|
Institut National De L'origine Et De La Qualité
The Institut national de l'origine et de la qualité (; INAO; previously Institut National des Appellations d'Origine) is the French organization charged with regulating French agricultural products with protected designation of origin (PDOs). It is controlled by the Government of France, and it forms part of the Ministry of Agriculture. The organization was co-founded by Châteauneuf-du-Pape producer Baron Pierre Le Roy.H. Karis ''The Chateauneuf-du-Pape Wine Book'' pg 18, 254-256, 473 First Edition Kavino Publishing 2009 Every ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC), the French term for PDOs, is produced according to rules codified by the INAO. Because its primary purpose is to regulate the use of noteworthy names, one of its primary tasks is to delimit the geographic area entitled to produce a product. For wine this means vineyards, but the INAO also regulates the places of processing and aging. The INAO, like many organizations charged with regulating and helping prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris - INAO
Paris () is the Capital city, capital and List of communes in France with over 20,000 inhabitants, largest city of France. With an estimated population of 2,048,472 residents in January 2025 in an area of more than , Paris is the List of cities in the European Union by population within city limits, fourth-most populous city in the European Union and the List of cities proper by population density, 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2022. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, culture, Fashion capital, fashion, and gastronomy. Because of its leading role in the French art, arts and Science and technology in France, sciences and its early adoption of extensive street lighting, Paris became known as the City of Light in the 19th century. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an official estimated population of 12,271,794 inhabitants in January 2023, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
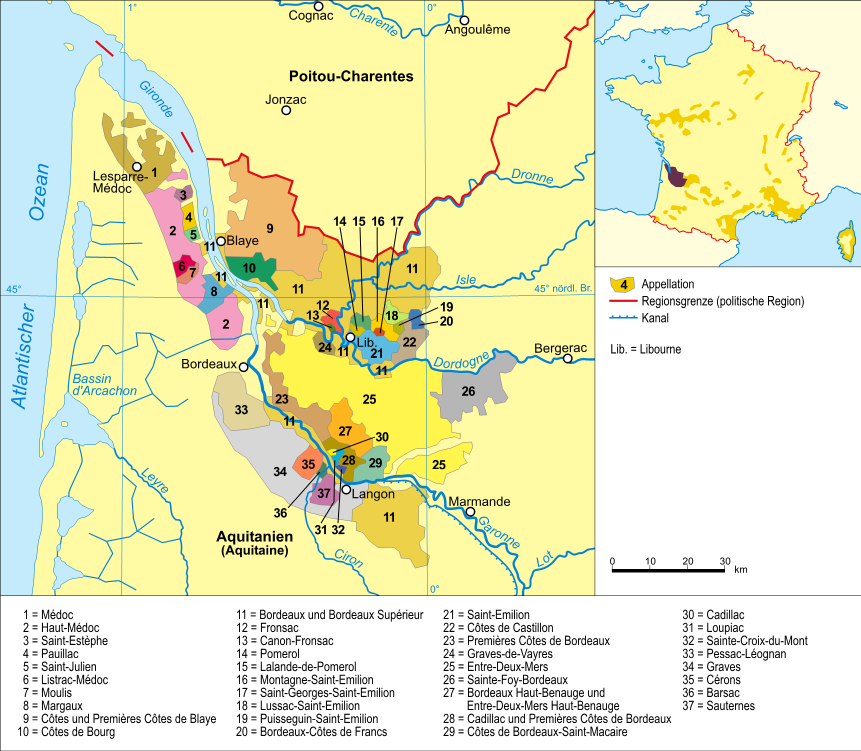
Bordeaux Wine
Bordeaux wine (; ) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city, the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the broad estuary called the Gironde; the Gironde department, with a total vineyard area of 110,800 hectares, is the second largest wine-growing area in France behind the Languedoc-Rousillon. Average vintages produce over 700 million bottles of wine, ranging from large quantities of daily table wine to some of the world's most expensive and prestigious wines. The vast majority of wine produced in Bordeaux is red (sometimes called "claret" in Britain), with sweet white wines (most notably Sauternes), dry whites, and (in much smaller quantities) rosé and sparkling wines ( Crémant de Bordeaux) collectively making up the remainder. Bordeaux wine is made by more than 5,660 producers or ''châteaux''. There are 65 appellations of Bordeaux wine. History Viticulture was introduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Wine
French wine is produced throughout all of France in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France is one of the largest wine producers in the world. French wine traces its history to the 6th century BCE, with many of France's regions dating their wine-making history to Roman times. The wines produced range from expensive wines sold internationally to modest wines usually only seen within France such as the Margnat wines of the post-war period. Two concepts central to the better French wines are the notion of ''terroir'', which links the style of the wines to the locations where the grapes are grown and the wine is made, and the Protected designation of origin (''Appellation d'Origine Protégée'', AOP) system, named ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) until 2012. Appellation rules closely define which grape varieties and winemaking practices are approved for classification in each of France's several hundred ge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
