|
I (Greek)
Iota (; uppercase Ι, lowercase ι; ) is the ninth letter of the Greek alphabet. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Yodh. Letters that arose from this letter include the Latin I and J, the Cyrillic І (І, і), Yi (Ї, ї), and Je (Ј, ј), and iotated letters (e.g. Yu (Ю, ю)). In the system of Greek numerals, iota has a value of 10. Iota represents the close front unrounded vowel . In early forms of ancient Greek, it occurred in both long and short versions, but this distinction was lost in Koine Greek. Iota participated as the second element in falling diphthongs, with both long and short vowels as the first element. Where the first element was long, the iota was lost in pronunciation at an early date, and was written in polytonic orthography as iota subscript, in other words as a very small ι under the main vowel. Examples include ᾼ ᾳ ῌ ῃ ῼ ῳ. The former diphthongs became digraphs for simple vowels in Koine Greek.see Koine Greek phonology The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BC. It was derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and is the earliest known alphabetic script to systematically write vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BC, the Ionia, Ionic-based Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard throughout the Greek-speaking world and is the version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of several scripts, such as the Latin script, Latin, Gothic alphabet, Gothic, Coptic script, Coptic, and Cyrillic scripts. Throughout antiquity, Greek had only a single uppercas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Koine Greek
Koine Greek (, ), also variously known as Hellenistic Greek, common Attic, the Alexandrian dialect, Biblical Greek, Septuagint Greek or New Testament Greek, was the koiné language, common supra-regional form of Greek language, Greek spoken and written during the Hellenistic period, the Roman Empire and the early Byzantine Empire. It evolved from the spread of Greek following the conquests of Alexander the Great in the fourth century BC, and served as the lingua franca of much of the Mediterranean region and the Middle East during the following centuries . It was based mainly on Attic Greek, Attic and related Ionic Greek, Ionic speech forms, with various admixtures brought about through dialect levelling with other varieties. Koine Greek included styles ranging from conservative literary forms to the spoken vernaculars of the time. As the dominant language of the Byzantine Empire, it developed further into Medieval Greek, which then turned into Modern Greek. Literary Koine was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
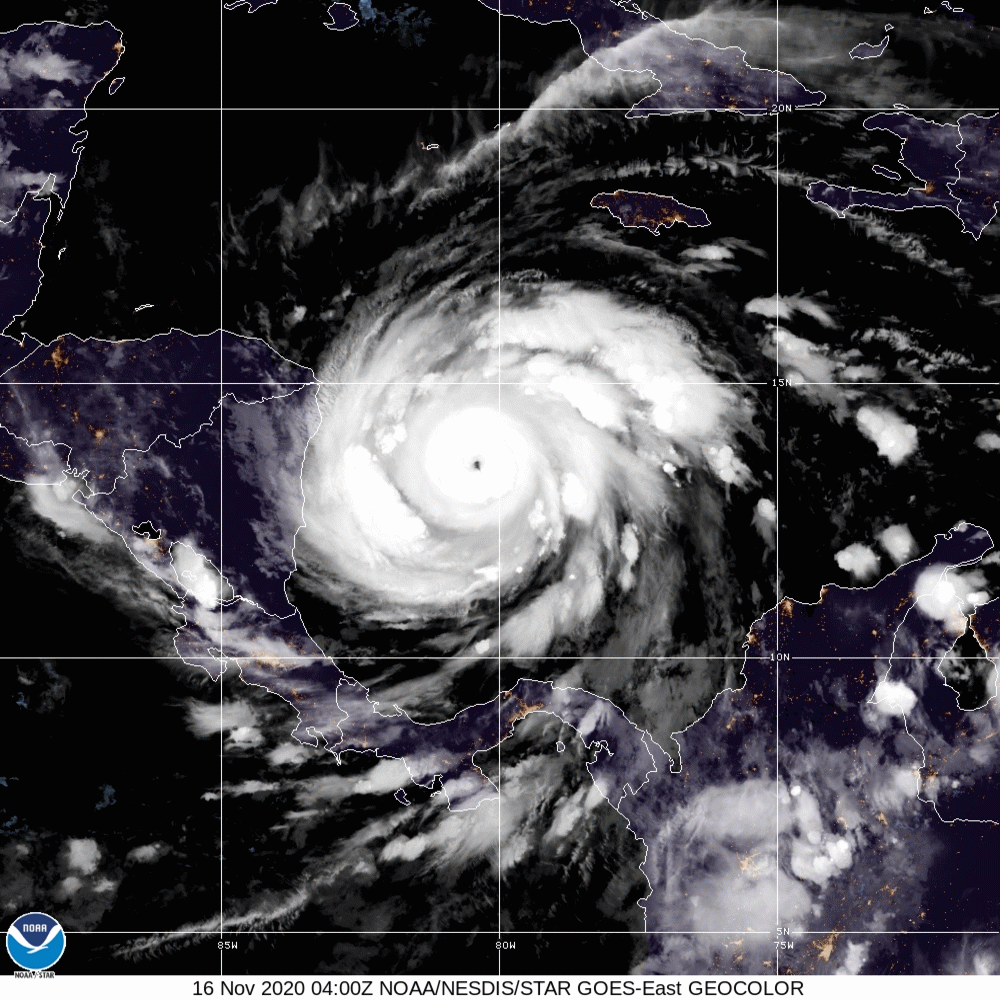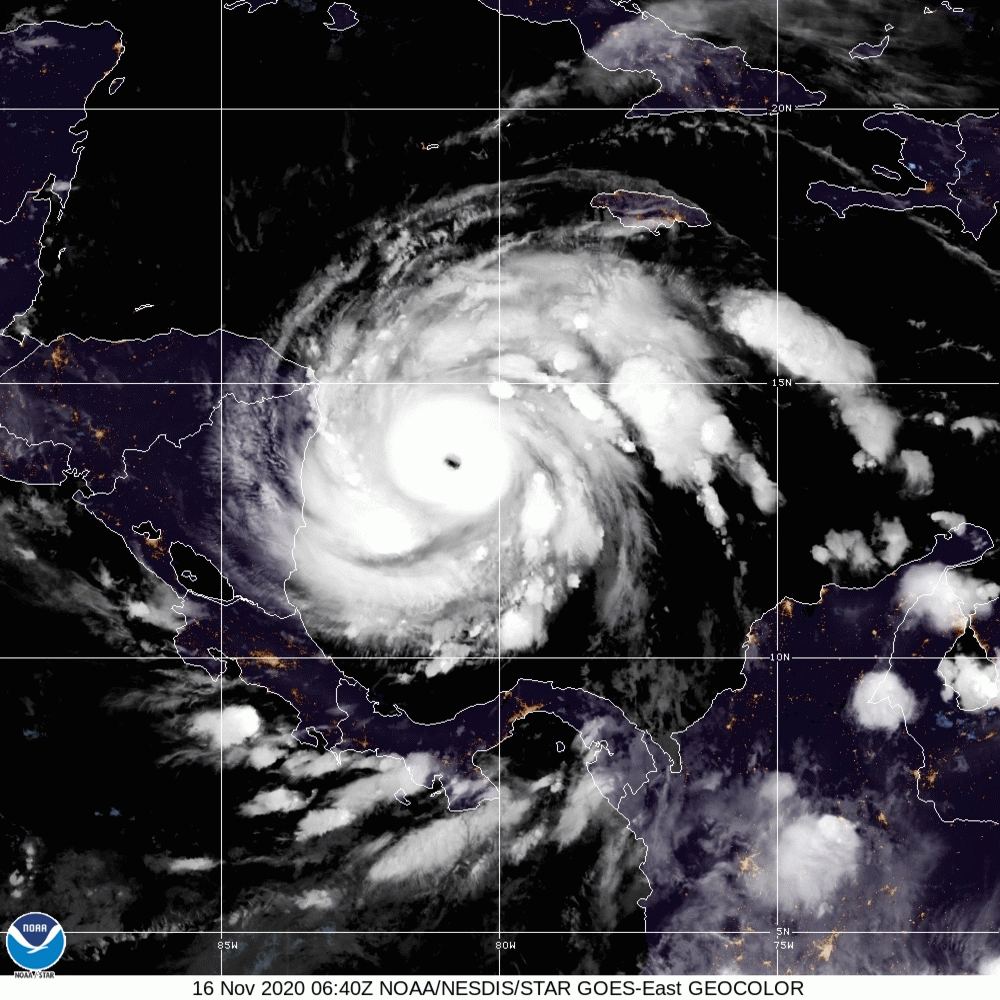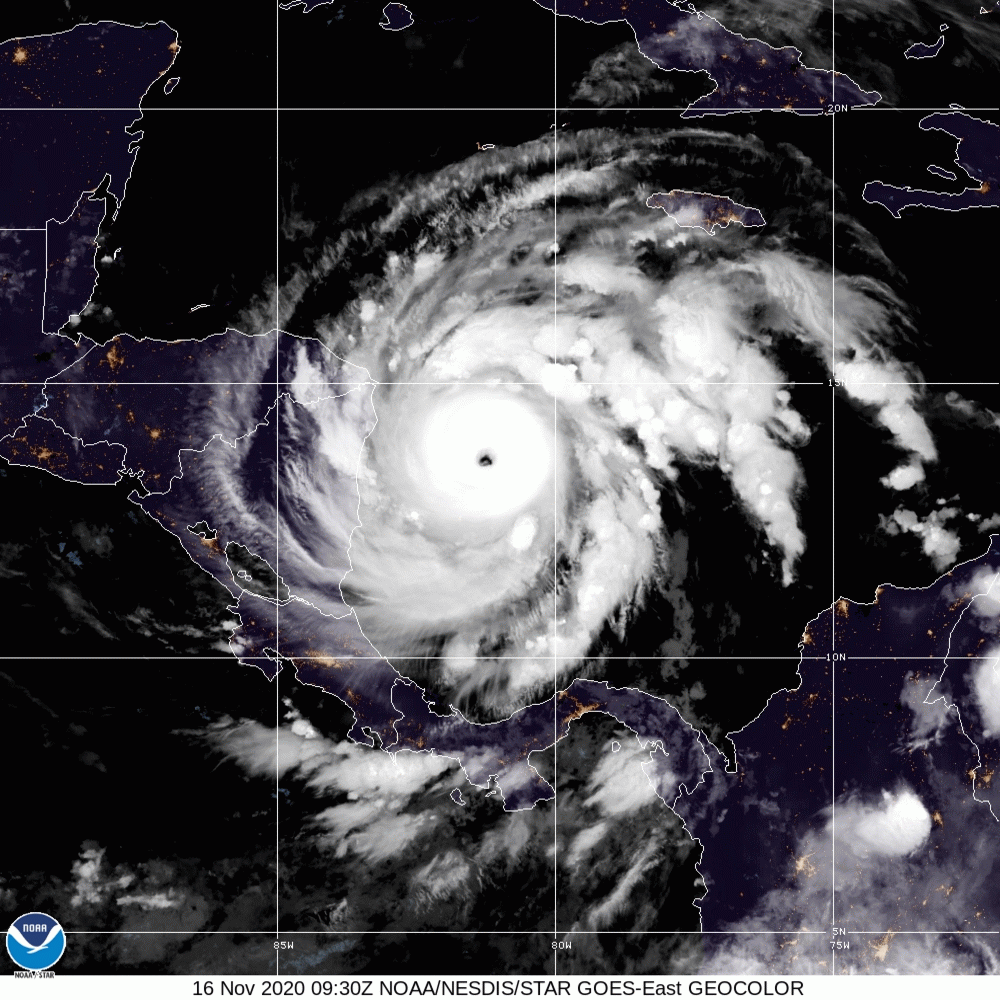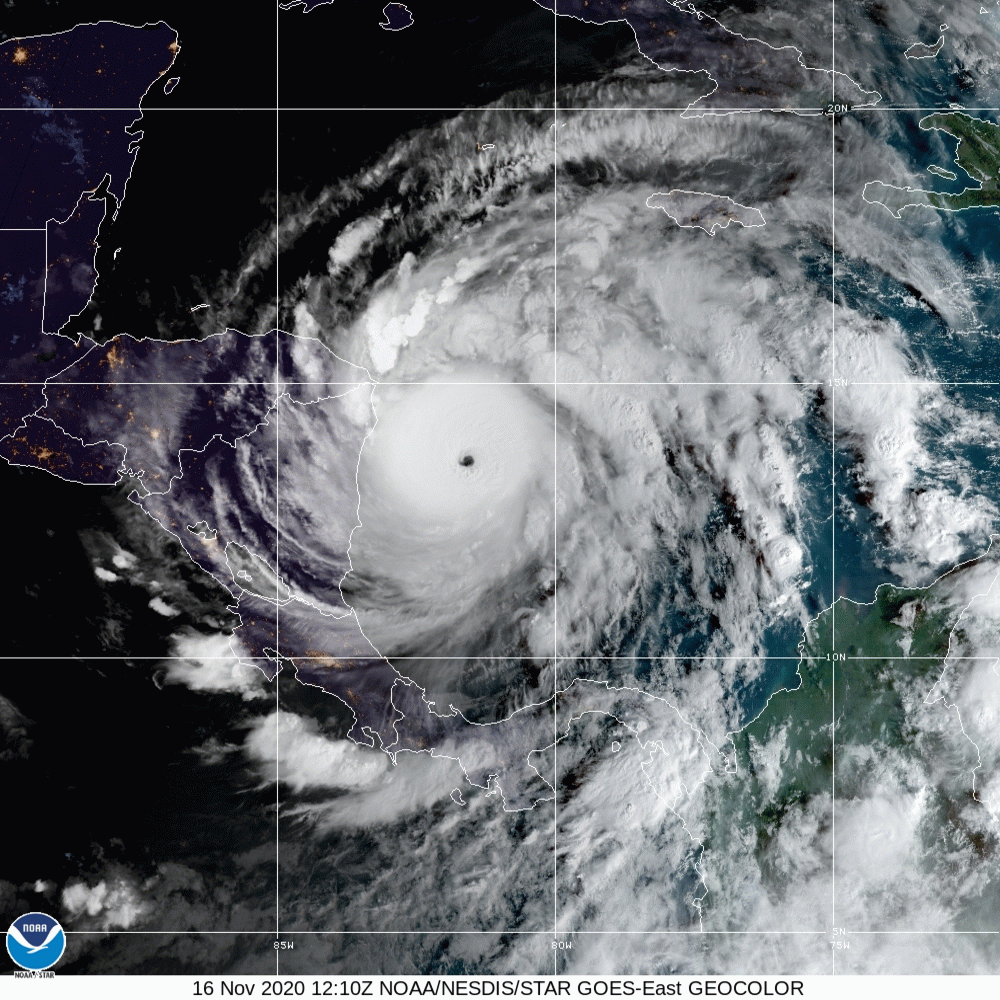
Hurricane Iota
Hurricane Iota was a devastating late-season tropical cyclone which caused severe damage to areas of Central America already devastated by Hurricane Eta two weeks prior. The 31st and final tropical cyclone, 30th named storm, 14th hurricane, and record-tying seventh major hurricane of the record-breaking 2020 Atlantic hurricane season, Iota originated as a tropical wave that moved into the Eastern Caribbean on 10 November. Over the next few days, the wave began to become better organized and by 13 November, it developed into a tropical depression north of Colombia. The depression strengthened into Tropical Storm Iota six hours later. The storm was initially impacted by some wind shear, but a center relocation and relaxed shear allowed Iota to quickly strengthen into a hurricane on 15 November, after which it underwent explosive intensification, peaking as a high-end Category 4 hurricane, with wind speeds of . After weakening slightly, Iota made landfall in northeastern Nicar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Encoding
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to automatically carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as ''programs'', which enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. The term computer system may refer to a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system, software, and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation; or to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems, including simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls, and factory devices like industrial robots. Computers are at the core of general-purpose devices such as personal computers and mobile devices such as smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which links billions of computers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definite Description
In formal semantics and philosophy of language, a definite description is a denoting phrase in the form of "the X" where X is a noun-phrase or a singular common noun. The definite description is ''proper'' if X applies to a unique individual or object. For example: " the first person in space" and " the 42nd President of the United States of America" are proper. The definite descriptions "the person in space" and "the Senator from Ohio" are ''improper'' because the noun phrase X applies to more than one thing, and the definite descriptions "the first man on Mars" and "the Senator from Washington D.C." are ''improper'' because X applies to nothing. Improper descriptions raise some difficult questions about the law of excluded middle, denotation, modality, and mental content. Russell's analysis As France is currently a republic, it has no king. Bertrand Russell pointed out that this raises a puzzle about the truth value of the sentence "The present King of France is bald." The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logic
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the study of deductively valid inferences or logical truths. It examines how conclusions follow from premises based on the structure of arguments alone, independent of their topic and content. Informal logic is associated with informal fallacies, critical thinking, and argumentation theory. Informal logic examines arguments expressed in natural language whereas formal logic uses formal language. When used as a countable noun, the term "a logic" refers to a specific logical formal system that articulates a proof system. Logic plays a central role in many fields, such as philosophy, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. Logic studies arguments, which consist of a set of premises that leads to a conclusion. An example is the argument from the premises "it's Sunday" and "if it's Sunday then I don't have to work" leading to the conclusion "I don't have to wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inclusion Map
In mathematics, if A is a subset of B, then the inclusion map is the function \iota that sends each element x of A to x, treated as an element of B: \iota : A\rightarrow B, \qquad \iota(x)=x. An inclusion map may also be referred to as an inclusion function, an insertion, or a canonical injection. A "hooked arrow" () is sometimes used in place of the function arrow above to denote an inclusion map; thus: \iota: A\hookrightarrow B. (However, some authors use this hooked arrow for any embedding.) This and other analogous injective functions from substructures are sometimes called natural injections. Given any morphism f between objects X and Y, if there is an inclusion map \iota : A \to X into the domain X, then one can form the restriction f\circ \iota of f. In many instances, one can also construct a canonical inclusion into the codomain R \to Y known as the range of f. Applications of inclusion maps Inclusion maps tend to be homomorphisms of algebraic structures; thus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaginary Unit
The imaginary unit or unit imaginary number () is a mathematical constant that is a solution to the quadratic equation Although there is no real number with this property, can be used to extend the real numbers to what are called complex numbers, using addition and multiplication. A simple example of the use of in a complex number is Imaginary numbers are an important mathematical concept; they extend the real number system \mathbb to the complex number system \mathbb, in which at least one Root of a function, root for every nonconstant polynomial exists (see Algebraic closure and Fundamental theorem of algebra). Here, the term ''imaginary'' is used because there is no real number having a negative square (algebra), square. There are two complex square roots of and , just as there are two complex square roots of every real number other than zero (which has one multiple root, double square root). In contexts in which use of the letter is ambiguous or problematic, the le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Go (programming Language)
Go is a high-level programming language, high-level general purpose programming language that is static typing, statically typed and compiled language, compiled. It is known for the simplicity of its syntax and the efficiency of development that it enables by the inclusion of a large standard library supplying many needs for common projects. It was designed at Google in 2007 by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson, and publicly announced in November of 2009. It is syntax (programming languages), syntactically similar to C (programming language), C, but also has memory safety, garbage collection (computer science), garbage collection, structural type system, structural typing, and communicating sequential processes, CSP-style concurrency (computer science), concurrency. It is often referred to as Golang to avoid ambiguity and because of its former domain name, golang.org, but its proper name is Go. There are two major implementations: * The original, Self-hosting (compi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
APL (programming Language)
APL (named after the book ''A Programming Language'') is a programming language developed in the 1960s by Kenneth E. Iverson. Its central datatype is the multidimensional array. It uses a large range of special graphic symbols to represent most functions and operators, leading to very concise code. It has been an important influence on the development of concept modeling, spreadsheets, functional programming, and computer math packages. It has also inspired several other programming languages. History Mathematical notation A mathematical notation for manipulating arrays was developed by Kenneth E. Iverson, starting in 1957 at Harvard University. In 1960, he began work for IBM where he developed this notation with Adin Falkoff and published it in his book ''A Programming Language'' in 1962. The preface states its premise: This notation was used inside IBM for short research reports on computer systems, such as the Burroughs B5000 and its stack mechanism when stack m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A+ (programming Language)
A+ is a high-level, interactive, interpreted array programming language designed for numerically intensive applications, especially those found in financial applications. History In 1985, Arthur Whitney created the A programming language to replace APL. Other developers at Morgan Stanley extended it to A+, adding a graphical user interface (GUI) and other language features. The GUI A+ was released in 1988. Arthur Whitney went on to create a proprietary array language named K. Like J, K omits the APL character set. It lacks some of the perceived complexities of A+, such as the existence of statements and two different modes of syntax. Features A+ provides an extended set of functions and operators, a graphical user interface with automatic synchronizing of widgets and variables, asynchronous executing of functions associated with variables and events, dynamic loading of user compiled subroutines, and other features. A+ runs on many Unix variants, including Linux. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |