|
Infectious Tolerance
Infectious tolerance is a term referring to a phenomenon where a tolerance-inducing state is transferred from one cell population to another. It can be induced in many ways; although it is often artificially induced, it is a natural ''in vivo'' process. A number of research deal with the development of a strategy utilizing this phenomenon in transplantation immunology. The goal is to achieve long-term tolerance of the transplant through short-term therapy. History The term "infectious tolerance" was originally used by Gershon and Kondo in 1970 for suppression of naive lymphocyte populations by cells with regulatory function and for the ability to transfer a state of unresponsiveness from one animal to another. Gershon and Kondo discovered that T cells can not only amplify but also diminish immune responses. The T cell population causing this down-regulation was called suppressor T cells and was intensively studied for the following years (nowadays they are called regulatory T ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transplant Rejection
Transplant rejection occurs when transplanted tissue is rejected by the recipient's immune system, which destroys the transplanted tissue. Transplant rejection can be lessened by determining the molecular similitude between donor and recipient and by use of immunosuppressant drugs after transplant. Types of transplant rejection Transplant rejection can be classified into three types: hyperacute, acute, and chronic. These types are differentiated by how quickly the recipient's immune system is activated and the specific aspect or aspects of immunity involved. Hyperacute rejection Hyperacute rejection is a form of rejection that manifests itself in the minutes to hours following transplantation. It is caused by the presence of pre-existing antibodies in the recipient that recognize antigens in the donor organ. These antigens are located on the endothelial lining of blood vessels within the transplanted organ and, once antibodies bind, will lead to the rapid activation of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FOXP3
FOXP3 ( forkhead box P3), also known as scurfin, is a protein involved in immune system responses. A member of the FOX protein family, FOXP3 appears to function as a master regulator of the regulatory pathway in the development and function of regulatory T cells. Regulatory T cells generally turn the immune response down. In cancer, an excess of regulatory T cell activity can prevent the immune system from destroying cancer cells. In autoimmune disease, a deficiency of regulatory T cell activity can allow other autoimmune cells to attack the body's own tissues. While the precise control mechanism has not yet been established, FOX proteins belong to the forkhead/ winged-helix family of transcriptional regulators and are presumed to exert control via similar DNA binding interactions during transcription. In regulatory T cell model systems, the FOXP3 transcription factor occupies the promoters for genes involved in regulatory T-cell function, and may inhibit transcription of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transplantation Medicine
Organ transplantation is a medical procedure in which an organ is removed from one body and placed in the body of a recipient, to replace a damaged or missing organ. The donor and recipient may be at the same location, or organs may be transported from a donor site to another location. Organs and/or tissues that are transplanted within the same person's body are called autografts. Transplants that are recently performed between two subjects of the same species are called allografts. Allografts can either be from a living or cadaveric source. Organs that have been successfully transplanted include the heart, kidneys, liver, lungs, pancreas, intestine, thymus and uterus. Tissues include bones, tendons (both referred to as musculoskeletal grafts), corneae, skin, heart valves, nerves and veins. Worldwide, the kidneys are the most commonly transplanted organs, followed by the liver and then the heart. Corneae and musculoskeletal grafts are the most commonly transplanted tissues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Tolerance In Pregnancy
Immune tolerance in pregnancy or maternal immune tolerance is the immune tolerance shown towards the fetus and placenta during pregnancy. This tolerance counters the immune response that would normally result in the rejection of something foreign in the body, as can happen in cases of spontaneous abortion. It is studied within the field of reproductive immunology. Mechanisms Placental mechanisms The placenta functions as an immunological barrier between the mother and the fetus, creating an immunologically privileged site. For this purpose, it uses several mechanisms: *It secretes neurokinin B containing phosphocholine molecules. This is the same mechanism used by parasitic nematodes to avoid detection by the immune system of their host. *Also, there is the presence of small lymphocytic suppressor cells in the fetus that inhibit maternal cytotoxic T cells by inhibiting the response to interleukin 2. * The placental trophoblast cells do not express the classical MHC class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
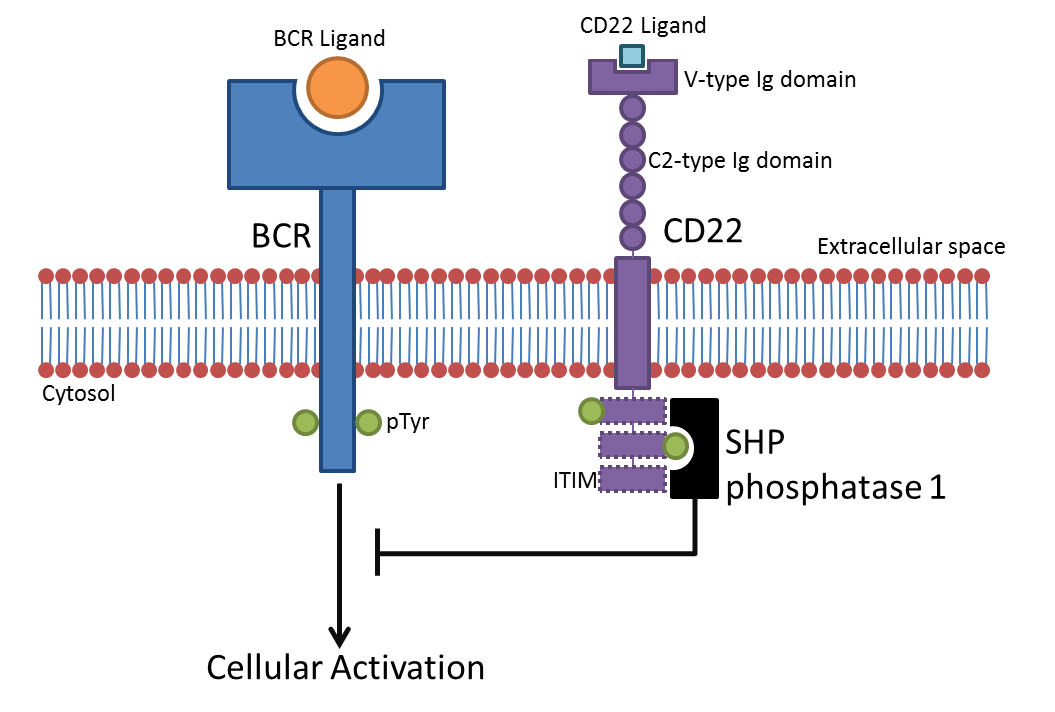
CD22
CD22, or cluster of differentiation-22, is a molecule belonging to the SIGLEC family of lectins. It is found on the surface of mature B cells and to a lesser extent on some immature B cells. Generally speaking, CD22 is a regulatory molecule that prevents the overactivation of the immune system and the development of autoimmune diseases. CD22 is a sugar binding transmembrane protein, which specifically binds sialic acid with an immunoglobulin domain, immunoglobulin (Ig) domain located at its N-terminus. The presence of Ig domains makes CD22 a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. CD22 functions as an inhibitory receptor for B cell receptor (BCR) signaling. It is also involved in the B cell trafficking to Peyer's patches in mice. In mice, it has been shown that CD22 blockade restores homeostatic microglial phagocytosis in aging brains. Structure CD22 is a transmembrane protein with a molecular weight of 140 kDa. The extracellular part of CD22 consists of seven immunoglobuli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
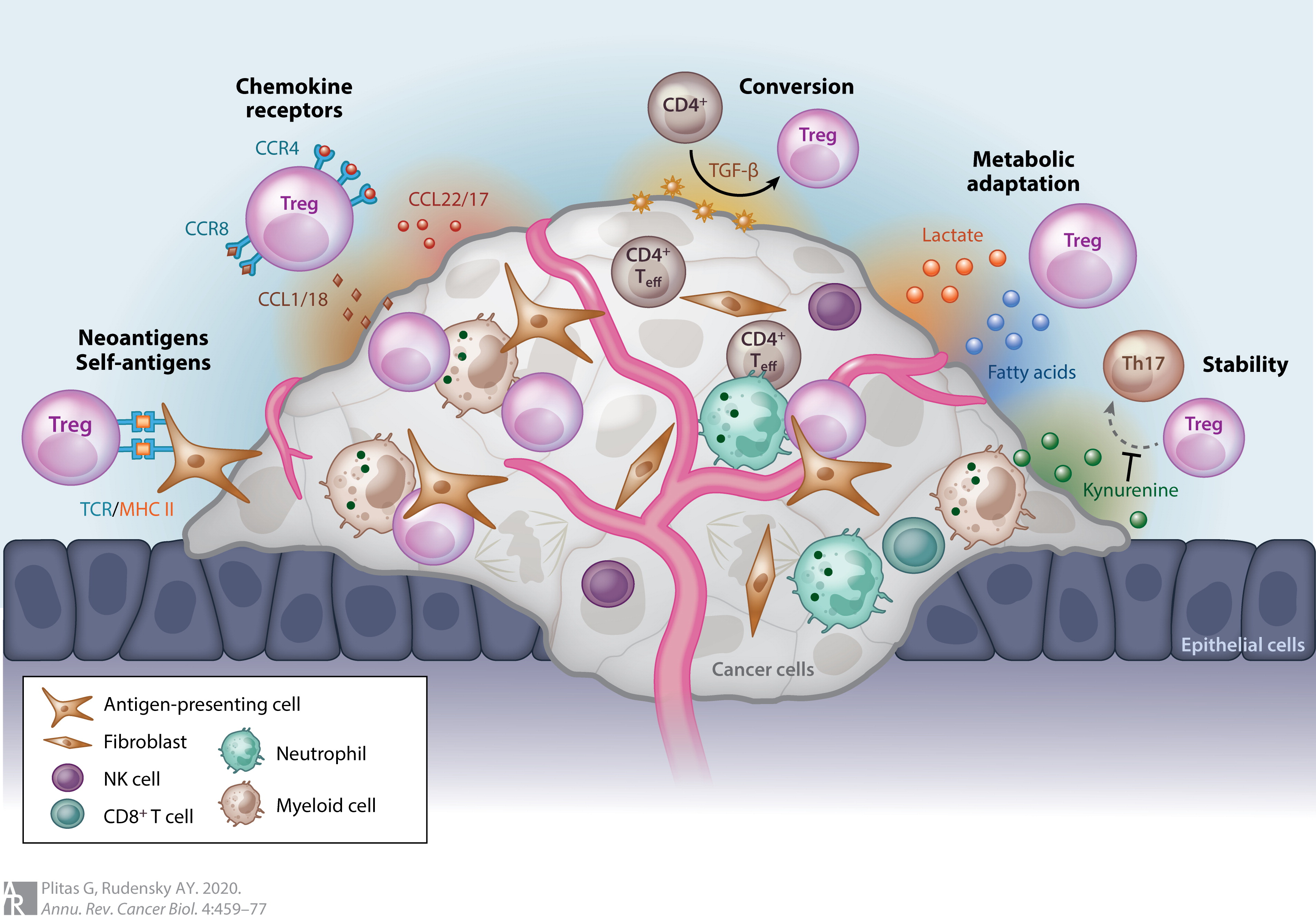
Regulatory T Cells
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peripheral Tolerance
In immunology, peripheral tolerance is the second branch of immunological tolerance, after central tolerance. It takes place in the immune periphery (after T and B cells egress from primary lymphoid organs). Its main purpose is to ensure that self-reactive T and B cells which escaped central tolerance do not cause autoimmune disease. Peripheral tolerance prevents immune response to harmless food antigens and allergens, too. Deletion of self-reactive T cells in the thymus is only 60-70% efficient, and naive T cell repertoire contains a significant portion of low-avidity self-reactive T cells. These cells can trigger an autoimmune response, and there are several mechanisms of peripheral tolerance to prevent their activation. Antigen-specific mechanisms of peripheral tolerance include persistent of T cell in quiescence, ignorance of antigen and direct inactivation of effector T cells by either clonal deletion, conversion to regulatory T cells (Tregs) or induction of anergy. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Tolerance
In immunology, central tolerance (also known as negative selection) is the process of eliminating any ''developing'' T or B lymphocytes that are autoreactive, i.e. reactive to the body itself. Through elimination of autoreactive lymphocytes, tolerance ensures that the immune system does not attack self peptides. Lymphocyte maturation (and central tolerance) occurs in primary lymphoid organs such as the bone marrow and the thymus. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow and T cells mature in the thymus. Central tolerance is not perfect, so peripheral tolerance exists as a secondary mechanism to ensure that T and B cells are not self-reactive once they leave primary lymphoid organs. Peripheral tolerance is distinct from central tolerance in that it occurs once developing immune cells exit primary lymphoid organs (the thymus and bone-marrow), prior to their export into the periphery. Function of central tolerance Central tolerance is essential to proper immune cell func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Tolerance
Immune tolerance, or immunological tolerance, or immunotolerance, is a state of unresponsiveness of the immune system to substances or tissue that would otherwise have the capacity to elicit an immune response in a given organism. It is induced by prior exposure to that specific antigen and contrasts with conventional immune-mediated elimination of foreign antigens (see Immune response). Tolerance is classified into central tolerance or peripheral tolerance depending on where the state is originally induced—in the thymus and bone marrow (central) or in other tissues and lymph nodes (peripheral). The mechanisms by which these forms of tolerance are established are distinct, but the resulting effect is similar. Immune tolerance is important for normal physiology. Central tolerance is the main way the immune system learns to discriminate self from non-self. Peripheral tolerance is key to preventing over-reactivity of the immune system to various environmental entities (allergens, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanistic Target Of Rapamycin
The mammalian target of sirolimus, rapamycin (mTOR), also referred to as the mechanistic target of rapamycin, and sometimes called FK506-binding protein 12-rapamycin-associated protein 1 (FRAP1), is a kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''MTOR'' gene. mTOR is a member of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-related kinase family of protein kinases. mTOR links with other proteins and serves as a core component of two distinct protein complexes, mTORC1, mTOR complex 1 and mTORC2, mTOR complex 2, which regulate different cellular processes. In particular, as a core component of both complexes, mTOR functions as a serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates cell growth, cell proliferation, cell motility, cell survival, protein synthesis, autophagy, and Transcription (genetics), transcription. As a core component of mTORC2, mTOR also functions as a tyrosine protein kinase that promotes the activation of insulin receptors and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptors. mTORC2 has also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tr1 Cells
Type 1 regulatory cells or Tr1 (TR1) cells are a class of regulatory T cells participating in peripheral immunity as a subsets of CD4+ T cells. Tr1 cells regulate tolerance towards antigens of any origin. Tr1 cells are self or non-self antigen specific and their key role is to induce and maintain peripheral tolerance and suppress tissue inflammation in autoimmunity and graft vs. host disease. Characterization and surface molecules The specific cell-surface markers for Tr1 cells in humans and mice are CD4+ CD49b+LAG-3+ CD226+ from which LAG-3+ and CD49b+ are indispensable. LAG-3 is a membrane protein on Tr1 cells that negatively regulates TCR-mediated signal transduction in cells. LAG-3 activates dendritic cells (DCs) and enhances the antigen-specific T-cell response which is necessary for Tr1 cells antigen specificity. CD49b belongs to the integrin family and is a receptor for many (extracellular) matrix and non-matrix molecules. CD49b provides only little contributi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
..jpg)