|
Indigenous Peoples In Ecuador
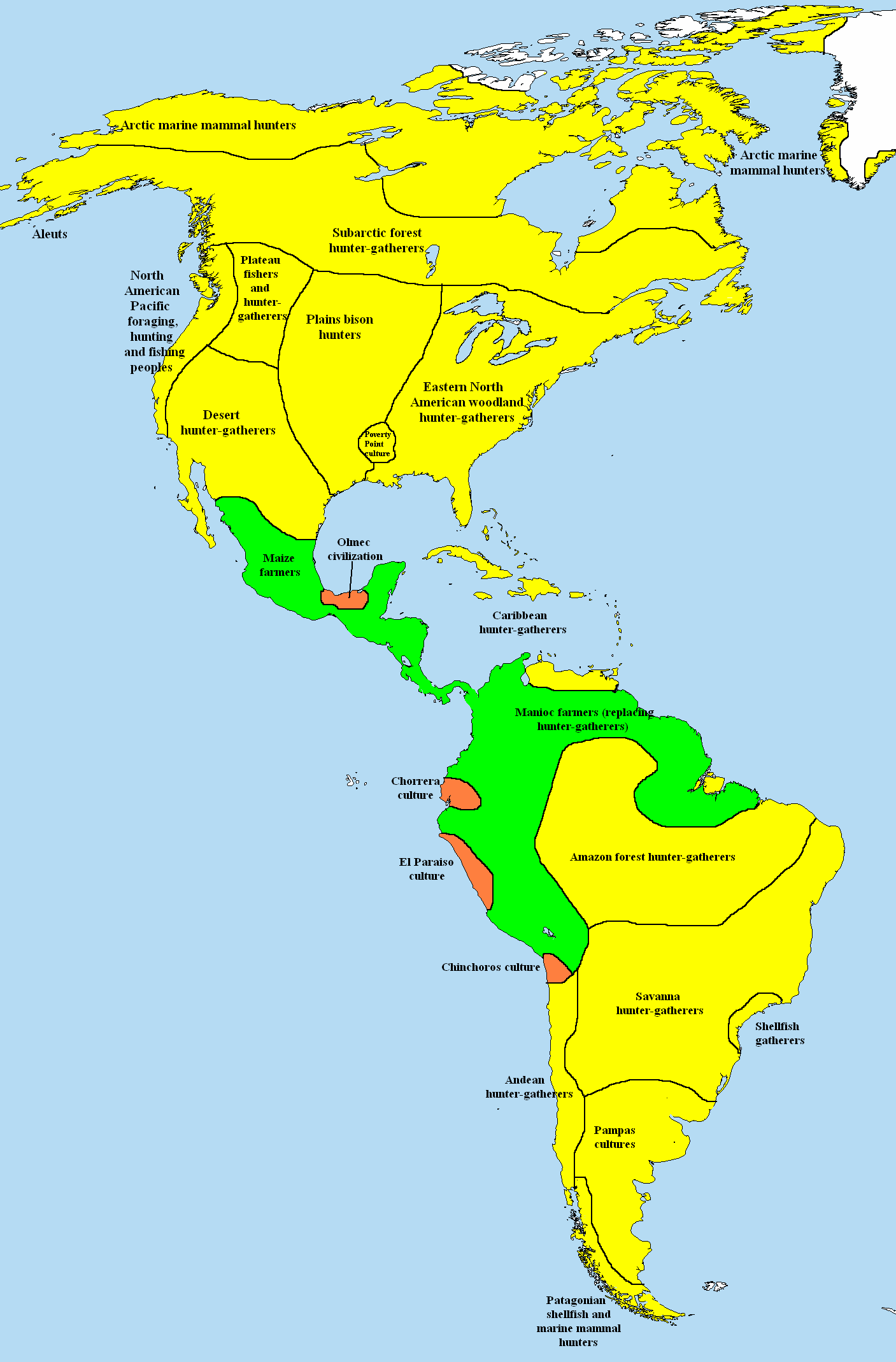
The Indigenous peoples in Ecuador or Native Ecuadorians () are the groups of people who were present in what became Ecuador before the Spanish colonization of the Americas. The term also includes their descendants from the time of the Spanish conquest to the present. Their history, which encompasses the last 11,000 years, reaches into the present; 7 percent of Ecuador's population is of Indigenous heritage, while another 70 percent are Mestizos of mixed Indigenous and European heritage. Genetic analysis indicates that Ecuadorian Mestizos are of three-hybrid genetic ancestry. Archaeological periods While archaeologists have proposed different temporal models at different times, the schematic currently in use divides prehistoric Ecuador into five major time periods: Lithic, Archaic, Formative, Regional Development, and Integration. These time periods are determined by the cultural development of groups being studied, and are not directly linked to specific dates, e.g. throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish () or Castilian () is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin spoken on the Iberian Peninsula of Europe. Today, it is a world language, global language with 483 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain, and about 558 million speakers total, including second-language speakers. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries, as well as one of the Official languages of the United Nations, six official languages of the United Nations. Spanish is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siona Language
Siona (otherwise known as Bain Coca, Pioje, Pioche-Sioni, Ganteyabain, Ganteya, Ceona, Zeona, Koka, Kanú) is a Tucanoan language of Colombia and Ecuador. Ecuadorian Siona and Colombian Siona, as well as Secoya, have a high level of mutual intelligibility, but have some lexical, morphological, and phonological differences between them. As of 2013, Siona is spoken by about 550 people. The Teteté dialect (Eteteguaje) is extinct.Hammarström (2015) Ethnologue 16/17/18th editions: a comprehensive review: online appendices Phonology Vowels There are 6 oral vowels and six nasal vowels. Only nasal vowels occur next to a nasal consonant or . Consonants There are two series of obstruent consonant. Both often produce a noticeable delay before the onset of the following vowel: the 'fortis' series (written ''p t č k kw s h hw'') tends to be aspirated, with a noisy transition to the vowel, while the 'lenis' series (written ''b d g gw ’ z''), optionally voiced, is glottalized, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaic Period In The Americas
In the classification of the archaeological cultures of North America, the Archaic period in North America, taken to last from around 8000 to 1000 BC in the sequence of North American pre-Columbian cultural stages, is a period defined by the ''archaic stage'' of cultural development. The Archaic stage is characterized by subsistence economies supported through the exploitation of nuts, seeds, and shellfish. As its ending is defined by the adoption of sedentary farming, this date can vary significantly across the Americas. The rest of the Americas also have an Archaic Period. Classifications This classification system was first proposed by Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips in the widely accepted 1958 book ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology''. In the organization of the system, the Archaic period followed the Lithic stage and is superseded by the Formative stage. # The Lithic stage # The Archaic stage # The Formative stage # The Classic stage # The Post-Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Tool
Stone tools have been used throughout human history but are most closely associated with prehistoric cultures and in particular those of the Stone Age. Stone tools may be made of either ground stone or knapped stone, the latter fashioned by a craftsman called a flintknapper. Stone has been used to make a wide variety of tools throughout history, including arrowheads, spearheads, hand axes, and querns. Knapped stone tools are nearly ubiquitous in pre-metal-using societies because they are easily manufactured, the tool stone raw material is usually plentiful, and they are easy to transport and sharpen. The study of stone tools is a cornerstone of prehistoric archaeology because they are essentially indestructible and therefore a ubiquitous component of the archaeological record. Ethnoarchaeology is used to further the understanding and cultural implications of stone tool use and manufacture. Knapped stone tools are made from cryptocrystalline materials such as chert, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Archaeological Periods (North America)
North American archaeological periods divides the history of pre-Columbian North America into a number of named successive eras or periods, from the earliest-known human habitation through to the early Colonial period which followed the European colonization of the Americas. Stage classification One of the most enduring classifications of archaeological periods and cultures was established in Gordon Willey and Philip Phillips' 1958 book, ''Method and Theory in American Archaeology''. They divided the archaeological record in the Americas into five phases, only three of which applied to North America. The use of these divisions has diminished in most of North America due to the development of local classifications with more elaborate breakdowns of times. :1. The Paleo-Indians stage and/or Lithic stage :2. The Archaic stage :3. Formative stage or Post-archaic stage – at this point, the North American classifications system differs from the rest of the Americas. For more de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historic Center Of Quito - World Heritage Site By UNESCO - Photo 437
History is the systematic study of the past, focusing primarily on the human past. As an academic discipline, it analyses and interprets evidence to construct narratives about what happened and explain why it happened. Some theorists categorize history as a social science, while others see it as part of the humanities or consider it a hybrid discipline. Similar debates surround the purpose of history—for example, whether its main aim is theoretical, to uncover the truth, or practical, to learn lessons from the past. In a more general sense, the term ''history'' refers not to an academic field but to the past itself, times in the past, or to individual texts about the past. Historical research relies on primary and secondary sources to reconstruct past events and validate interpretations. Source criticism is used to evaluate these sources, assessing their authenticity, content, and reliability. Historians strive to integrate the perspectives of several sources to devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though their ancestors were Indigenous American or Austronesian. The term was used as an ethno-racial exonym for mixed-race that evolved during the Spanish Empire. It was a formal label for individuals in official documents, such as censuses, parish registers, Inquisition trials, and others. Priests and royal officials might have classified persons as mestizos, but individuals also used the term in self-identification. With the Bourbon reforms and the independence of the Americas, the caste system disappeared and terms like "mestizo" fell in popularity. The noun , derived from the adjective , is a term for racial mixing that did not come into usage until the 20th century; it was not a colonial-era term.Rappaport, Joa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of South America
In South America, Indigenous peoples comprise the Pre-Columbian peoples and their descendants, as contrasted with people of European ancestry and those of African descent. In Spanish, Indigenous peoples are referred to as (), or (). The term () is used in Argentina, and () is commonly used in Colombia. The English term ''Amerindian'' (short for "Indians of the Americas") is often used in the Guianas. Latin Americans of mixed European and Indigenous descent are usually referred to as (Spanish) and (Portuguese), while those of mixed African and Indigenous ancestry are referred to as . It is believed that the first human populations of South America either arrived from Asia into North America via the Bering Land Bridge and migrated southwards or alternatively from Polynesia across the Pacific. The earliest generally accepted archaeological evidence for human habitation in South America dates to 14,000 years ago, and is located at the Monte Verde site in southern Chile. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of The Inca Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Inca Empire, also known as the Conquest of Peru, was one of the most important campaigns in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. After years of preliminary exploration and military skirmishes, 168 Spaniards, Spanish soldiers under conquistador Francisco Pizarro, along with his brothers in arms and their Indigenous peoples of South America, indigenous Indian auxiliaries, allies, captured the last Sapa Inca, Atahualpa, at the Battle of Cajamarca in 1532. It was the first step in a long campaign that took decades of fighting but ended in Spanish victory in 1572 and colonization of the region as the Viceroyalty of Peru. The conquest of the Inca Empire (called "Tahuantinsuyu" or "Tawantinsuyu" in Quechuan languages, Quechua, meaning "Realm of the Four Parts"), led to spin-off campaigns into present-day Chile and Colombia, as well as expeditions to the Amazon basin, Amazon Basin and surrounding rainforest. When the Spanish arrived at the borders of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Colonization Of The Americas
The Spanish colonization of the Americas began in 1493 on the Caribbean island of Hispaniola (now Haiti and the Dominican Republic) after the initial 1492 voyage of Genoa, Genoese mariner Christopher Columbus under license from Queen Isabella I of Castile. These overseas territories of the Spanish Empire were under the jurisdiction of Crown of Castile until the last territory was lost in Spanish–American War, 1898. Spaniards saw the dense populations of indigenous peoples of the Americas, Indigenous peoples as an important economic resource and the territory claimed as potentially producing great wealth for individual Spaniards and the crown. Religion played an important role in the Spanish conquest and incorporation of indigenous peoples, bringing them into the Catholic Church peacefully or by force. The crown created civil and religious structures to administer the vast territory. Spanish men and women settled in greatest numbers where there were dense indigenous populations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Peoples Of The Americas
In the Americas, Indigenous peoples comprise the two continents' pre-Columbian inhabitants, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with them in the 15th century, as well as the ethnic groups that identify with the pre-Columbian population of the Americas as such. These populations exhibit significant diversity; some Indigenous peoples were historically hunter-gatherers, while others practiced agriculture and aquaculture. Various Indigenous societies developed complex social structures, including pre-contact monumental architecture, organized city, cities, city-states, chiefdoms, state (polity), states, monarchy, kingdoms, republics, confederation, confederacies, and empires. These societies possessed varying levels of knowledge in fields such as Pre-Columbian engineering in the Americas, engineering, Pre-Columbian architecture, architecture, mathematics, astronomy, History of writing, writing, physics, medicine, Pre-Columbian agriculture, agriculture, irrigation, geology, minin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indigenous Religion
Indigenous religion or native religion is a category used in the study of religion to demarcate the religious belief systems of communities described as being " indigenous". This category is often juxtaposed against others such as the " world religions" and " new religious movements". The term is commonly applied to a range of different belief systems across the Americas, Australasia, Asia, Africa, and Northern Europe, particularly to those practiced by communities living under the impact of colonialism. The term "indigenous religions" is usually applied to the localised belief systems of small-scale societies. These belief systems do not typically engage in proselytization, thus distinguishing them from movements like Christianity, Islam, Hinduism, and Buddhism that all seek converts and which are typically classified as "world religions". They are also often characterised as being distinct from the "world religions" because they are orally transmitted, intertwined with traditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |