|
Interleaved Polling With Adaptive Cycle Time
Interleaved polling with adaptive cycle time (IPACT) is an algorithm designed by Glen Kramer, Biswanath Mukherjee and Gerry Pesavento of the Advanced Technology Lab at the University of California, Davis in 2002. IPACT is a dynamic bandwidth allocation algorithm for use in Ethernet passive optical networks (EPONs). IPACT uses the Gate and Report messages provided by the EPON Multi-Point Control Protocol (MPCP) to allocate bandwidth to Optical Network Units (ONUs). If the optical line terminal grants bandwidth to an ONU and waits until it has received that particular ONU's transmission before granting bandwidth to another ONU, then time equivalent to a whole messaging round-trip is wasted during which the upstream may remain idle. IPACT eliminates this idle time by sending downstream grant messages to succeeding ONUs while receiving transmission Transmission may refer to: Medicine, science and technology * Power transmission ** Electric power transmission ** Propulsion trans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing calculations and data processing. More advanced algorithms can perform automated deductions (referred to as automated reasoning) and use mathematical and logical tests to divert the code execution through various routes (referred to as automated decision-making). Using human characteristics as descriptors of machines in metaphorical ways was already practiced by Alan Turing with terms such as "memory", "search" and "stimulus". In contrast, a heuristic is an approach to problem solving that may not be fully specified or may not guarantee correct or optimal results, especially in problem domains where there is no well-defined correct or optimal result. As an effective method, an algorithm can be expressed within a finite amount of spac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of California, Davis
The University of California, Davis (UC Davis, UCD, or Davis) is a public land-grant research university near Davis, California. Named a Public Ivy, it is the northernmost of the ten campuses of the University of California system. The institution was first founded as an agricultural branch of the system in 1905 and became the seventh campus of the University of California in 1959. The university is classified among "R1: Doctoral Universities – Very high research activity". The UC Davis faculty includes 23 members of the National Academy of Sciences, 30 members of the American Academy of Arts and Sciences, 17 members of the American Law Institute, 14 members of the Institute of Medicine, and 14 members of the National Academy of Engineering. Among other honors that university faculty, alumni, and researchers have won are two Nobel Prizes, one Fields Medal, a Presidential Medal of Freedom, three Pulitzer Prizes, three MacArthur Fellowships, and a National Medal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation
Dynamic bandwidth allocation is a technique by which traffic bandwidth in a shared telecommunications medium can be allocated on demand and fairly between different users of that bandwidth. This is a form of bandwidth management, and is essentially the same thing as statistical multiplexing. Where the sharing of a link adapts in some way to the instantaneous traffic demands of the nodes connected to the link. Dynamic bandwidth allocation takes advantage of several attributes of shared networks: # all users are typically not connected to the network at one time # even when connected, users are not transmitting data (or voice or video) at all times # most traffic occurs in bursts—there are gaps between packets of information that can be filled with other user traffic Different network protocols implement dynamic bandwidth allocation in different ways. These methods are typically defined in standards developed by standards bodies such as the ITU, IEEE, FSAN, or IETF. One ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 1983 as IEEE 802.3. Ethernet has since been refined to support higher bit rates, a greater number of nodes, and longer link distances, but retains much backward compatibility. Over time, Ethernet has largely replaced competing wired LAN technologies such as Token Ring, FDDI and ARCNET. The original 10BASE5 Ethernet uses coaxial cable as a shared medium, while the newer Ethernet variants use twisted pair and fiber optic links in conjunction with switches. Over the course of its history, Ethernet data transfer rates have been increased from the original to the latest , with rates up to under development. The Ethernet standards include several wiring and signaling variants of the OSI physical layer. Systems communicating over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
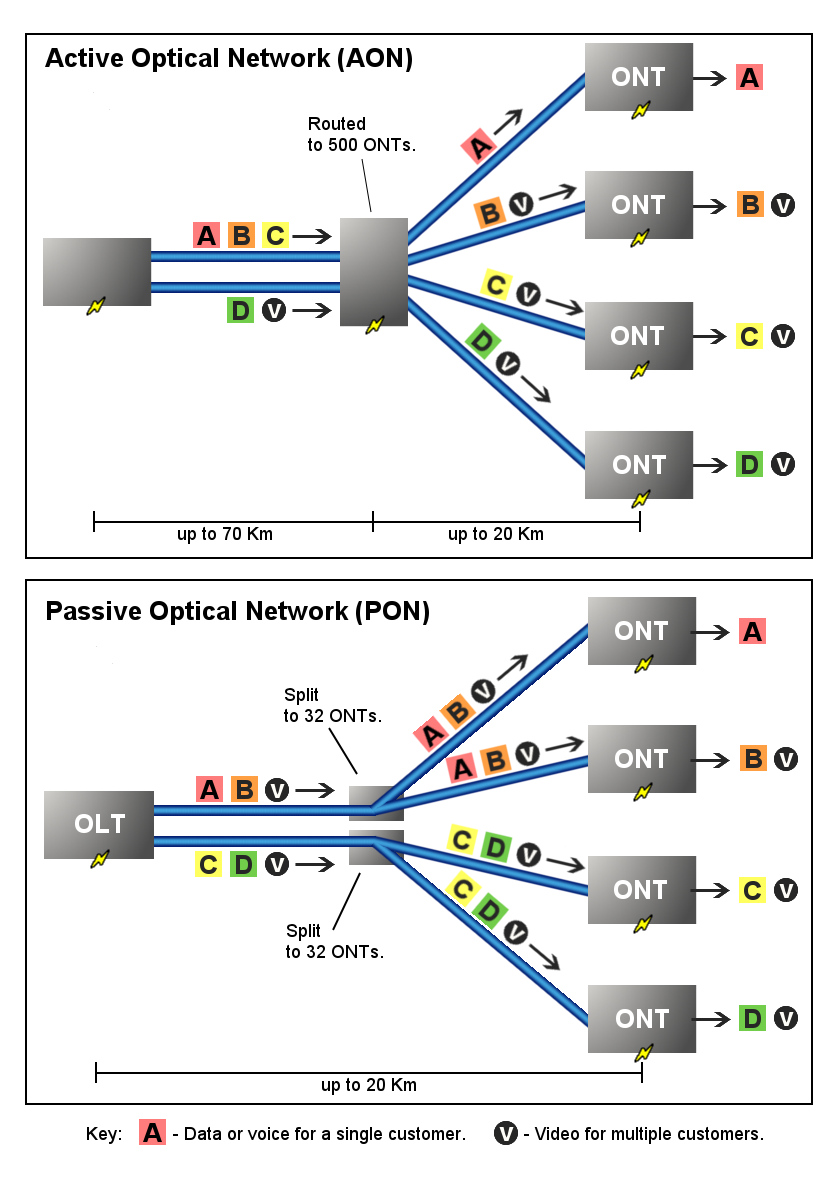
Passive Optical Network
A passive optical network (PON) is a fiber-optic telecommunications technology for delivering broadband network access to end-customers. Its architecture implements a point-to-multipoint topology in which a single optical fiber serves multiple endpoints by using unpowered (''passive'') fiber optic splitters to divide the fiber bandwidth among the endpoints. Passive optical networks are often referred to as the ''last mile'' between an Internet service provider (ISP) and its customers. Components and characteristics A passive optical network consists of an optical line terminal (OLT) at the service provider's central office (hub) and a number of optical network units (ONUs) or optical network terminals (ONTs), near end users. A PON reduces the amount of fiber and central office equipment required compared with point-to-point architectures. A passive optical network is a form of fiber-optic access network. In most cases, downstream signals are broadcast to all premises shari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower frequencies in a continuous band of frequencies. It is typically measured in hertz, and depending on context, may specifically refer to '' passband bandwidth'' or '' baseband bandwidth''. Passband bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. Baseband bandwidth applies to a low-pass filter or baseband signal; the bandwidth is equal to its upper cutoff frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the frequency spectrum. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Line Terminal
{{unreferenced, date=April 2016 An optical line termination (OLT), also called an optical line terminal, is a device which serves as the service provider endpoint of a passive optical network. It provides two main functions: # to perform conversion between the electrical signals used by the service provider's equipment and the fiber optic signals used by the passive optical network. # to coordinate the multiplexing between the conversion devices on the other end of that network (called either optical network terminals or optical network units). The diagram below depicts an OLT within a fiber-optic network. Features OLTs include the following features: * A downstream frame processing means for receiving and churning an Asynchronous Transfer Mode cell to generate a downstream frame, and converting a parallel data of the downstream frame into a serial data thereof. * A wavelength division multiplexing means for performing an electro/optical conversion of the serial data of the dow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Downstream (computer Science)
In a telecommunications network or computer network, downstream refers to data sent from a network service provider to a customer. One process sending data primarily in the downstream direction is downloading. However, the overall download speed depends on the downstream speed of the user, the upstream speed of the Server (computing), server, and the network between them. In the client–server model, downstream can refer to the direction from the server to the client (computing), client. References Data transmission Orientation (geometry) {{Network-stub nl:Downstream ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmission (telecommunications)
In telecommunications, transmission is the process of sending or propagating an analog or digital signal via a medium that is wired, wireless, or fiber-optic. Transmission technologies typically refer to physical layer protocol duties such as modulation, demodulation, line coding, equalization, error control, bit synchronization and multiplexing, but it may also involve higher-layer protocol duties, for example, digitizing an analog signal, and data compression. Transmission of a digital message, or of a digitized analog signal, is known as data transmission Data transmission and data reception or, more broadly, data communication or digital communications is the transfer and reception of data in the form of a digital bitstream or a digitized analog signal transmitted over a point-to-point o .... Examples of transmission are the sending of signals with limited duration, for example, a block or packet of data, a phone call, or an email. See also * R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)