|
Hupda People
The Hupda (also known as Hup, Hupd'äh, or Húpd’əh) are an Amazonian indigenous people who live in Brazil and Colombia. They speak the Hup language. Residence and neighbors The Hupd'äh people live in the region bordered by the rivers Tiquié and Papuri, tributaries that join the left hand bank of the river Vaupés in the Upper Rio Negro region of the state of Amazonas in Brazil and the Department of Vaupés in Colombia. They are known as part of the Naduhup language family, and have been in contact with the frontiers of colonization since the 18th century. There are records of countless epidemics of measles, smallpox, and influenza, which decimated the population. Currently they are distributed in approximately 35 villages (local groups) estimated at a total of 1500 individuals. The Hupda villages are, in general, close to areas of Tukanoan, Tariana, Tuyuka and Piratapuyo population, populations which speak languages of the Tukanoan language family, living near t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
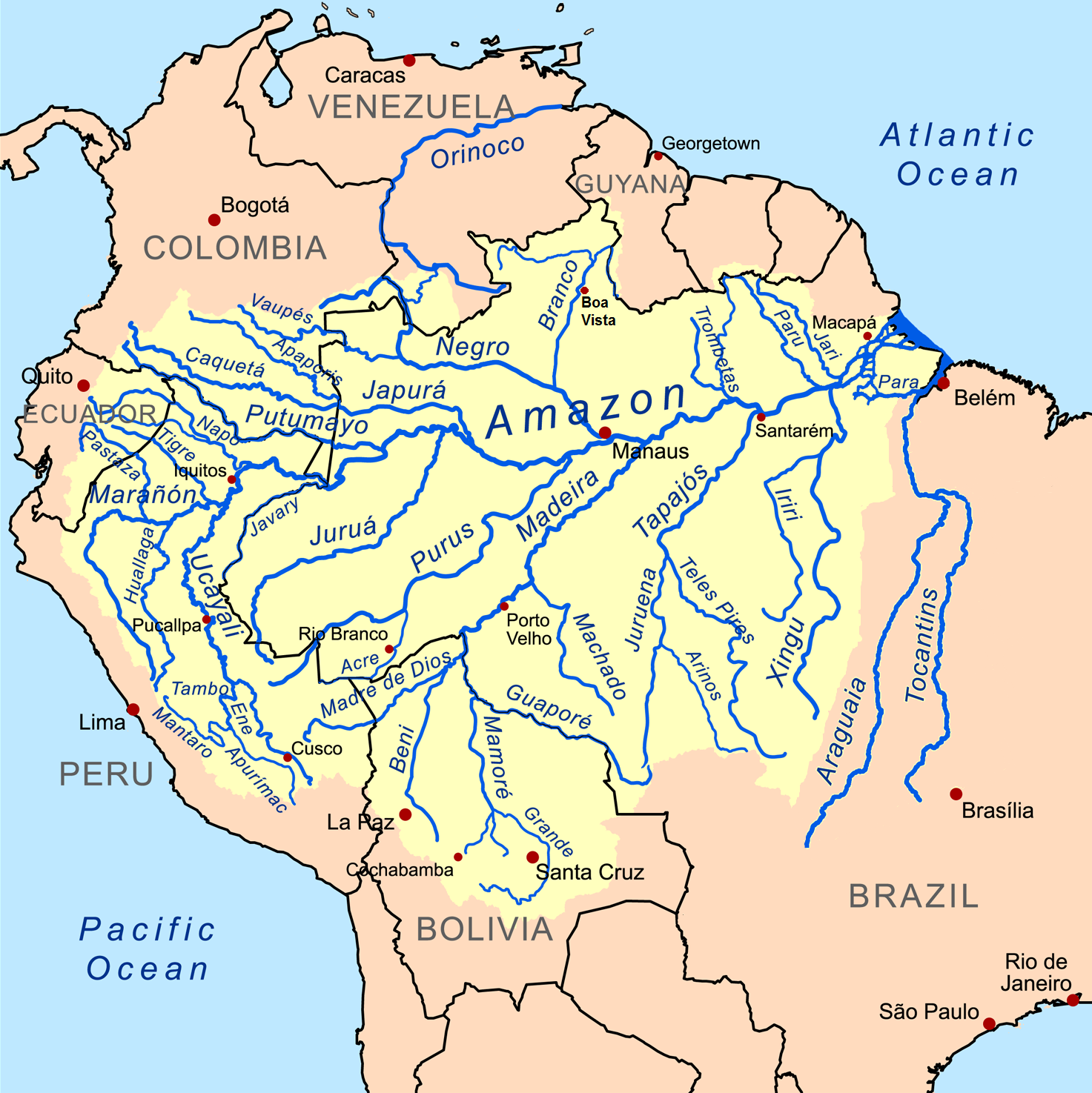
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, this is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . With a length of about before it drains into the Atlantic Ocean, it is one of the two longest rivers in the world. A team of scientists has claimed that the Amazon is longer than the Nile, but debate about its exact length continues. The Amazon s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kãkwã People
Kãkwã, Cacua or Bará-maku is an indigenous people living in northwestern Amazonia, between Vaupés, Querarí and Papuri rivers, in Colombia, close to the border with Brazil, within Vaupés indigenous Resguardo. The Kãkwã are approximately 250 people, who speak their own language, which is part of the Macu family and is closely related to the Nukak language The Nukak language ( mbr, Guaviare) is a language of uncertain classification, perhaps part of the macrofamily Puinave-Maku. It is very closely related to Kakwa.Gustavo Politis, ''Nukak: Ethnoarchaeology of an Amazonian People,'' Left Coast Pre .... Each kãkwã is part of an exogamous patrilineal clan. The clans engage in marital exchanges and consider themselves "baih", brothers-in-law or bilateral cross-cousins.Silverwood-Cope, Peter L. (1990). ''Os Makú: Povo cazador no noroeste da Amazònia''. Universidade de Brasília. Originally nomadic hunter-gatherers, later subjected to the neighboring ethnic groups ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tariano People
The Tariana or Taliaseri are an indigenous people of the Vaupés or Uaupés River in the Amazon region of Brazil and Colombia. Starting in the 19th century missionaries tried to persuade them to abandon their traditional beliefs and practices, with some level of success. The government made efforts to convert them to a "colony" system in exchange for health, education and economic benefits starting in the 1980s. They are now relatively autonomous within several indigenous territories. Languages The Tariana language belongs to the Arawakan linguistic family. The Tariana language, closely related to the Baniwa language, is only spoken by individuals from sibs of low rank. The reason given by the Tariana is that once they settled along the Uaupés the men of most families married Wanano and Tucano women, and their children grew up speaking their mothers' tongues. Almost all Tariana can speak Tucano, the lingua franca of the Uaupés. In 1996 there were no speakers of the Taria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desana
Desana (''Dzan-a'' in Piedmontese) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Vercelli in the Italian region Piedmont, located about northeast of Turin and about southwest of Vercelli. Desana borders the following municipalities: Asigliano Vercellese, Costanzana, Lignana, Ronsecco, Tricerro, and Vercelli Vercelli (; pms, Vërsèj ), is a city and ''comune'' of 46,552 inhabitants (January 1, 2017) in the Province of Vercelli, Piedmont, northern Italy. One of the oldest urban sites in northern Italy, it was founded, according to most historians, .... References Cities and towns in Piedmont {{Vercelli-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tukanos
The Tucano people (sometimes spelt Tukano) are a group of Indigenous South Americans in the northwestern Amazon, along the Vaupés River and the surrounding area. They are mostly in Colombia, but some are in Brazil. They are usually described as being made up of many separate tribes, but that oversimplifies the social and linguistic structure of the region. Culture The Tucano are multilingual because men must marry outside their language group: no man may have a wife who speaks his language, which would be viewed as a kind of incest. Men choose women from various neighboring tribes who speak other languages. Furthermore, on marriage, women move into the men's households or longhouses. Consequently, in any village several languages are used: the language of the men; the various languages spoken by women who originate from different neighboring tribes; and a widespread regional 'trade' language. Children are born into the multilingual environment: the child's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baniwa People
Baniwa (also known with local variants as Baniva, Baniua, Curipaco, Vaniva, Walimanai, Wakuenai) are indigenous South Americans, who speak the Baniwa language belonging to the Maipurean (Arawak) language family. They live in the Amazon Region, in the border area of Brazil, Colombia and Venezuela and along the Rio Negro and its tributaries. There are an estimated 7,145 Baniwa in Brazil, 7,000 in Colombia and 3,501 in Venezuela's Amazonas State, according to Brazil's Instituto Socioambiental, but accurate figures are almost impossible to come by given the nature of the rainforest. The Baniwa people rely mainly on manioc cultivation and fishing for subsistence. They are also known for the fine basketry that they skillfully produce. See also * Baniwa language, Curripako language * Indigenous peoples in Brazil * Indigenous peoples in Colombia * Indigenous peoples in Venezuela Indigenous people in Venezuela, Amerindians or Native Venezuelans, form about 2% of the total pop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baniwa Of Içana
Karu, one of several languages called Baniwa (Baniva), or in older sources ''Itayaine (Iyaine)'', is an Arawakan language spoken in Guainía, Colombia, Venezuela, and Amazonas, Brazil. It forms a subgroup with the Tariana, Piapoco, Resígaro and Guarequena languages. There are 10,000 speakers. Varieties Aikhenvald (1999) considers the three main varieties to be dialects; Kaufman (1994) considers them to be distinct languages, in a group he calls "Karu". They are: *Baniwa of Içana (''Baniua do Içana'') *Curripaco (Kurripako, Ipeka-Tapuia-Curripako) *Katapolítani-Moriwene-Mapanai (Catapolitani, Kadaupuritana) Various of all three are called ''tapuya'', a Brazilian Portuguese and Nheengatu word for non-Tupi/non-Guarani Indigenous peoples of Brazil (from a Tupi word meaning "enemy, barbarian"). All are spoken by the Baniwa people. Ruhlen lists all as "Izaneni"; Greenberg's ''Adzánani'' (= Izaneni) presumably belongs here. Ramirez (2020) gives the following classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arawakan Languages
Arawakan (''Arahuacan, Maipuran Arawakan, "mainstream" Arawakan, Arawakan proper''), also known as Maipurean (also ''Maipuran, Maipureano, Maipúre''), is a language family that developed among ancient indigenous peoples in South America. Branches migrated to Central America and the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean and the Atlantic, including what is now the Bahamas. Almost all present-day South American countries are known to have been home to speakers of Arawakan languages, the exceptions being Ecuador, Uruguay, and Chile. Maipurean may be related to other language families in a hypothetical Macro-Arawakan stock. Name The name ''Maipure'' was given to the family by Filippo S. Gilij in 1782, after the Maipure language of Venezuela, which he used as a basis of his comparisons. It was renamed after the culturally more important Arawak language a century later. The term ''Arawak'' took over, until its use was extended by North American scholars to the broader Macro-Arawakan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maku People
Maku (Macu, Máku, Mácu, Makú, Macú) or Maco (Mako, Máko, Macó, Makó) is a pejorative term referring to several hunter-gatherer peoples of the upper Amazon, derived from an Arawakan term ''ma-aku'' "do not speak / without speech". Nimuendajú (1950), for example, notes six peoples of Colombia, Venezuela, and Brazil that are known as 'Maku'. In linguistic literature, the term refers primarily to: * the Nadahup languages, a small language family in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela, sometimes disambiguated from other Maku languages as ''Makú'' or ''Macú'', though those forms can apply to any of the languages, or as ''Makuan''. Such languages include Hup, spoken by Hupda, (''Hupdá Makú'', ''Makú-Hupdá'', ''Macú De'') and Guariba Maku * the closely related Nukak Makú and Kakwa (''Macu de Cubeo'', ''Macu de Desano'', ''Macu de Guanano'', ''Macú-Paraná'') * the Maku-Auari language, the 'Maku' of Roraima and the Auari River, a possible language isolate of Brazil and V ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |