|
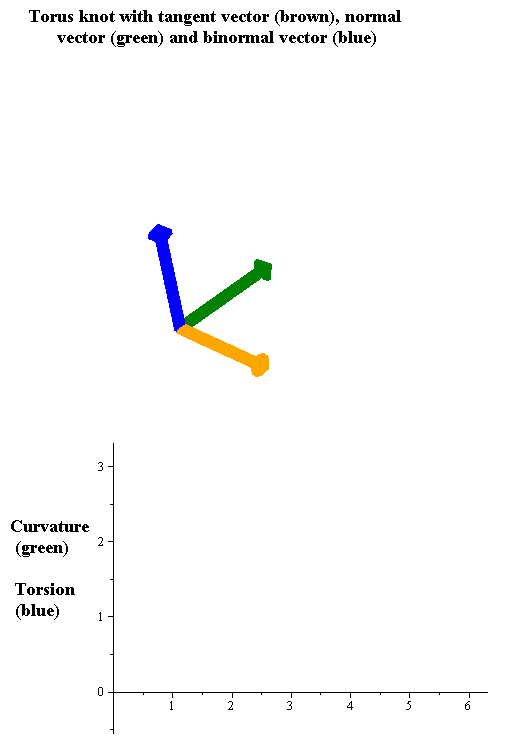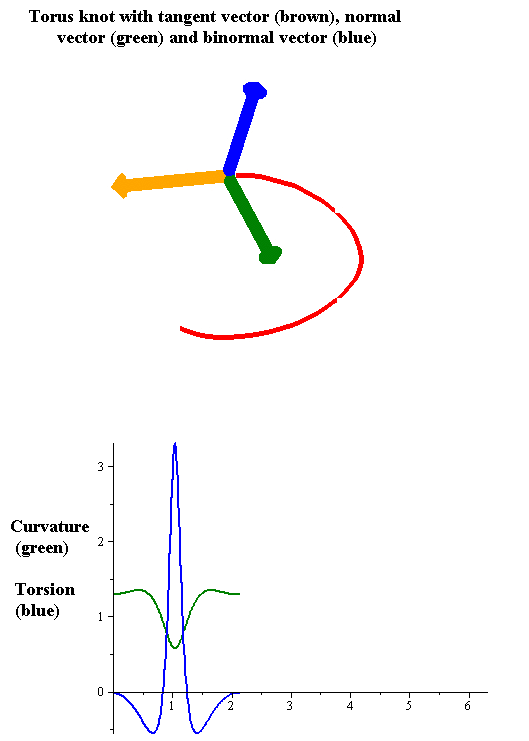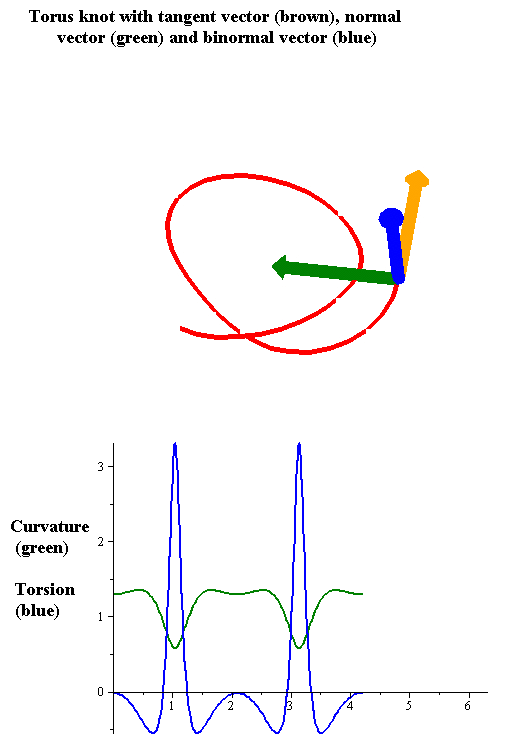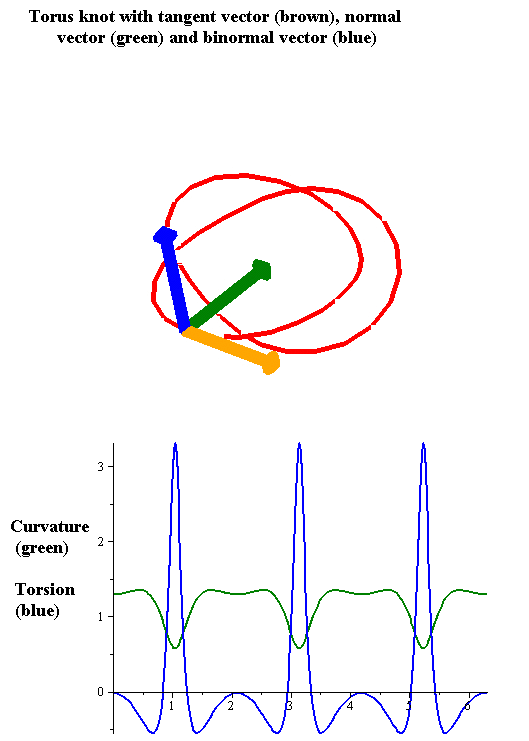
Intrinsic Curve
In geometry, an intrinsic equation of a curve is an equation that defines the curve using a relation between the curve's intrinsic properties, that is, properties that do not depend on the location and possibly the orientation of the curve. Therefore an intrinsic equation defines the shape of the curve without specifying its position relative to an arbitrarily defined coordinate system. The intrinsic quantities used most often are arc length s , tangential angle \theta , curvature \kappa or radius of curvature, and, for 3-dimensional curves, torsion \tau . Specifically: * The natural equation is the curve given by its curvature and torsion. * The Whewell equation is obtained as a relation between arc length and tangential angle. * The Cesàro equation In geometry, the Cesàro equation of a plane curve is an equation relating the curvature () at a point of the curve to the arc length () from the start of the curve to the given point. It may also be given as an equation rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is a branch of mathematics concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. Geometry is, along with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''List of geometers, geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point (geometry), point, line (geometry), line, plane (geometry), plane, distance, angle, surface (mathematics), surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. Originally developed to model the physical world, geometry has applications in almost all sciences, and also in art, architecture, and other activities that are related to graphics. Geometry also has applications in areas of mathematics that are apparently unrelated. For example, methods of algebraic geometry are fundamental in Wiles's proof of Fermat's Last Theorem, Wiles's proof of Fermat's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve
In mathematics, a curve (also called a curved line in older texts) is an object similar to a line, but that does not have to be straight. Intuitively, a curve may be thought of as the trace left by a moving point. This is the definition that appeared more than 2000 years ago in Euclid's ''Elements'': "The urvedline is ��the first species of quantity, which has only one dimension, namely length, without any width nor depth, and is nothing else than the flow or run of the point which ��will leave from its imaginary moving some vestige in length, exempt of any width." This definition of a curve has been formalized in modern mathematics as: ''A curve is the image of an interval to a topological space by a continuous function''. In some contexts, the function that defines the curve is called a ''parametrization'', and the curve is a parametric curve. In this article, these curves are sometimes called ''topological curves'' to distinguish them from more constrained curves su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation
In mathematics, an equation is a mathematical formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. Solving an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. The " =" symbol, which appears in every equati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Relation (mathematics)
In mathematics, a relation denotes some kind of ''relationship'' between two mathematical object, objects in a Set (mathematics), set, which may or may not hold. As an example, "''is less than''" is a relation on the set of natural numbers; it holds, for instance, between the values and (denoted as ), and likewise between and (denoted as ), but not between the values and nor between and , that is, and both evaluate to false. As another example, "''is sister of'' is a relation on the set of all people, it holds e.g. between Marie Curie and Bronisława Dłuska, and likewise vice versa. Set members may not be in relation "to a certain degree" – either they are in relation or they are not. Formally, a relation over a set can be seen as a set of ordered pairs of members of . The relation holds between and if is a member of . For example, the relation "''is less than''" on the natural numbers is an infinite set of pairs of natural numbers that contains both and , b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordinate System
In geometry, a coordinate system is a system that uses one or more numbers, or coordinates, to uniquely determine and standardize the position of the points or other geometric elements on a manifold such as Euclidean space. The coordinates are not interchangeable; they are commonly distinguished by their position in an ordered tuple, or by a label, such as in "the ''x''-coordinate". The coordinates are taken to be real numbers in elementary mathematics, but may be complex numbers or elements of a more abstract system such as a commutative ring. The use of a coordinate system allows problems in geometry to be translated into problems about numbers and ''vice versa''; this is the basis of analytic geometry. Common coordinate systems Number line The simplest example of a coordinate system is the identification of points on a line with real numbers using the '' number line''. In this system, an arbitrary point ''O'' (the ''origin'') is chosen on a given line. The coordinate o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Length
Arc length is the distance between two points along a section of a curve. Development of a formulation of arc length suitable for applications to mathematics and the sciences is a problem in vector calculus and in differential geometry. In the most basic formulation of arc length for a vector valued curve (thought of as the trajectory of a particle), the arc length is obtained by integrating speed, the magnitude of the velocity vector over the curve with respect to time. Thus the length of a continuously differentiable curve (x(t),y(t)), for a\le t\le b, in the Euclidean plane is given as the integral L = \int_a^b \sqrt\,dt, (because \sqrt is the magnitude of the velocity vector (x'(t),y'(t)), i.e., the particle's speed). The defining integral of arc length does not always have a closed-form expression, and numerical integration may be used instead to obtain numerical values of arc length. Determining the length of an irregular arc segment by approximating the arc segment as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangential Angle
In geometry, the tangential angle of a curve in the Cartesian plane, at a specific point, is the angle between the tangent line to the curve at the given point and the -axis. (Some authors define the angle as the deviation from the direction of the curve at some fixed starting point. This is equivalent to the definition given here by the addition of a constant to the angle or by rotating the curve.) Equations Parametric If a curve is given parametrically by , then the tangential angle at is defined (up to a multiple of ) by : \frac = (\cos \varphi,\ \sin \varphi). Here, the prime symbol denotes the derivative with respect to . Thus, the tangential angle specifies the direction of the velocity vector , while the speed specifies its magnitude. The vector :\frac is called the unit tangent vector, so an equivalent definition is that the tangential angle at is the angle such that is the unit tangent vector at . If the curve is parametrized by arc length , so , then the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry that intuitively measure the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line or by which a surface deviates from being a plane. If a curve or surface is contained in a larger space, curvature can be defined ''extrinsically'' relative to the ambient space. Curvature of Riemannian manifolds of dimension at least two can be defined ''intrinsically'' without reference to a larger space. For curves, the canonical example is that of a circle, which has a curvature equal to the reciprocal of its radius. Smaller circles bend more sharply, and hence have higher curvature. The curvature ''at a point'' of a differentiable curve is the curvature of its osculating circle — that is, the circle that best approximates the curve near this point. The curvature of a straight line is zero. In contrast to the tangent, which is a vector quantity, the curvature at a point is typically a scalar q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius Of Curvature (mathematics)
In differential geometry, the radius of curvature, , is the reciprocal of the curvature. For a curve, it equals the radius of the circular arc which best approximates the curve at that point. For surfaces, the radius of curvature is the radius of a circle that best fits a normal section or combinations thereof. Definition In the case of a space curve, the radius of curvature is the length of the curvature vector. In the case of a plane curve, then is the absolute value of : R \equiv \left, \frac \ = \frac, where is the arc length from a fixed point on the curve, is the tangential angle and is the curvature. Formula In two dimensions If the curve is given in Cartesian coordinates as , i.e., as the graph of a function, then the radius of curvature is (assuming the curve is differentiable up to order 2) R =\left, \frac \\,, where y' = \frac\,, y'' = \frac, and denotes the absolute value of . If the curve is given parametrically by functions and , then the radiu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torsion Of A Curve
In the differential geometry of curves in three dimensions, the torsion of a curve measures how sharply it is twisting out of the osculating plane. Taken together, the curvature and the torsion of a space curve are analogous to the curvature of a plane curve. For example, they are coefficients in the system of differential equations for the Frenet frame given by the Frenet–Serret formulas. Definition Let be a space curve parametrized by arc length and with the unit tangent vector . If the curvature of at a certain point is not zero then the principal normal vector and the binormal vector at that point are the unit vectors : \mathbf=\frac, \quad \mathbf=\mathbf\times\mathbf respectively, where the prime denotes the derivative of the vector with respect to the parameter . The torsion measures the speed of rotation of the binormal vector at the given point. It is found from the equation : \mathbf' = -\tau\mathbf. which means : \tau = -\mathbf\cdot\math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Equation
Nature is an inherent character or constitution, particularly of the ecosphere or the universe as a whole. In this general sense nature refers to the laws, elements and phenomena of the physical world, including life. Although humans are part of nature, human activity or humans as a whole are often described as at times at odds, or outright separate and even superior to nature. During the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries, nature became the passive reality, organized and moved by divine laws. With the Industrial Revolution, nature increasingly became seen as the part of reality deprived from intentional intervention: it was hence considered as sacred by some traditions (Rousseau, American transcendentalism) or a mere decorum for divine providence or human history (Hegel, Marx). However, a vitalist vision of nature, closer to the pre-Socratic one, got reborn at the same time, especially after Charles Darwin. Within the various uses of the word t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whewell Equation
The Whewell equation of a plane curve is an equation that relates the tangential angle () with arc length (), where the tangential angle is the angle between the tangent to the curve at some point and the -axis, and the arc length is the distance along the curve from a fixed point. These quantities do not depend on the coordinate system used except for the choice of the direction of the -axis, so this is an intrinsic equation of the curve, or, less precisely, ''the'' intrinsic equation. If one curve is obtained from another curve by translation then their Whewell equations will be the same. When the relation is a function, so that tangential angle is given as a function of arc length, certain properties become easy to manipulate. In particular, the derivative of the tangential angle with respect to arc length is equal to the curvature. Thus, taking the derivative of the Whewell equation yields a Cesàro equation for the same curve. The concept is named after William Whewell, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |