|
Hywel Ap Rhodri Molwynog
Hywel ap Rhodri Molwynog as he was improperly called due to lack of knowledge of the genealogies by men like John Edward Lloyd, but in fact was Hywel ap Caradog ( en, Hywel, son of Caradog ap Meirion) was King of Gwynedd (reigned 816–825). He rose to power following a destructive dynastic struggle in which he deposed his cousin, King Cynan Dindaethwy ap Rhodri (reigned 798–816). During Hywel's reign Gwynedd's power was largely confined to Anglesey. It was a time of substantial territorial loss to Mercia. Hywel is said to be the son of Rhodri Molwynog on the assumption that he was Cynan's brother, for example as stated in Lloyd's ''History of Wales'', which does not cite its source. Sources such as the ''Annales Cambriae'' mention him by name only. The genealogy of Jesus College MS. 20 gives him as the son of Caradog ap Meirion, while it gives Cynan as the son of Rhodri Molwynog. A destructive war between King Cynan and Hywel raged on Anglesey between 812 and 816, ultimately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caradog Ap Meirion
Caradog ap Meirion (died ) was an 8th-century king of Gwynedd in northwest Wales. This era in the history of Gwynedd was not notable and, given the lack of reliable information available, serious histories such that as by Davies do not mention Caradog or (like that of Lloyd) mention his name only in a footnote quoting the year of his death in the ''Annales Cambriae''., ''A History of Wales, Vol. I'' It is assumed Caradog rose to the throne upon the death of King Rhodri Molwynog, which Phillimore's reconstruction of the ''Annals of Wales'' dates to AD 754. However, there is no other basis for the date and, as the records are quite sparse in this era, intervening kings cannot be precluded. The sole references to Caradog in the historical record are the appearance of his name in genealogies such as those in Jesus College MS. 20, and the entry of his death in the ''Annales Cambriae'' (Phillimore's year 798), noting he was killed (lit. "throat-slit") by the Saxons (probably the Mer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Court
A royal court, often called simply a court when the royal context is clear, is an extended royal household in a monarchy, including all those who regularly attend on a monarch, or another central figure. Hence, the word "court" may also be applied to the coterie of a senior member of the nobility. Royal courts may have their seat in a designated place, several specific places, or be a mobile, itinerant court. In the largest courts, the royal households, many thousands of individuals comprised the court. These courtiers included the monarch or noble's camarilla and retinue, household, nobility, clergy, those with court appointments, bodyguards, and may also include emissaries from other kingdoms or visitors to the court. Foreign princes and foreign nobility in exile may also seek refuge at a court. Near Eastern and Far Eastern courts often included the harem and concubines as well as eunuchs who fulfilled a variety of functions. At times, the harem was walled off and separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchs Of Gwynedd
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power in the state, or others may wield that power on behalf of the monarch. Usually a monarch either personally inherits the lawful right to exercise the state's sovereign rights (often referred to as ''the throne'' or ''the crown'') or is selected by an established process from a family or cohort eligible to provide the nation's monarch. Alternatively, an individual may proclaim themself monarch, which may be backed and legitimated through acclamation, right of conquest or a combination of means. If a young child is crowned the monarch, then a regent is often appointed to govern until the monarch reaches the requisite adult age to rule. Monarchs' actual powers vary from one monarchy to another and in different eras; on one extreme, they may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
825 Deaths
8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the first number of the form , being an integer greater than 1. * the first number which is neither prime nor semiprime. * the base of the octal number system, which is mostly used with computers. In octal, one digit represents three bits. In modern computers, a byte is a grouping of eight bits, also called an octet. * a Fibonacci number, being plus . The next Fibonacci number is . 8 is the only positive Fibonacci number, aside from 1, that is a perfect cube. * the only nonzero perfect power that is one less than another perfect power, by Mihăilescu's Theorem. * the order of the smallest non-abelian group all of whose subgroups are normal. * the dimension of the octonions and is the highest possible dimension of a normed division algebra. * the first number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kings Of Wales Family Trees
{{Family trees ...
Family trees of the kings of Gwynedd, Deheubarth and Powys and some of their more prominent relatives and heirs. The early generations of these genealogies are traditional and their historical accuracy is debated by scholars. Wales, monarchs of Wales Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merfyn Frych
Merfyn Frych ('Merfyn the Freckled'; Old Welsh ''Mermin''), also known as Merfyn ap Gwriad ('Merfyn son of Gwriad') and Merfyn Camwri ('Merfyn the Oppressor'), was King of Gwynedd from around 825 to 844, the first of its kings known not to have descended from the male line of King Cunedda. Little is known of his reign, and his primary notability is as the father of Rhodri the Great and founder of his dynasty, which was sometimes called the Merfynion after him. Merfyn came to the throne in the aftermath of a bloody dynastic struggle between two rivals named Cynan and Hywel generally identified with the sons of Rhodri Molwynog. The ''Annales Cambriae'' say Merfyn died around 844, the same year in which a battle occurred at Cetyll, but it is unclear whether those were two unrelated events or he fell in battle. Political background The times leading up to Merfyn's reign were unsettled for both Gwynedd and neighbouring Powys. Both kingdoms were beset by internal dynastic strife, e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cunedda Wledig
Cunedda ap Edern, also called Cunedda ''Wledig'' ( 5th century), was an important early Welsh leader, and the progenitor of the Royal dynasty of Gwynedd, one of the very oldest of western Europe. Name The name ''Cunedda'' (spelled ''Cunedag'' in the AD 828 pseudo-history ''Historia Brittonum'') derives from the Brythonic word ', meaning "Good Hound/Warrior" or "Having Good Hounds/Warriors". Genealogy His genealogy is traced back to a grandfather living in late Roman Britain named Padarn Beisrudd. His name literally translates as Paternus of the "red tunic" or the scarlet cloak, a color attributed to Roman officers during the Roman Empire. One traditional interpretation identifies Padarn as a Roman (Romano-British) official of reasonably high rank who had been placed in command of the Votadini troops stationed in the Clackmannanshire region of Scotland in the 380s or earlier by the Roman Emperor Magnus Maximus. Alternatively, he may have been a frontier chieftain who was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
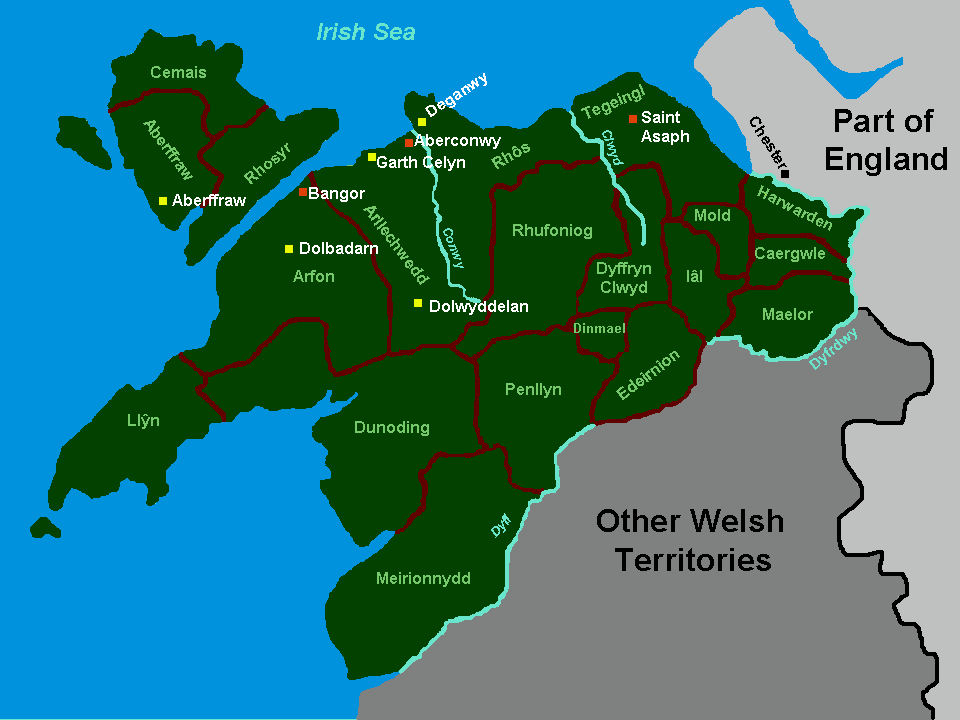
Deganwy
Deganwy (Middle Welsh ''Degannwy'', Brythonic *''Decantouion'') is a town and electoral ward in Conwy County Borough in Wales with a population of 3,936 (2011). It lies in the Creuddyn Peninsula alongside Llandudno (to the north) and Rhos-on-Sea (to its east). Historically part of Caernarfonshire, the peninsula is in a region of north Wales where as many as 1 in 3 of residents are able to speak Welsh, and is home to some of the most expensive streets in Wales. Deganwy is located to the east of the town of Conwy (which is on the opposite side of the River Conwy) and with it forms the Conwy community. The name ''Deganwy'' has been interpreted in modern times as ''Din-Gonwy'', which would mean "Fort on the River Conwy", but the historical spellings make it impossible for this to be the actual origin of the name although mentioned in Domesday Book is "the territory of the Decanae tribe". The original wooden castle was rebuilt in stone after 1210. Deganwy is in the ecclesiastical pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basingwerk Abbey
Basingwerk Abbey ( cy, Abaty Dinas Basing) is a Grade I listed ruined abbey near Holywell, Flintshire, Wales. The abbey, which was founded in the 12th century, belonged to the Order of Cistercians. It maintained significant lands in the English county of Derbyshire. The abbey was abandoned and its assets sold following the Dissolution of the Monasteries in 1536. The site is now managed by Cadw – the national Welsh heritage agency. Medieval history The abbey was founded in 1132 by Ranulf de Gernon, 4th Earl of Chester, who had already brought Benedictine monks from Savigny Abbey in southern Normandy. Likely the first location of the abbey was not at the current location at Greenfields but at the nearby Hen Blas. The abbey became part of the Cistercian Order in 1147. It was a daughter house of Combermere Abbey in Cheshire, of which Earl Ranulf was a great benefactor. However, in 1147 the abbot and convent of Savigny transferred it to Buildwas Abbey in Shropshire. Twenty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dee Estuary
The Dee Estuary ( cy, Aber Dyfrdwy) is a large estuary by means of which the River Dee flows into Liverpool Bay. The estuary starts near Shotton after a five-mile (8 km) 'canalised' section and the river soon swells to be several miles wide forming the boundary between the Wirral Peninsula in north-west England and Flintshire in north-east Wales. The Dee Estuary's largest towns along it include Hollywell, Flint, Connah's Quay, Shotton, Queensferry, Saltney Ferry, Chester (City), Heswall, West Kirby and Neston as well as other villages and towns alongside it. The A548 also passes along the estuary in Wales and parts of Cheshire West and Chester and Merseyside in England. The North Wales Coast Line follows the course of the Dee Estuary between Prestatyn and Chester. Geology The estuary is unusual in that comparatively little water occupies so large a basin. One theory is that larger rivers such as the Severn and/or Mersey once flowed into the Dee. The current view is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden), who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and settled throughout parts of Europe.Roesdahl, pp. 9–22. They also voyaged as far as the Mediterranean, North Africa, Volga Bulgaria, the Middle East, and North America. In some of the countries they raided and settled in, this period is popularly known as the Viking Age, and the term "Viking" also commonly includes the inhabitants of the Scandinavian homelands as a collective whole. The Vikings had a profound impact on the early medieval history of Scandinavia, the British Isles, France, Estonia, and Kievan Rus'. Expert sailors and navigators aboard their characteristic longships, Vikings established Norse settlements and governments in the Viking activity in the British Isles, British Isles, the Faroe Islands, Settlement of Iceland, Icela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egbert Of Wessex
Ecgberht (770/775 – 839), also spelled Egbert, Ecgbert, Ecgbriht, Ecgbeorht, and Ecbert, was King of Wessex from 802 until his death in 839. His father was King Ealhmund of Kent. In the 780s, Ecgberht was forced into exile to Charlemagne's court in the Frankish Empire by the kings Offa of Mercia and Beorhtric of Wessex, but on Beorhtric's death in 802, Ecgberht returned and took the throne. Little is known of the first 20 years of Ecgberht's reign, but it is thought that he was able to maintain the independence of Wessex against the kingdom of Mercia, which at that time dominated the other southern English kingdoms. In 825, Ecgberht defeated Beornwulf of Mercia, ended Mercian Supremacy, Mercia's supremacy at the Battle of Ellandun, and proceeded to take control of the Mercian dependencies in southeastern England. In 829, he defeated Wiglaf of Mercia and drove him out of his kingdom, temporarily ruling Mercia directly. Later that year Ecgberht received the submission of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_1845.jpeg)


