|
Ikhwan As-Safa'
The Ikhwān (, ), commonly known as Ikhwān man Aṭāʿa Allah (, 'Brethren of those who obey God'), was a Wahhabi religious militia made up of traditionally nomadic tribesmen which formed a significant military force of the ruler Ibn Saud and played an important role during the unification of Saudi Arabia whereby establishing him as ruler of most of the Arabian Peninsula in Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The Ikhwan first appeared around 1902. They were the product of clergy who aimed to break up the Bedouin tribes and settle them around the wells and oases of the sedentary Arabian populations, mainly those of the Najd, on the grounds that nomadic life was incompatible with the strict conformity of their interpretation of Islam. The newly Islamicized Bedouin would be converted from nomad raiders to soldiers for Islam. The cleric/teachers of the Ikhwan were dedicated to their idea of the purification and the unification of Islam, and some of the newly converted Ikhwan rebelled against t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries by area, fifth-largest country in Asia, the largest in the Middle East, and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 12th-largest in the world. It is bordered by the Red Sea to the west; Jordan, Iraq, and Kuwait to the north; the Persian Gulf, Bahrain, Qatar and the United Arab Emirates to the east; Oman to the southeast; and Yemen to Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, the south. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northwest separates Saudi Arabia from Egypt and Israel. Saudi Arabia is the only country with a coastline along both the Red Sea and the Persian Gulf, and most of Geography of Saudi Arabia, its terrain consists of Arabian Desert, arid desert, lowland, steppe, and List of mountains in Saudi Arabia, mountains. The capital and List of cities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saudi Conquest Of Hejaz
The Saudi conquest of Hejaz or the also known as the Hejaz-Nejd War, was a campaign by Abdulaziz al-Saud of the Saudi Sultanate of Nejd to take over the Hashemite Kingdom of Hejaz in 1924–25, ending with conquest and incorporation of Hejaz into the Saudi domain. Background The 1924 campaign came within the scope of the historic conflict between the Hashemites of Hejaz and the Saudis of Riyadh (Nejd), which had already sparked the First Saudi-Hashemite War in 1919. The decisive moment that led to the conquest of the Hejaz was the decision in late 1923 by the British government as an economic measure to cease paying subsidies to both the feuding families of Arabia, namely the al-Hashemites of the Hejaz and the al-Saud of the Nejd. Without the £60,000 annual subsidy in gold coins paid to him by the British government, the principle restraint on Ibn Saud was removed. Likewise, the end of the subsidies amounting to £25,000 gold coins per month to Hussein bin Ali al-Hashemite, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islam
Islam is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the Quran, and the teachings of Muhammad. Adherents of Islam are called Muslims, who are estimated to number Islam by country, 2 billion worldwide and are the world's Major religious groups, second-largest religious population after Christians. Muslims believe that Islam is the complete and universal version of a Fitra, primordial faith that was revealed many times through earlier Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophets and messengers, including Adam in Islam, Adam, Noah in Islam, Noah, Abraham in Islam, Abraham, Moses in Islam, Moses, and Jesus in Islam, Jesus. Muslims consider the Quran to be the verbatim word of God in Islam, God and the unaltered, final revelation. Alongside the Quran, Muslims also believe in previous Islamic holy books, revelations, such as the Torah in Islam, Tawrat (the Torah), the Zabur (Psalms), and the Gospel in Islam, Injil (Gospel). They believe that Muhammad in Islam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Pre-Islamic Arabia
In pre-Islamic Arabia, the dominant religious practice was that of Arab polytheism, which was based on the veneration of various deities and spirits, such as the god Hubal and the goddesses al-Lāt, al-‘Uzzā, and Manāt. Worship was centred around local shrines and temples, most notably including the Kaaba in Mecca. Deities were venerated and invoked through pilgrimages, divination, and ritual sacrifice, among other traditions. Different theories have been proposed regarding the role of "Allah" (a word in Arabic that is now chiefly associated with God in Islam) in the Meccan religion. Many of the physical descriptions of the pre-Islamic gods and goddesses are traced to idols, especially near the Kaaba, which is said to have contained up to 360 of them. Other religions—namely Christianity, Judaism, and Zoroastrianism—were also represented in the region. The influence of the Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Aksum enabled the nurturing of Christianity in pre-Islamic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulama
In Islam, the ''ulama'' ( ; also spelled ''ulema''; ; singular ; feminine singular , plural ) are scholars of Islamic doctrine and law. They are considered the guardians, transmitters, and interpreters of religious knowledge in Islam. "Ulama" may refer broadly to the educated class of such religious scholars, including Theology, theologians, Religious law, canon lawyers (muftis), judges (qadis), professors, and high state religious officials. Alternatively, "ulama" may refer specifically to those holding governmental positions in an Islamic state. By longstanding tradition, ulama are educated in religious institutions (''madrasas''). The Quran and sunnah (authentic hadith) are the scriptural sources of Sharia, traditional Islamic law. Traditional way of education Students of Islamic doctrine do not seek out a specific educational institution, but rather seek to join renowned teachers. By tradition, a scholar who has completed their studies is approved by their teacher. At ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salafi
The Salafi movement or Salafism () is a fundamentalist revival movement within Sunni Islam, originating in the late 19th century and influential in the Islamic world to this day. The name "''Salafiyya''" is a self-designation, claiming a return to the traditions of the "pious predecessors" (), the first three generations of Muslims (the Islamic prophet Muhammad and the is companions then the , and the third generation, the ), who are believed to exemplify the pure form of Islam. In practice, Salafis claim that they rely on the Qur'an, the and the (consensus) of the , giving these writings precedence over what they claim as "later religious interpretations".Bin Ali Mohamed ''Roots Of Religious Extremism, The: Understanding The Salafi Doctrine Of Al-wala' Wal Bara'' World Scientific, 2015 p. 61 The Salafi movement aimed to achieve a renewal of Muslim life, and had a major influence on many Muslim thinkers and movements across the Islamic world. Salafi Muslims oppose ' (reli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ahsa Oasis
Al-Ahsa Oasis (, ''al-ʾAhsā''), also known as al-Ḥasāʾ () or Hajar (), is an oasis and historical region in eastern Saudi Arabia. Al-Ahsa Governorate, which makes up much of the country's Eastern Province, is named after it. The oasis is located about inland from the coast of the Persian Gulf. Al-Ahsa Oasis comprises four main cities and 22 villages. The cities include Al-Mubarraz and Al-Hofuf, two of the largest cities in Saudi Arabia. Description With an area of around , Al-Ahsa Oasis is the largest oasis in the world. A large part of the oasis is located in the Empty Quarter, also referred to as Rub' al Khali in Arabic. This covers almost three-quarters of the land in the oasis, while residential areas constitute 18%. There are more than 2.5 million palm trees including date palms in the oasis, which is fed from a huge underground aquifer and irrigated by the flow of more than 280 artesian springs, allowing year-round agriculture in a region that is otherwise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Commins
David Commins (born 1954) is an American scholar and Professor of History and Benjamin Rush Chair in the Liberal Arts and Sciences (1987) at Dickinson College. He is known for his works on Wahhabism. See also * Namira Nahouza Namira Nahouza (born July 1979) is a French author, academic researcher, university lecturer, teacher of Arabic and religious studies, and research fellow at Cambridge Muslim College, whose research focusses on contemporary Salafi-Wahhabi theories ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Commins, David 1954 births American Islamic studies scholars Living people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultan Al-Otaibi
Sultan Al-Otaibi (; born May 21, 1970) is a Kuwaiti former swimmer, who specialized in individual medley, but also competed in backstroke, breaststroke, and butterfly. He represented Kuwait in all of the four editions of the Olympic Games since 1988, and also held numerous Kuwaiti records in the same disciplines, particularly in the 200 m individual medley. Al-Otaibi made his official debut, as an 18-year-old, at the 1988 Summer Olympics in Seoul. He failed to reach the top 16 final in any of his individual events, finishing thirty-eighth in the 200 m butterfly (2:12.89), forty-second in the 200 m individual medley (2:15.63), and thirty-first in the 400 m individual medley (4:50.16), his best all-time Olympic result. Al-Otaibi also competed at the 1992 Summer Olympics in Barcelona, and at the 1996 Summer Olympics in Atlanta, but finished outside the top 25 field in most of his swimming events, including the 200 m individual medley. Twelve years after competing in his first Oly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faisal Al Duwaish 1930 Sketch
Faisal, Faisel, Fayçal or Faysal () is an Arabic given name. Faisal, Fayçal or Faysal may also refer to: People * King Faisal (other) ** Faisal I of Iraq and Syria (1885–1933), leader during the Arab Revolt ** Faisal II of Iraq (1935–1958), last King of the Kingdom of Iraq ** Faisal of Saudi Arabia (1906–1975), third King of Saudi Arabia * Faisal Al-Fayez (born 1952), Prime Minister of Jordan * Faisal al-Duwaish (1882–1931), Arabian tribe sheik * Faisal Amin Abu-Rass (born 1957), Yemeni diplomat * Faisal Basri (1959-2024), Indonesian economist and politician * Faisal Buressli (born 1961), Kuwaiti basketball player and coach * Faisal Karami (born 1971), Lebanese politician * Faisal bin Abdullah Al Saud (born 1950), Saudi royal * Faisal bin Bandar Al Saud (born 1945), Saudi government official * Faisal bin Bandar Al Saud, Saudi royal and businessman * Faisal bin Khalid Al Saud (born 1973), Saudi government official * Faisal bin Mishaal Al Saud (born 1959 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
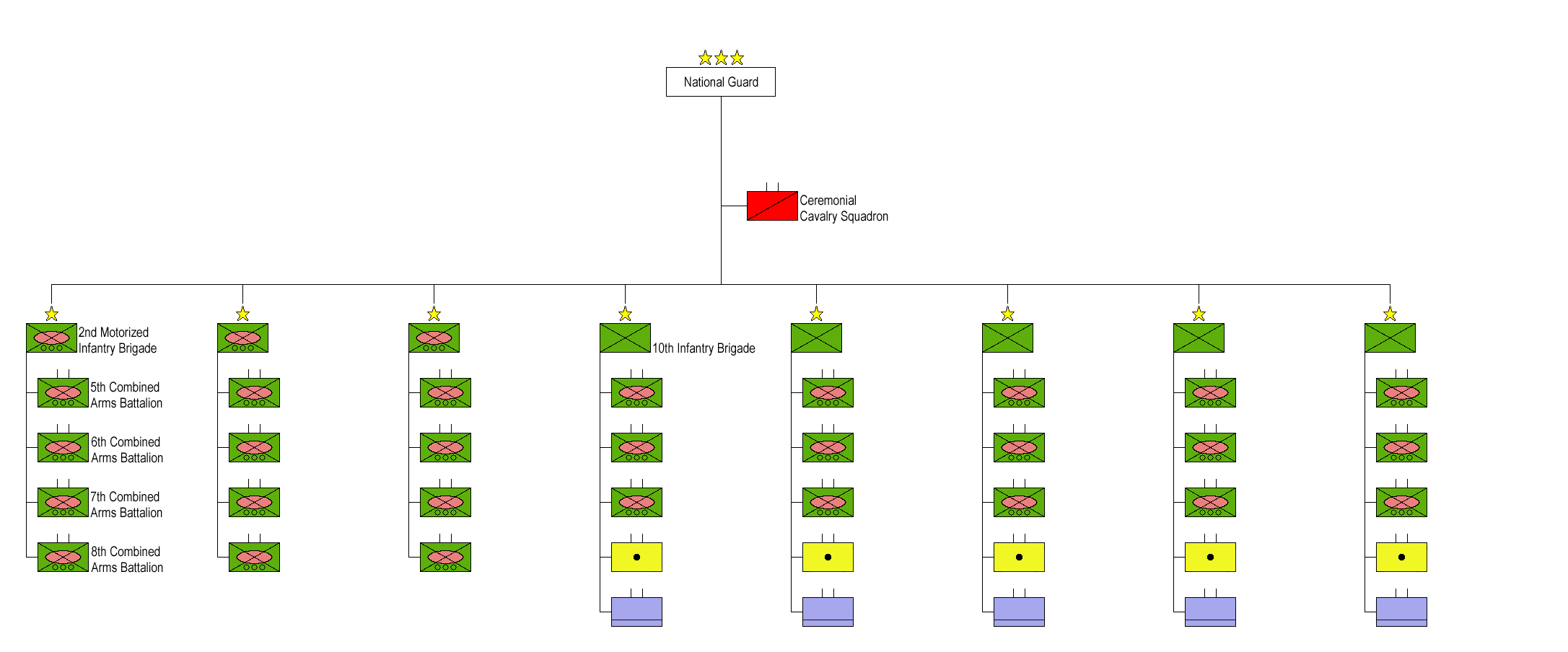
Saudi Arabian National Guard
The Saudi Arabian National Guard (SANG), also known as the White Army, is one of the three major branches of the military forces of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. The national guard is under the administrative control of the Ministry of National Guard, instead of the Minister of Defense (Saudi Arabia), Ministry of Defence. It differs from the regular Saudi Arabian Army in being forged out of tribal elements loyal to the House of Saud and tasked with protecting the royal family from internal dangers such as a coup d'état. Organisation and roles The Saudi Arabian National Guard has a standing force of 125,000 troops and a tribal militia of some 28,000 Fouj (tribal levies). It serves both as a defence force against external attack and an internal security force. Its duties include protecting the House of Saud, Saudi ruling family, guarding against military coups, safeguarding strategic facilities and resources, and providing security for the cities of Mecca and Medina. It reports ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Sands
''Arabian Sands'' is a 1959 book by explorer and travel writer Wilfred Thesiger. The book focuses on the author's travels in the Arabian Peninsula between 1945 and 1950, and details his two crossings of the Empty Quarter undertaken between 1946 and 1948. Thesiger’s first crossing, from Mughshin in Oman to Liwa across the eastern sands, was followed by a crossing of the western sands from Manwakh in Yemen, via Laila, to Abu Dhabi. The book attempted to capture the lives of the Bedu people and other inhabitants of the Arabian peninsula. It is considered a classic of travel literature. The book largely reflects on the changes and large scale development that took place after the Second World War and the subsequent gradual erosion of traditional Bedouin ways of life that had previously existed unaltered for thousands of years. Context Wilfred Thesiger was born into a privileged English background, the son of a diplomat, educated at Eton and Oxford. As soon as he could, on his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |