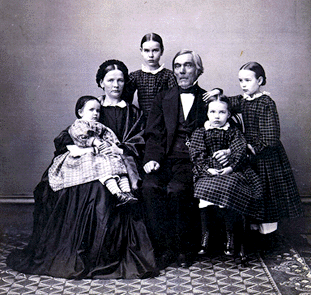|
Independence Of Finland
Finland declared its independence on 6 December 1917. The formal Declaration of Independence was only part of the long process leading to the independence of Finland. History Proclamation of Empress Elizabeth (1742) The subject of an independent Finland was first mentioned in the 18th century, when present-day Finland was still ruled by Sweden. On 18 March 1742, during the Russian occupation in the Russo-Swedish War (1741–1743), Empress Elizabeth of Russia issued a proclamation in the Finnish language to the Finnish people asking them to create a Finland which would be independent from both Sweden and Russia. This led to preparations to create a Kingdom of Finland in 1742. Elizabeth's nephew Duke Peter of Holstein-Gottorp (who later became heir to the throne of Russia and Tsar as Peter III) was proclaimed King of Finland. However, the political situation outgrew the idea of a Finnish kingdom and the concept quickly evaporated. Anjala conspiracy (1788) The Anjala conspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suomineito
The Maiden of Finland ( , ) is the national personification of Finland. Personification She is a barefoot young woman in her mid-twenties with blonde hair, blue eyes, wearing a blue and white national costume or a white dress. She was originally called Aura after the Aura River in Turku. As a symbol, the Finnish Maiden has been used since the 19th century when she was pictured as a woman wearing a turreted crown, and then developing as Finland gained a national consciousness and independence. She was depicted in poetry and fine arts. Zachris Topelius and Walter Runeberg were important in establishing the Finnish Maiden as a symbol. Like the Mother Svea of neighbouring Sweden, the Finnish maiden was, at first, a mature woman, but gradually became younger. File:Suomineito (Isto).jpg, In the painting '' The Attack'' by Edvard Isto, the Finnish Maiden is being attacked by the Russian eagle, which is tearing away the law book from her hands. It was painted when the Russificati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elisabeth Järnefelt
Elisabeth Järnefelt (née Clodt von Jürgensburg; 11 January 1839 – 3 February 1929) was a Finnish salonist, known as "the mother of Finnish art and culture".Biografiskt lexikon för Finland 2. Ryska tiden (2009). Life Elisabeth's parents were the general and wood engraver and Catharina Vigné. She was educated first at a girls school and then at home, and raised in Saint Petersburg in Russia. Elisabeth married August Aleksander Järnefelt on 22 December 1857 at Saint Petersburg, and settled with him in Helsinki in Finland. Their children were , Arvid, Erik, Ellida, Ellen, Armas, Aino, Hilja and Sigrid. Armas, Arvid and Erik were famous Finnish cultural figures. Daughter Aino Järnefelt was married to composer Jean Sibelius. Elisabeth Järnefelt was also a good friend of the writer Juhani Aho. Her marriage was not a happy one. After the birth of their last child, her spouse decided to live in chastity: he was described as a strict patriarch who disliked spending money ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Famine Of 1866–1868
The Finnish famine of 1866–1868 was the last famine in Finland, and (along with the subsequent Swedish famine of 1867–1869) the last major famine in Northern Europe. In Finland, the famine is known as "the great hunger years", or . About 8.5% of the entire population died of hunger; in the hardest-hit areas up to 20%. The total death toll was 270,000 in three years, about 150,000 in excess of normal mortality. The worst-hit areas were Satakunta, Tavastia, Ostrobothnia, and North Karelia. Causes Parts of the country had suffered poor harvests in previous years, most notably in 1862. The summer of 1866 was extremely rainy, and staple crops failed widely: potatoes and root vegetables rotted in the fields, and conditions for sowing grain in the autumn were unfavourable. When stored food ran out, thousands took to the roads to beg. The following winter was hard, and spring was late. In Helsinki, the average temperature in May 1867 was +, about below the long-time average a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Ruble
The ruble or rouble (; Currency symbol, symbol: ₽; ISO 4217, ISO code: RUB) is the currency of the Russia, Russian Federation. Banknotes and coins are issued by the Central Bank of Russia, which is Russia's central bank, monetary authority independent of all other government bodies.wikisource:en:Constitution of Russia#Article 75, Article 75 - Constitution of the Russian Federation (English translation) The ruble is the second-oldest currency in continuous use and the first Decimalisation, decimal currency. The ruble was the currency of the Russian Empire, which was replaced by the Soviet ruble (code: SUR) during the Soviet Union, Soviet period. Following the dissolution of the Soviet Union, by 1992, the Soviet ruble was replaced in the Russian Federation by the Russian ruble (code: RUR) Par value, at par. The Russian ruble then further continued to be used in 11 post-Soviet states, forming a "ruble zone" until 1993. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bank Of Finland
The Bank of Finland (, ) is the national central bank for Finland within the Eurosystem. It was the Finnish central bank from 1865 to 1998, issuing the markka. It views itself as the fourth oldest surviving central bank in the world, after Sweden's Riksbank, the Bank of England, and the Bank of France, having been originally created in 1811-1812 as the Office of Exchange, Lending, and Deposits of the Grand Duchy of Finland () before taking its current name in 1840. Unlike many other longstanding central banks, it has always been government-owned. History Russian Empire In 1809, the Russian Empire annexed Finland and made it a Grand Duchy with its own administrative structure. One aim of the new authorities was to sever Finland's previous economic integration with Sweden, including the use of the Swedish riksdaler as currency. To that effect, the Office of Exchange, Lending, and Deposits was chartered on and established on in Turku by Alexander I of Russia, partly model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Markka
The markka (; ; currency symbol, sign: mk; ISO 4217, ISO code: FIM), also known as the Finnish mark, was the currency of Finland from 1860 until 28 February 2002, when it ceased to be legal tender. The markka was divided into 100 penny, pennies (; ), abbreviated as "p". At the point of conversion, the rate was fixed at €1 = 5.94573 mk. The markka was replaced by the euro (€), which had been introduced, in cash form, on 1 January 2002. This was after a transitional period of three years, when the euro was the official currency but only existed as "book money" outside of the monetary base. The dual circulation period, when both the markka and the euro had legal tender status, ended on 28 February 2002. Etymology The name "markka" was based on a medieval unit of weight. Both "markka" and "penni" are similar to words used in Germany for that country's former currency, based on the same etymological roots as the Deutsche Mark and pfennig. Although the word "markka" pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finland's Language Strife
Finland's language strife (; ) was a major conflict in mid-19th century Finland. Both the Swedish and Finnish languages were commonly used in Finland at the time, associated with descendants of Swedish colonisation and leading to class tensions among the speakers of the different languages. It became acute in the mid-19th century. Background Finland had once been under Swedish rule. Swedish (with some Latin) was the language of administration and education in the Swedish Realm. Swedish was therefore the most-used language of administration and higher education among the Finns. To gain higher education, one had to learn Swedish, and Finnish was considered by the upper classes to be a "language of peasants". Immigration of Swedish peasants to Finland's coastal regions also boosted the status of Swedish by sheer number of speakers. Although Mikael Agricola had started written Finnish with '' Abckiria'' in the 1500s, and a Finnish translation of the Civil Code of 1734 was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elias Lönnrot
Elias Lönnrot (; 9 April 1802 – 19 March 1884) was a Finnish polymath, physician, philosopher, poet, musician, linguist, journalist, philologist and collector of traditional Finnish language, Finnish Oral literature, oral poetry. He is best known for synthesizing the Finnish national epic, ''Kalevala'' (1835, enlarged 1849) from short ballads and lyric poetry, lyric poems he gathered from Finnish folklore, Finnish oral tradition during several field expeditions in Finland, Russian Karelia, the Kola Peninsula and Baltic countries. In botany, he is remembered as the author of the 1860 ''Flora Fennica'', the first scientific text written in Finnish rather than in Latin. Education and early life Lönnrot was born in Sammatti, in the province of Uusimaa, Finland, which was then Finland under Swedish rule, part of Sweden. From 1814 to 1815, he attended the school of Tammisaari Pedagogio. He studied at Katedralskolan i Åbo, Turku Cathedral School from 5April1816 until he droppe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Ludvig Runeberg
Johan Ludvig Runeberg (; 5 February 1804 – 6 May 1877) was a Finnish priest, lyric and epic poet. He wrote exclusively in Swedish. He is considered a national poet of Finland. He is the author of the lyrics to (''Our Land'', in Finnish) which became the Finnish national anthem. Runeberg was also involved in the modernization of the Finnish Lutheran hymnal and produced many texts for the new edition. Background Childhood Runeberg was born into a Swedish-speaking family in Jakobstad, Finland, on the shores of the Gulf of Bothnia. His parents were sea captain Lorentz Ulrik Runeberg (1772–1828) and Anna Maria Malm (1782–1834). His paternal grandfather Ludvig had moved to Finland from Sweden, and Anna Maria Malm was born to a merchant family from Jakobstad, which probably also had their roots in Sweden.Helge Pohjolan-Pirhonen: ''Kansakunnan historia 3: kansakunta löytää itsensä'', p. 529–550. Helsinki: WSOY, 1973. ISBN 951-0-05774-6. (in Finnish) As a child, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diet Of Finland
The Diet of Finland (Finnish language, Finnish ''Suomen maapäivät'', later ''valtiopäivät''; Swedish language, Swedish ''Finlands Lantdagar''), was the Diet (assembly), legislative assembly of the Grand Duchy of Finland from 1809 to 1906 and the recipient of the powers of the Swedish Riksdag of the Estates. (The term ''valtiopäivät'' today means an annual session of the Parliament of Finland, while in Swedish ''Riksdagen'' is now the name for both the Parliament and its sessions.) ''Åbo Lantdag'' The first The Estates, States of Finland were held in Helsinki in 1616. Aatos Other assemblies ''(Åbo landtag, lantdag)'' were held in Turku (Åbo), for example in 1676. The assembly was called together by Axel Julius De la Gardie. The estate of peasants was chaired by Heikki Heikinpoika Vaanila. The Porvoo Diet ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander I Of Russia
Alexander I (, ; – ), nicknamed "the Blessed", was Emperor of Russia from 1801, the first king of Congress Poland from 1815, and the grand duke of Finland from 1809 to his death in 1825. He ruled Russian Empire, Russia during the chaotic period of the Napoleonic Wars. The eldest son of Emperor Paul I and Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg, Alexander succeeded to the throne after his father was murdered. As prince and during the early years of his reign, he often used liberal rhetoric but continued Russian absolutism, Russia's absolutist policies in practice. In the first years of his reign, he initiated some minor social reforms and (in 1803–04) major liberal educational reforms, such as building more universities. Alexander appointed Mikhail Speransky, the son of a village priest, as one of his closest advisors. The over-centralized Collegium (ministry), Collegium ministries were abolished and replaced by the Committee of Ministers of the Russian Empire, Committee of Ministers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |