|
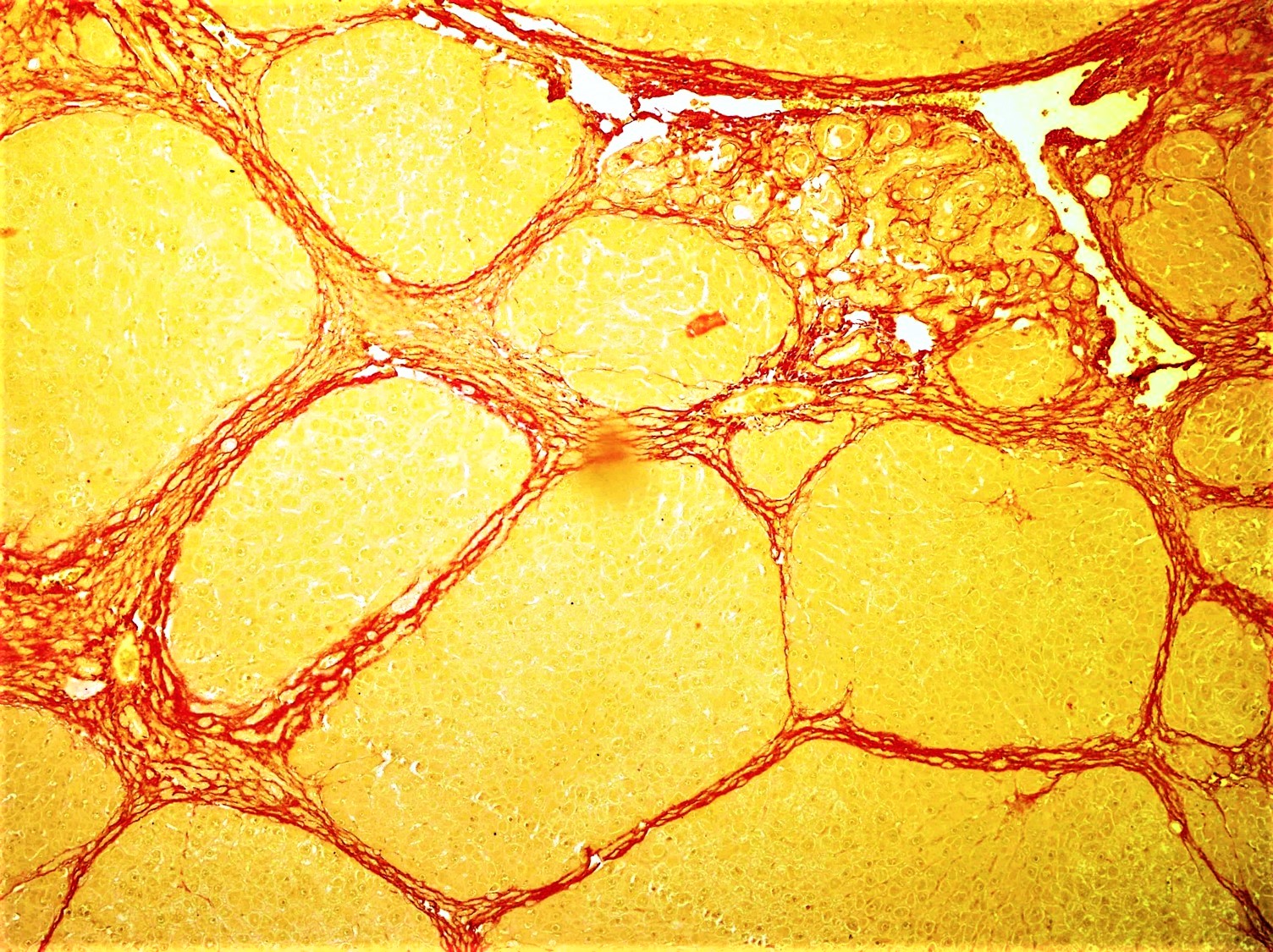
Injection Fibrosis
Injection fibrosis is a complication of intramuscular injection, occurring especially often in infants and children. Injections are often delivered to the quadriceps, triceps, and gluteal muscles, and thus the complication often manifests itself in those muscles. Patients are unable to fully flex the affected muscle. The condition is painless, but progressively worsens over time. Orthopedic surgery is the typical treatment. See also * Fibrosis Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease. Repeated injuries, ch ... References Musculoskeletal disorders {{musculoskeletal-disease-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, often abbreviated IM, is the medical injection, injection of a substance into a muscle. In medicine, it is one of several methods for parenteral, parenteral administration of medications. Intramuscular injection may be preferred because muscles have larger and more numerous blood vessels than subcutaneous tissue, leading to faster absorption than subcutaneous injection, subcutaneous or intradermal injections. Medication administered via intramuscular injection is not subject to the first-pass metabolism effect which affects oral medications. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle of the upper arm and the gluteal muscle of the buttock. In infants, the vastus lateralis muscle of the thigh is commonly used. The injection site must be cleaned before administering the injection, and the injection is then administered in a fast, darting motion to decrease the discomfort to the individual. The volume to be injected in the muscle is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infant
In common terminology, a baby is the very young offspring of adult human beings, while infant (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'baby' or 'child') is a formal or specialised synonym. The terms may also be used to refer to juveniles of other organisms. A newborn is, in colloquial use, a baby who is only hours, days, or weeks old; while in medical contexts, a newborn or neonate (from Latin, ''neonatus'', newborn) is an infant in the first 28 days after birth (the term applies to premature, full term, and postmature infants). Infants born prior to 37 weeks of gestation are called "premature", those born between 39 and 40 weeks are "full term", those born through 41 weeks are "late term", and anything beyond 42 weeks is considered "post term". Before birth, the offspring is called a fetus. The term ''infant'' is typically applied to very young children under one year of age; however, definitions may vary and may include children up to two years of age. When a human chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadriceps
The quadriceps femoris muscle (, also called the quadriceps extensor, quadriceps or quads) is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the sole extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy mass which covers the front and sides of the femur. The name derives . Structure Parts The quadriceps femoris muscle is subdivided into four separate muscles (the 'heads'), with the first superficial to the other three over the femur (from the trochanters to the condyles): * The rectus femoris muscle occupies the middle of the thigh, covering most of the other three quadriceps muscles. It originates on the ilium. It is named for its straight course. * The vastus lateralis muscle is on the ''lateral side'' of the femur (i.e. on the outer side of the thigh). * The vastus medialis muscle is on the ''medial side'' of the femur (i.e. on the inner part thigh). * The vastus intermedius muscle lies between vastus lateralis and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triceps
The triceps, or triceps brachii (Latin for "three-headed muscle of the arm"), is a large muscle on the ventral, back of the upper limb of many vertebrates. It consists of three parts: the medial, lateral, and long head. All three heads cross the elbow joint. However, the long head also crosses the shoulder joint. The triceps muscle contracts when the elbow is straightened and expands when the elbow is bent. The long head gets a further contraction when the arm is behind the torso due to how it crosses the shoulder joint. It is the muscle principally responsible for Extension (kinesiology), extension of the elbow joint (straightening of the arm). Structure * The long head arises from the infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula. It extends distally anterior to the Teres minor muscle, teres minor and posterior to the Teres major muscle, teres major. * The medial head arises proximally in the humerus, just inferior to the Radial sulcus, groove of the radial nerve; from the dorsal (b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gluteal Muscles
The gluteal muscles, often called glutes, are a group of three muscles which make up the gluteal region commonly known as the buttocks: the gluteus maximus muscle, gluteus maximus, gluteus medius muscle, gluteus medius and gluteus minimus muscle, gluteus minimus. The three muscles originate from the ilium bone, ilium and sacrum and insert on the femur. The functions of the muscles include Extension (kinesiology), extension, Abduction (kinesiology), abduction, external rotation, and internal rotation of the hip joint. Structure The gluteus maximus is the largest and most wiktionary:superficial, superficial of the three gluteal muscles. It makes up a large part of the shape and appearance of the hips. It is a narrow and thick fleshy mass of a quadrilateral shape, and forms the prominence of the buttocks. The gluteus medius is a broad, thick, radiating muscle, situated on the outer surface of the pelvis. It lies profound to the gluteus maximus and its posterior third is covered by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flexion
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terminology, anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of Organ (anatomy), organs, joints, Limb (anatomy), limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relative to the anatomical position of the body parts involved. Anatomy, Anatomists and others use a unified set of terms to describe most of the movements, although other, more specialized terms are necessary for describing unique movements such as those of the hands, feet, and eyes. In general, motion is classified according to the anatomical plane it occurs in. ''Flexion'' and ''extension'' are examples of ''angular'' motions, in which two axes of a joint are brought closer together or moved further apart. ''Rotational'' motion may occur at other joints, for example the shoulder, and are described as ''internal'' or ''external''. Other terms, such as ''elevation'' and ''depression'', descri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthopedic Surgery
Orthopedic surgery or orthopedics ( alternative spelling orthopaedics) is the branch of surgery concerned with conditions involving the musculoskeletal system. Orthopedic surgeons use both surgical and nonsurgical means to treat musculoskeletal trauma, spine diseases, sports injuries, degenerative diseases, infections, tumors and congenital disorders. Etymology Nicholas Andry coined the word in French as ', derived from the Ancient Greek words ("correct", "straight") and ("child"), and published ''Orthopedie'' (translated as ''Orthopædia: Or the Art of Correcting and Preventing Deformities in Children'') in 1741. The word was assimilated into English as ''orthopædics''; the ligature ''æ'' was common in that era for ''ae'' in Greek- and Latin-based words. As the name implies, the discipline was initially developed with attention to children, but the correction of spinal and bone deformities in all stages of life eventually became the cornerstone of orthopedic pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibrosis
Fibrosis, also known as fibrotic scarring, is the development of fibrous connective tissue in response to an injury. Fibrosis can be a normal connective tissue deposition or excessive tissue deposition caused by a disease. Repeated injuries, chronic inflammation and repair are susceptible to fibrosis, where an accidental excessive accumulation of extracellular matrix components, such as the collagen, is produced by fibroblasts, leading to the formation of a permanent fibrotic scar. In response to injury, this is called scarring, and if fibrosis arises from a single cell line, this is called a fibroma. Physiologically, fibrosis acts to deposit connective tissue, which can interfere with or totally inhibit the normal architecture and function of the underlying organ or tissue. Fibrosis can be used to describe the pathological state of excess deposition of fibrous tissue, as well as the process of connective tissue deposition in healing. Defined by the pathological accumulation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |