida-type writing system used in Canada by the Inuktitut-speaking Inuit of the Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Nunavut and the Nunavik region of Quebec. In 1976, the Language Commission of ... corresponding to ''h'' and ''┼Ī'': æ¬┤ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Inuktitut Syllabics
Inuktitut syllabics (, or , ) is an abugida-type writing system used in Canada by the Inuktitut-speaking Inuit of the Provinces and territories of Canada, territory of Nunavut and the Nunavik region of Quebec. In 1976, the Language Commission of the Inuit Cultural Institute made it the co-official script for the Inuit languages, along with the Latin script. The name derives from the root , meaning "mouth". The alternative, Latin-based writing system is named Inuit languages#Writing, (), and it derives from , a word describing the markings or the grain in rocks. meaning "new writing system" is to be seen in contrast to (), the "old syllabics" used before the reforms of 1976. Inuktitut is one variation on Canadian Aboriginal syllabics, and can be digitally encoded using the Unicode standard. The Unicode block for Inuktitut characters is called Unified Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics (Unicode block), Unified Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics. History The first efforts to write In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Canadian Broadcasting Corporation
The Canadian Broadcasting Corporation (), branded as CBC/Radio-Canada, is the Canadian Public broadcasting, public broadcaster for both radio and television. It is a Crown corporation that serves as the national public broadcaster, with its English-language and French-language service units known as CBC and Radio-Canada, respectively. Although some local stations in Canada predate its founding, the CBC is the oldest continually-existing broadcasting network in Canada. The CBC was established on November 2, 1936. The CBC operates four terrestrial radio networks: The English-language CBC Radio One and CBC Music, and the French-language Ici Radio-Canada Premi├©re and Ici Musique (international radio service Radio Canada International historically transmitted via shortwave radio, but since 2012 its content is only available as podcasts on its website). The CBC also operates two terrestrial television networks, the English-language CBC Television and the French-language Ici Radio-C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Latin Script
The Latin script, also known as the Roman script, is a writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae in Magna Graecia. The Greek alphabet was altered by the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans, and subsequently their alphabet was altered by the Ancient Romans. Several Latin-script alphabets exist, which differ in graphemes, collation and phonetic values from the classical Latin alphabet. The Latin script is the basis of the International Phonetic Alphabet (IPA), and the 26 most widespread letters are the letters contained in the ISO basic Latin alphabet, which are the same letters as the English alphabet. Latin script is the basis for the largest number of alphabets of any writing system and is the List of writing systems by adoption, most widely adopted writing system in the world. Latin script is used as the standard method of writing the languages of Western and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kangiryuarmiutun
''Kangiryuarmiutun'' (sometimes ''Kangirjuarmiut(un)'') is a dialect of Inuit languages, Inuit language spoken in Ulukhaktok, Northwest Territories, Canada by the Kangiryuarmiut, a Copper Inuit group. The dialect is part of the Inuvialuktun language. The people of Ulukhaktok prefer to think of it as Inuinnaqtun and it is essentially the same. It is derived from Prince Albert Sound, Kangiryuak (meaning "the big bay"), and named for the people that lived there, the Kangiryuarmiut, which is known by its English language, English name Prince Albert Sound, Victoria Island (Canada), Victoria Island. Victoria Island is the ancestral home of the Copper Inuit. Vocabulary comparison The comparison of some animal names in the Siglitun and Kangiryuarmiutun subdialects of the Inuinnaqtun dialect of Inuvialuktun: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
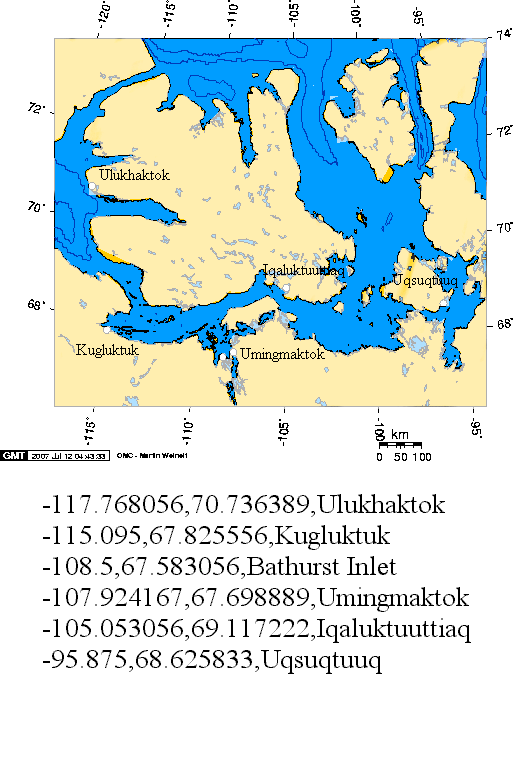
Ulukhaktok
Ulukhaktok ((Kangiryuarmiutun (Inuit): , ) and known until 1 April 2006 as ''Holman'' or ''Holman Island'') is a small Inuvialuit Settlement Region hamlet on the west coast of Victoria Island, in the Inuvik Region of the Northwest Territories, Canada. Like other small traditional communities in the territories, hunting, trapping, and fishing are major sources of income, but printmaking has taken over as the primary source of income in recent years. The two principal languages in Ulukhaktok are the Kangiryuarmiutun dialect of Inuinnaqtun, which is part of the Inuvialuktun group, and English. The village has the world's most northerly golf course. The community was covered in the Inuvialuit Final Agreement as part of their land claims and is in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. History The first people to settle in the area were Natkusiak and his family in 1937. Two years later, the Hudson's Bay Company relocated from Walker Bay and a Roman Catholic mission was opened the sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kitikmeot Region
Kitikmeot Region (; Inuktitut: ''Qitirmiut'' ) is an List of regions of Nunavut, administrative region of Nunavut, Canada. It consists of the southern and eastern parts of Victoria Island with the adjacent part of the mainland as far as the Boothia Peninsula, together with King William Island and the southern portion of Prince of Wales Island (Nunavut), Prince of Wales Island. The regional centre is Cambridge Bay (population 1,760). Before 1999, Kitikmeot Region existed under slightly different boundaries as Kitikmeot Region, Northwest Territories. Transportation Access to the territorial capital of Iqaluit is difficult and expensive as there are no direct flights from Kitikmeot Region communities to Iqaluit. For example, Iqaluit is approximately from Kugaaruk, the closest Kitikmeot community. A one-way flight to the capital costs between $3,000 and $4,000 (as of April 2025) and involves flying to, along with an overnight stay in, Yellowknife, Northwest Territories, approxi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gjoa Haven
Gjoa Haven (; Inuktitut: Uqsuqtuuq, syllabics: ßÉģߢģßō▒ߢģßææߢģ , meaning "lots of fat", referring to the abundance of sea mammals in the nearby waters; or Ī╩Æ╔öa ev╔Ön is an Inuit hamlet in Nunavut, above the Arctic Circle, located in the Kitikmeot Region, northeast of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories. It is the only settlement on King William Island. Etymology The name Gjoa Haven is from the Norwegian or "Gj├Ėa's Harbour"; it was named by early 20th-century polar explorer Roald Amundsen after his ship '' Gj├Ėa.'' History In 1903, the Norwegian explorer Roald Amundsen had entered the area on his ship ''Gj├Ėa'' in an expedition intending to travel through the Northwest Passage. By October the straits through which he was travelling began to ice up. Amundsen put ''Gj├Ėa'' into a natural harbour on the southeast coast of King William Island. He stayed there, in what Amundsen called "the finest little harbor in the world", for nearly two years. He and his crew spent m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |