|
Icon-class Cruise Ship
The ''Icon'' class (formally Project Icon) is a planned class of cruise ships ordered by Royal Caribbean International and to be built by Meyer Turku in Turku, Finland. Royal Caribbean plans to have 3 ''Icon''-class ships by 2030. History On 10 October 2016, Royal Caribbean and Meyer Turku announced an order to build two ships under the project name "Icon". The first two ships are planned to be delivered in the second quarters of 2022 and 2024. The ships will be classified by DNV GL. Royal Caribbean applied to register a trademark for "Icon of the Seas" in 2016, which was at the time suggested as an indication of the name of the first ship. On 2 July 2019, Royal Caribbean announced an order for a third ship in the "Icon" class. The third ship is planned to be delivered in 2025, one year after the second "Icon" ship. Steel-cutting for ''Icon of the Seas'' began on 14 June 2021, and the keel was laid on 5 April 2022. Steel-cutting for the second "Icon" class ship began on 15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Icon Of The Seas
''Icon of the Seas'' is a cruise ship built for Royal Caribbean International and will be the lead ship of the . She is scheduled to enter service in early 2024 out of PortMiami in the US. At , ''Icon of the Seas'' is the List of largest cruise ships, largest cruise ship in the world. History In October 2016, Royal Caribbean and Meyer Turku announced an order to build two ships under the project name "Icon". The ships are expected to be delivered in the third quarter of 2023 and in 2025. The ships will be classified by DNV. Royal Caribbean applied to register a trademark for "Icon of the Seas" in 2016. Steel-cutting for ''Icon of the Seas'' began in June 2021. In October 2021, Royal Caribbean announced that the first Liquefied natural gas, LNG tank for the ship was installed at the Neptun Werft in Rostock, Germany. In December 2021, the floating engine room unit, including the LNG tanks, was towed to Turku in Finland by tug. The keel was laid in April 2022. In May 2022, Royal C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNV GL
DNV (formerly DNV GL) is an international accredited registrar and classification society headquartered in Høvik, Norway. The company currently has about 12,000 employees and 350 offices operating in more than 100 countries, and provides services for several industries including maritime, oil and gas, renewable energy, electrification, food and beverage and healthcare. DNV GL was created in 2013 as a result of a merger between two leading organizations in the field — (Norway) and (Germany). In 2021, DNV GL changed its name to DNV, while retaining its post-merger structure. DNV is the world's largest classification society, providing services for 13,175 vessels and mobile offshore units (MOUs) amounting to 265.4 million gross tonnes, which represents a global market share of 21%. It is also the largest technical consultancy and supervisory to the global renewable energy (particularly wind, wave, tidal and solar) and oil and gas industry — 65% of the world's of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruise Ship Classes
This is a list of cruise ships, both those in service and those that have ceased to operate. Ocean liners are included on this list only if they also functioned as cruise ships. (See: list of ocean liners.) As some cruise ships have operated under multiple names, all names will be listed in the Status section, along with the history of the vessel, under the vessel's ''current or most recent name''. If a vessel is not currently operating as a cruise ship, only the most recent operation will be listed here. Likewise, if a vessel fulfilled another role before becoming a cruise ship, the first entry for the vessel will occur when the vessel began its career as a cruise ship. A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y Z Classes of cruise ships Cruise ship classes are sets of ships that have similar weight, height, length, passenger capacity and accommodation. *Belorussiya-class cruiseferry *Break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Tonnage
Gross tonnage (GT, G.T. or gt) is a nonlinear measure of a ship's overall internal volume. Gross tonnage is different from gross register tonnage. Neither gross tonnage nor gross register tonnage should be confused with measures of mass or weight such as deadweight tonnage or displacement. Gross tonnage, along with net tonnage, was defined by the ''International Convention on Tonnage Measurement of Ships, 1969'', adopted by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) in 1969, and came into force on 18 July 1982. These two measurements replaced gross register tonnage (GRT) and net register tonnage (NRT). Gross tonnage is calculated based on "the moulded volume of all enclosed spaces of the ship" and is used to determine things such as a ship's manning regulations, safety rules, registration fees, and port dues, whereas the older gross register tonnage is a measure of the volume of only certain enclosed spaces. History The International Convention on Tonnage Measurement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oasis-class Cruise Ship
The ''Oasis'' class is a class of 5 Royal Caribbean International cruise ships. The first two ships in the class, and , were delivered respectively in 2009 and 2010 by STX Europe Turku Shipyard, Finland. A third ''Oasis''-class vessel, , was delivered in 2016 built by STX France, and a fourth vessel, , was completed in March 2018. As of March 2022, the fifth ''Oasis''-class ship, '' Wonder of the Seas'', is currently in service. A sixth ship, to be named ''Utopia of the Seas'' has also been ordered by the company. The first two ships in the class, ''Oasis of the Seas'' and ''Allure of the Seas'', are slightly exceeded in size by the third ship, ''Harmony of the Seas'', while ''Symphony of the Seas'' is the second largest cruise ship in the world. ''Wonder of the Seas'', which was completed in 2022, is larger than ''Symphony of the Seas''. As of 2022, all ships of the Oasis class rank as the world's largest passenger ships. Ship features The ''Oasis''-class ships surpassed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gross Tonnage
Gross tonnage (GT, G.T. or gt) is a nonlinear measure of a ship's overall internal volume. Gross tonnage is different from gross register tonnage. Neither gross tonnage nor gross register tonnage should be confused with measures of mass or weight such as deadweight tonnage or displacement. Gross tonnage, along with net tonnage, was defined by the ''International Convention on Tonnage Measurement of Ships, 1969'', adopted by the International Maritime Organization (IMO) in 1969, and came into force on 18 July 1982. These two measurements replaced gross register tonnage (GRT) and net register tonnage (NRT). Gross tonnage is calculated based on "the moulded volume of all enclosed spaces of the ship" and is used to determine things such as a ship's manning regulations, safety rules, registration fees, and port dues, whereas the older gross register tonnage is a measure of the volume of only certain enclosed spaces. History The International Convention on Tonnage Measurement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
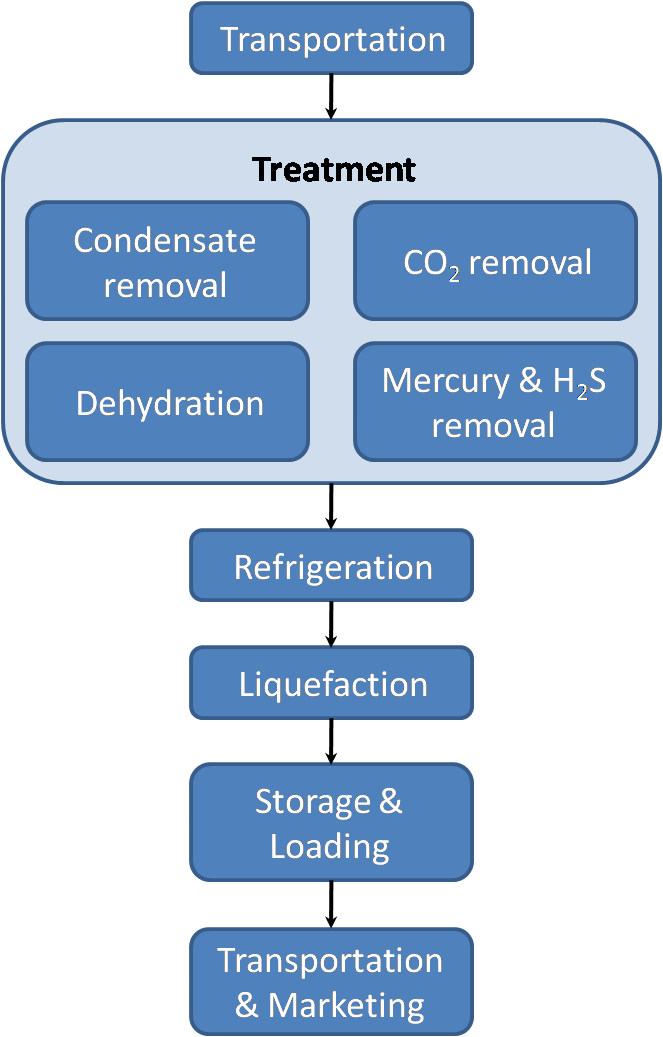
Liquified Natural Gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume of natural gas in the gaseous state (at standard conditions for temperature and pressure). LNG is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive. Hazards include flammability after vaporization into a gaseous state, freezing and asphyxia. The liquefaction process involves removal of certain components, such as dust, acid gases, helium, water, and heavy hydrocarbons, which could cause difficulty downstream. The natural gas is then condensed into a liquid at close to atmospheric pressure by cooling it to approximately ; maximum transport pressure is set at around ( gauge pressure), which is about one-fourth times atmospheric pressure at sea level. The gas extracted from underground hydrocarbon deposits contains a varying mix of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd
Royal Caribbean Group, formerly known as Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd., is a global cruise holding company incorporated in Liberia and based in Miami, Florida, United States. It is the world's second-largest cruise line operator, after Carnival Corporation & plc. As of January 2021, Royal Caribbean Group fully owns three cruise lines: Royal Caribbean International, Celebrity Cruises, and Silversea Cruises. They also hold a 50% stake in TUI Cruises and the now-defunct Pullmantur Cruises and CDF Croisières de France. Previously Royal Caribbean Group also fully owned Azamara Cruises selling the cruise line to Sycamore Partners in January 2021, and 50% of Island Cruises, selling their stake to TUI Travel PLC in October 2008. History Royal Caribbean Group was formed as Royal Caribbean Cruises Ltd. in 1997 when Royal Caribbean Cruise Line purchased Celebrity Cruises. The decision was made to keep the two cruise line brands separate following the merger; as a result Royal Caribbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cruise Ship
Cruise ships are large passenger ships used mainly for vacationing. Unlike ocean liners, which are used for transport, cruise ships typically embark on round-trip voyages to various ports-of-call, where passengers may go on Tourism, tours known as "shore excursions". On "cruises to nowhere" or "nowhere voyages", cruise ships make two- to three-night round trips without visiting any ports of call.Compare: Modern cruise ships tend to have less hull strength, speed, and agility compared to ocean liners. However, they have added amenities to cater to water tourism, water tourists, with recent vessels being described as "balcony-laden floating condominiums". As of December 2018, there were 314 cruise ships operating worldwide, with a combined capacity of 537,000 passengers. Cruising has become a major part of the tourism industry, with an estimated market of $29.4 billion per year, and over 19 million passengers carried worldwide annually . The industry's rapid growth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meyer Turku
Meyer Turku Oy is a Finnish shipbuilding company located in Turku, Finland Proper. The company is fully owned by German shipbuilder Meyer Werft GmbH. The main products are cruise ships and cruiseferries. The shipbuilding facility is Perno shipyard in Turku. The yard area is 144 hectares and it is equipped with a 365-metre-long dry dock and two bridge cranes with capacities of 600 and 1,200 tonnes. Additionally, the company owns subsidiaries Shipbuilding Completion Oy, Rauma-based ENG'nD Oy and Piikkiö-located cabin builder Piikkio Works Oy. The company was founded in November 1989 under name Masa-Yards Oy to continue operations of the previously bankrupted Wärtsilä Marine. The heritage, however, goes back to 1737 when industrial shipbuilding was first started in Turku. Company Meyer Turku Oy is fully owned by Germany-based Meyer Werft GmbH. Perno shipyard The main facility is Turku shipyard that is situated in Perno, Turku. The yard area is 144 hectares and it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuel Cell
A fuel cell is an electrochemical cell that converts the chemical energy of a fuel (often hydrogen fuel, hydrogen) and an oxidizing agent (often oxygen) into electricity through a pair of redox reactions. Fuel cells are different from most battery (electricity), batteries in requiring a continuous source of fuel and oxygen (usually from air) to sustain the chemical reaction, whereas in a battery the chemical energy usually comes from substances that are already present in the battery. Fuel cells can produce electricity continuously for as long as fuel and oxygen are supplied. The first fuel cells were invented by Sir William Robert Grove, William Grove in 1838. The first commercial use of fuel cells came more than a century later following the invention of the hydrogen–oxygen fuel cell by Francis Thomas Bacon in 1932. The alkaline fuel cell, also known as the Bacon fuel cell after its inventor, has been used in NASA space programs since the mid-1960s to generate power for sat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquified Natural Gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the volume of natural gas in the gaseous state (at standard conditions for temperature and pressure). LNG is odorless, colorless, non-toxic and non-corrosive. Hazards include flammability after vaporization into a gaseous state, freezing and asphyxia. The liquefaction process involves removal of certain components, such as dust, acid gases, helium, water, and heavy hydrocarbons, which could cause difficulty downstream. The natural gas is then condensed into a liquid at close to atmospheric pressure by cooling it to approximately ; maximum transport pressure is set at around ( gauge pressure), which is about one-fourth times atmospheric pressure at sea level. The gas extracted from underground hydrocarbon deposits contains a varying mix of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)