René Renou
René Bernard Renou (16 June 1952 – 19 June 2006) was president of the Institut National des Appellations d'Origine (INAO) at the time of his death and was "one of the most influential men in French winemaking.". Renou argued that France's ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) system was hindering the country's competitiveness in the world wine market. He said that the AOC system was "conceived for producers rather than consumers", that there are too many AOCs, they are not meaningful, that they confuse consumers, and that reform was essential. His proposals for reform met strong resistance and defense of the status quo. ''BettaneDesseauve'' named Renou Man of the Year in 2005. He was a Chevalier de la Legion of Honour, Légion d’Honneur and Commander in the Ordre du Mérite Agricole. The René Renou winery is located in the Anjou (wine), Anjou district of the Loire Valley (wine), Loire Valley wine region, and makes wine from Coteaux du Layon and other AOCs. See a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Label Rouge
Label Rouge (''Red Label'') is a sign of quality assurance in France as defined by Law No. 2006-11 (5 January 2006). Products eligible for the Label Rouge are food items, and non-food and unprocessed agricultural products such as flowers. According to the French Ministry of Agriculture: "The Red Label certifies that a product has a specific set of characteristics establishing a superior level to that of a similar current product". Certification To obtain the Label Rouge, a very stringent set of standards prepared by a group of producers must be approved. These standards establish the criteria which the product must meet throughout the production chain, including farming techniques, feed, processing and distribution. Approval is officially announced through a joint decree from the Minister for Agriculture and Fisheries and the Minister for Consumer Affairs, on the recommendations of the National Institute for Origin and Quality (INAO). INAO is the French public body responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhône Wine
The Rhône wine region in Southern France is situated in the Rhône valley and produces numerous wines under various ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) designations. The region's major appellation in production volume is Côtes du Rhône AOC. The Rhône is generally divided into two sub-regions with distinct vinicultural traditions, the Northern Rhône (referred to in French as ''Rhône septentrional'') and the Southern Rhône (in French ''Rhône méridional''). The northern sub-region produces red wines from the Syrah grape, sometimes blended with up to 20% of white wine grapes, and white wines from Marsanne, Roussanne and Viognier grapes. The southern sub-region produces an array of red, white and rosé wines, often blends of several grapes such as in Châteauneuf-du-Pape. History The first cultivated vines in the region were probably planted around 600 BC. The origins of the two most important grape varieties in the northern Rhone (Syrah and Viognier) have in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Champagne
Champagne (; ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, which demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, specific grape-pressing methods and secondary fermentation (wine), secondary fermentation of the wine in the bottle to cause carbonation. The grapes Pinot noir, Pinot meunier, and Chardonnay are used to produce almost all Champagne, but small amounts of Pinot blanc, Pinot gris (called Fromenteau in Champagne), Arbane, and Petit Meslier are vinified as well. Champagne became associated with royalty in the 17th, 18th, and 19th centuries. The leading manufacturers made efforts to associate their Champagnes with nobility and royal family, royalty through advertising and packaging, which led to its popularity among the emerging middle class. Origins Still wines from the Champagne region were known before Middle Ages, medieval times. The Anci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burgundy Wine
Burgundy wine ( or ') is made in the Burgundy region of eastern France, in the valleys and slopes west of the Saône, a tributary of the Rhône. The most famous wines produced here, and those commonly referred to as "Burgundies", are dry (wine), dry red wines made from pinot noir grapes and white wines made from chardonnay grapes. Red and white wines are also made from other grape varieties, such as gamay and aligoté, respectively. Small amounts of rosé and sparkling wines are also produced in the region. Chardonnay-dominated Chablis (wine), Chablis and gamay-dominated Beaujolais wine, Beaujolais are recognised as part of the Burgundy wine region, but wines from those subregions are usually referred to by their own names rather than as "Burgundy wines". Burgundy has a higher number of ' (AOCs) than any other French region, and is often seen as the most '-conscious of the French wine regions. The various Burgundy AOCs are classification of wine, classified from carefully deline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Capus
Joseph Marie Capus (; 18 August 1867 – 1 May 1947) was a French agriculturalist and expert on grape vines. He became a deputy in the French national parliament, and was Minister of Agriculture for a few months in 1924. He was active in legislation related to agriculture and was the driving force behind introduction of the ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' for French wines. Early years Joseph Marie Capus was born on 18 August 1867 in Marseille. His father was a lawyer in Marseille and his mother, who died while he was a child, was the daughter of a notary from Vaucluse. His brother Alfred Capus, ten years his senior, was a writer who became editor of ''Le Figaro''. Capus studied at the ''Lycée Condorcet'' in Marseille, the ''École de Grignon'', the ''École Pratique d'Ondes'' and the ''École Pratique de Cézany''. He became a professor of agriculture at Cadillac, Gironde. He was appointed director of the Cadillac station of plant diseases from 1900, and in 1915 became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlantic, North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and List of islands of France, many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean, giving it Exclusive economic zone of France, one of the largest discontiguous exclusive economic zones in the world. Metropolitan France shares borders with Belgium and Luxembourg to the north; Germany to the northeast; Switzerland to the east; Italy and Monaco to the southeast; Andorra and Spain to the south; and a maritime border with the United Kingdom to the northwest. Its metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea. Its Regions of France, eighteen integral regions—five of which are overseas—span a combined area of and hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
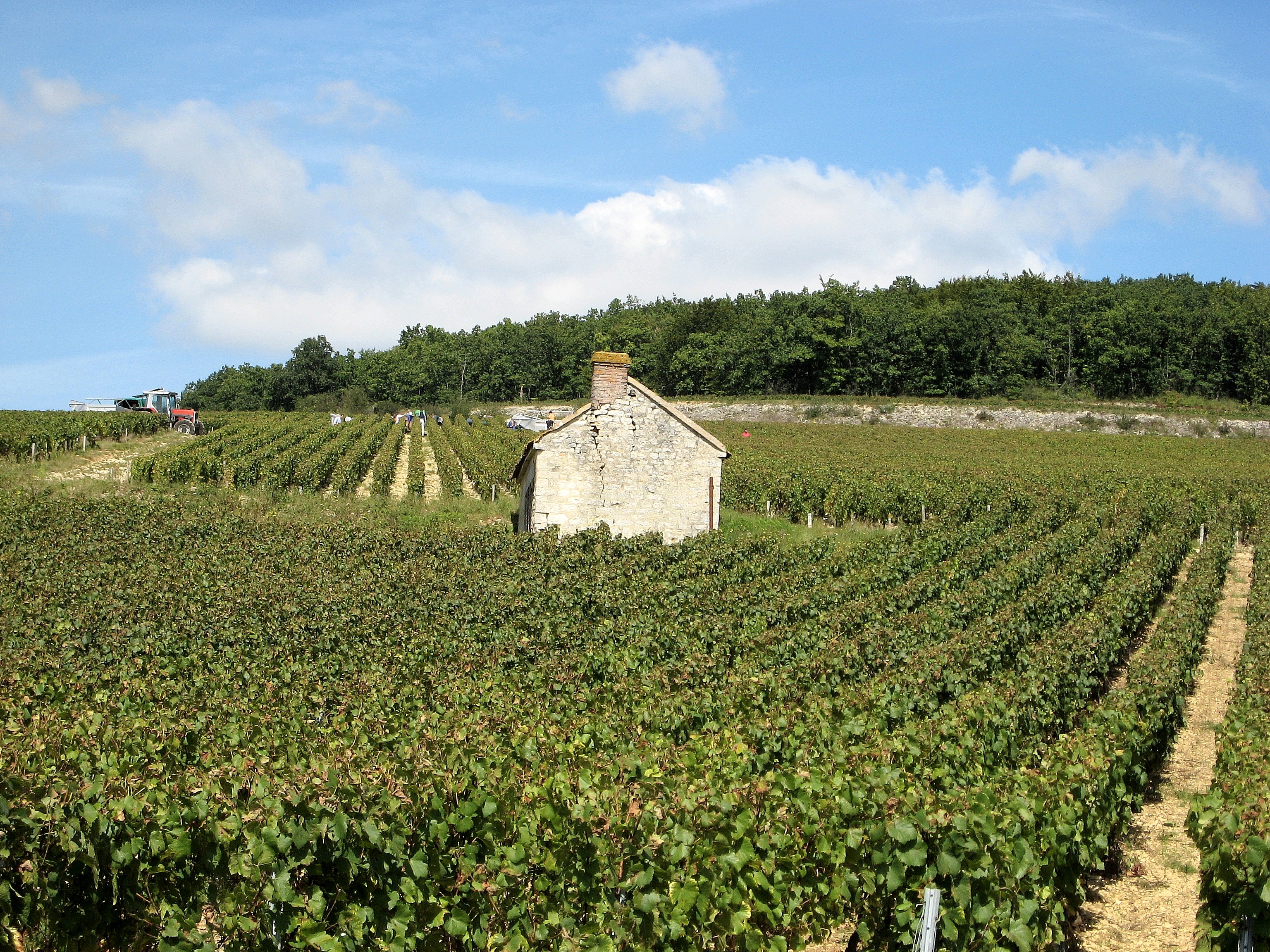
Vineyard
A vineyard ( , ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines. Many vineyards exist for winemaking; others for the production of raisins, table grapes, and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyards are often characterised by their , a French term loosely translating as "a sense of place" that refers to the specific geographical and geological characteristics of grapevine plantations, which may be imparted to the wine itself. History The earliest evidence of wine production dates from between 6000 and 5000 BC. Wine making technology improved considerably with the ancient Greeks but it was not until the end of the Roman Empire that cultivation techniques as we know them were common throughout Europe. In medieval Europe the Catholic Church was a staunch supporter of wine, which was necessary for the celebration of the Mass (liturgy), Mass. During the lengthy instability of the Middle Ages, the monasteries m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |