|
Hyperbaric Treatment Schedules
Hyperbaric treatment schedules or hyperbaric treatment tables, are planned sequences of events in chronological order for hyperbaric pressure exposures specifying the pressure profile over time and the breathing gas to be used during specified periods, for medical treatment. Hyperbaric therapy is based on exposure to pressures greater than normal atmospheric pressure, and in many cases the use of breathing gases with oxygen content greater than that of air. A large number of hyperbaric treatment schedules are intended primarily for treatment of underwater divers and hyperbaric workers who present symptoms of decompression illness during or after a dive or hyperbaric shift, but hyperbaric oxygen therapy may also be used for other conditions. Most hyperbaric treatment is done in hyperbaric chambers where environmental hazards can be controlled, but occasionally treatment is done in the field by in-water recompression when a suitable chamber cannot be reached in time. The risks of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy 091117-N-1291E-102 Navy Diver 2nd Class Ryan Arnold Monitors The Decompression Chamber During A Simulated Medical Emergency
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine United States Minor Outlying Islands, Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in Compact of Free Association, free association with three Oceania, Pacific Island Sovereign state, sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Palau, Republic of Palau. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders Canada–United States border, with Canada to its north and Mexico–United States border, with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Sea Water
The metre (or meter) sea water (msw) is a metric unit of pressure used in underwater diving. It is defined as one tenth of a bar. The unit used in the US is the foot sea water (fsw), based on standard gravity and a sea-water density of 64 lb/ft3. According to the US Navy Diving Manual, one fsw equals 0.30643 msw, , or , though elsewhere it states that 33 fsw is (one atmosphere), which gives one fsw equal to about 0.445 psi.Page 2-12. The msw and fsw are the conventional units for measurement of diver pressure exposure used in decompression tables and the unit of calibration for pneumofathometers and hyperbaric chamber pressure gauges. Feet of sea water One atmosphere is approximately equal to 33 feet of sea water or 14.7 psi, which gives 4.9/11 or about 0.445 psi per foot. Atmospheric pressure may be considered constant at sea level, and minor fluctuations caused by the weather are usually ignored. Pressures measured in fsw and msw are gauge pressure, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
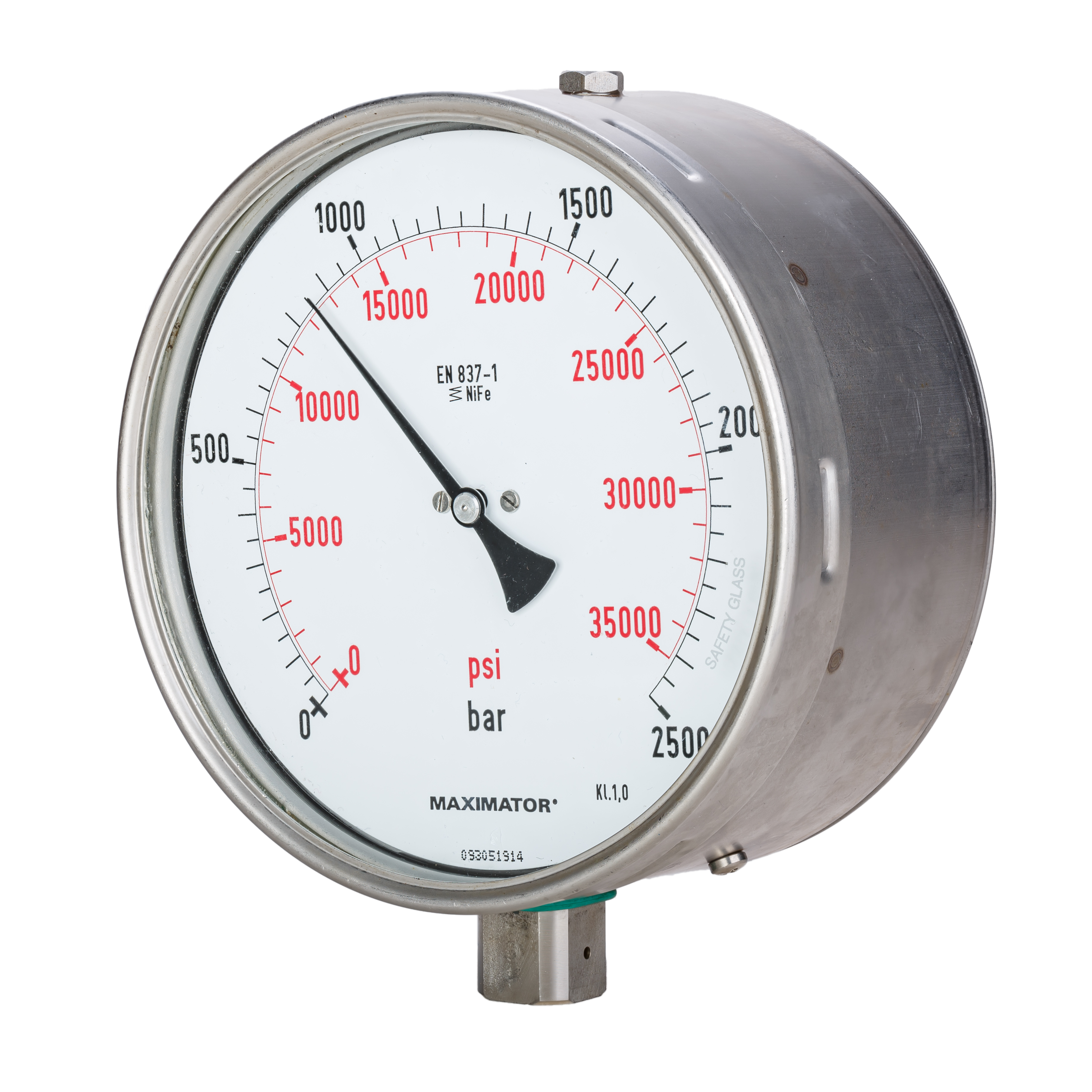
Manometer
Pressure measurement is the measurement of an applied force by a fluid (liquid or gas) on a surface. Pressure is typically measured in units of force per unit of surface area. Many techniques have been developed for the measurement of pressure and vacuum. Instruments used to measure and display pressure mechanically are called pressure gauges, vacuum gauges or compound gauges (vacuum & pressure). The widely used Bourdon gauge is a mechanical device, which both measures and indicates and is probably the best known type of gauge. A vacuum gauge is used to measure pressures lower than the ambient atmospheric pressure, which is set as the zero point, in negative values (for instance, −1 bar or −760 mmHg equals total vacuum). Most gauges measure pressure relative to atmospheric pressure as the zero point, so this form of reading is simply referred to as "gauge pressure". However, anything greater than total vacuum is technically a form of pressure. For very low press ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electro-galvanic Oxygen Sensor
An electro-galvanic fuel cell is an electrochemical device which consumes a fuel to produce an electrical output by a chemical reaction. One form of electro-galvanic fuel cell based on the oxidation of lead is commonly used to measure the concentration of oxygen gas in underwater diving and medical breathing gases. Electronically monitored or controlled diving rebreather systems, saturation diving systems, and many medical life-support systems use galvanic oxygen sensors in their control circuits to directly monitor oxygen partial pressure during operation. They are also used in oxygen analysers in recreational, technical diving and surface supplied mixed gas diving to analyse the proportion of oxygen in a nitrox, heliox or trimix breathing gas before a dive. These cells are lead/oxygen galvanic cells where oxygen molecules are dissociated and reduced to hydroxyl ions at the cathode. The ions diffuse through the electrolyte and oxidize the lead anode. A current proportional to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Built In Breathing System
A built-in breathing system is a source of breathing gas installed in a confined space where an alternative to the ambient gas may be required for medical treatment, emergency use, or to minimise a hazard. They are found in diving chambers, hyperbaric treatment chambers, and submarines. The use in hyperbaric treatment chambers is usually to supply an oxygen rich treatment gas which if used as the chamber atmosphere, would constitute an unacceptable fire hazard. In this application the exhaust gas is vented outside of the chamber. In saturation diving chambers and surface decompression chamber the application is similar, but a further function is a supply of breathable gas in case of toxic contamination of the chamber atmosphere. This function does not require external venting, but the same equipment is typically used for supply of oxygen enriched gases, so they are generally vented to the exterior. In submarines the function is to supply a breathable gas in an emergency, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BIBS Mask Side View
BIBS may refer to: * A Built-In Breathing System, a source of breathable gas for emergencies * The Bath Investment and Building Society, a British financial institution * The Beanstalk International Bilingual School system, based in Beijing, China {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
US Navy 070208-N-8268B-001 Navy Diver 1st Class Mike Barnett And Navy Diver 1st Class Chad Christensen Test Built-in Breathing Masks Inside A Recompression Chamber
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Ameri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Narcosis
Narcosis while diving (also known as nitrogen narcosis, inert gas narcosis, raptures of the deep, Martini effect) is a reversible alteration in consciousness that occurs while diving at depth. It is caused by the anesthetic effect of certain gases at high pressure. The Greek word (narkōsis), "the act of making numb", is derived from (narkē), "numbness, torpor", a term used by Homer and Hippocrates. Narcosis produces a state similar to drunkenness (alcohol intoxication), or nitrous oxide inhalation. It can occur during shallow dives, but does not usually become noticeable at depths less than . Except for helium and probably neon, all gases that can be breathed have a narcotic effect, although widely varying in degree. The effect is consistently greater for gases with a higher lipid solubility, and although the mechanism of this phenomenon is still not fully clear, there is good evidence that the two properties are mechanistically related. As depth increases, the mental ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heliox
Heliox is a breathing gas mixture of helium (He) and oxygen (O2). It is used as a medical treatment for patients with difficulty breathing because mixture generates less resistance than atmospheric air when passing through the airways of the lungs, and thus requires less effort by a patient to breathe in and out of the lungs. It is also used as a breathing gas diluent for deep ambient pressure diving as it is not narcotic at high pressure, and for its low work of breathing. Heliox has been used medically since the 1930s, and although the medical community adopted it initially to alleviate symptoms of upper airway obstruction, its range of medical uses has since expanded greatly, mostly because of the low density of the gas. Heliox is also used in saturation diving and sometimes during the deep phase of technical dives. Medical uses In medicine heliox may refer to a mixture of 21% O2 (the same as air) and 79% He, although other combinations are available (70/30 and 60/40). He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrox
Nitrox refers to any breathing gas, gas mixture composed (excepting trace gases) of nitrogen and oxygen. This includes atmospheric air, which is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, and 1% other gases, primarily argon. In the usual application, underwater diving, nitrox is normally distinguished from air and handled differently. The most common use of nitrox mixtures containing oxygen in higher proportions than atmospheric air is in scuba diving, where the reduced partial pressure of nitrogen is advantageous in reducing nitrogen uptake in the Tissue (biology), body's tissues, thereby extending the practicable underwater dive time by reducing the Decompression (diving), decompression requirement, or reducing the risk of decompression sickness (also known as ''the bends''). Nitrox is used to a lesser extent in surface-supplied diving, as these advantages are reduced by the more complex logistical requirements for nitrox compared to the use of simple low-pressure compressors for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
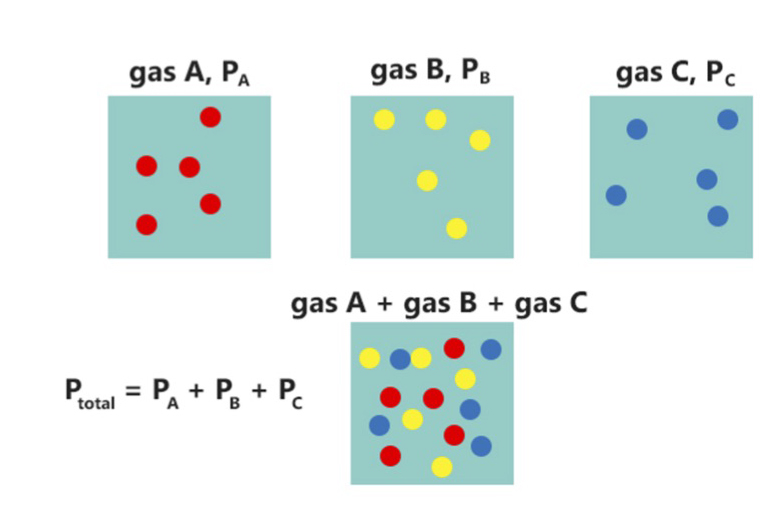
Partial Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture ( Dalton's Law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of thermodynamic activity of the gas's molecules. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react according to their partial pressures but not according to their concentrations in gas mixtures or liquids. This general property of gases is also true in chemical reactions of gases in biology. For example, the necessary amount of oxygen for human respiration, and the amount that is toxic, is set by the partial pressure of oxygen alone. This is true across a very wide range of different concentrations of oxygen present in various inhaled breathing gases or dissolved in blood; consequently, mixture ratios, like that of breat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |