|
Human Reliability
Human reliability (also known as human performance or HU) is related to the field of human factors and ergonomics, and refers to the reliability of humans in fields including manufacturing, medicine and nuclear power. Human performance can be affected by many factors such as age, state of mind, physical health, attitude, emotions, propensity for certain common mistakes, errors and cognitive biases, etc. Human reliability is very important due to the contributions of humans to the resilience of systems and to possible adverse consequences of human errors or oversights, especially when the human is a crucial part of the large socio-technical systems as is common today. User-centered design and error-tolerant design are just two of many terms used to describe efforts to make technology better suited to operation by humans. Common Traps of Human Nature People tend to overestimate their ability to maintain control when they are doing work. The common characteristics of human nat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Human Factors And Ergonomics
Human factors and ergonomics (commonly referred to as human factors) is the application of psychological and physiological principles to the engineering and design of products, processes, and systems. Four primary goals of human factors learning are to reduce human error, increase productivity, and enhance safety, system availability, and comfort with a specific focus on the interaction between the human and the engineered system. The field is a combination of numerous disciplines, such as psychology, sociology, engineering, biomechanics, industrial design, physiology, anthropometry, interaction design, visual design, user experience, and user interface design. Human factors research employs methods and approaches from these and other knowledge disciplines to study human behavior and generate data relevant to the four primary goals above. In studying and sharing learning on the design of equipment, devices, and processes that fit the human body and its cognitive abilities, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technology
Technology is the application of knowledge to reach practical goals in a specifiable and reproducible way. The word ''technology'' may also mean the product of such an endeavor. The use of technology is widely prevalent in medicine, science, industry, communication, transportation, and daily life. Technologies include physical objects like utensils or machines and intangible tools such as software. Many technological advancements have led to societal changes. The earliest known technology is the stone tool, used in the prehistoric era, followed by fire use, which contributed to the growth of the human brain and the development of language in the Ice Age. The invention of the wheel in the Bronze Age enabled wider travel and the creation of more complex machines. Recent technological developments, including the printing press, the telephone, and the Internet have lowered communication barriers and ushered in the knowledge economy. While technology contributes to econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swiss Cheese Model
The Swiss cheese model of accident causation is a model used in risk analysis and risk management, including aviation safety, engineering, healthcare, emergency service organizations, and as the principle behind layered security, as used in computer security and defense in depth. It likens human systems to multiple slices of Swiss cheese, stacked side by side, in which the risk of a threat becoming a reality is mitigated by the differing layers and types of defenses which are "layered" behind each other. Therefore, in theory, lapses and weaknesses in one defense do not allow a risk to materialize, since other defenses also exist, to prevent a single point of failure. The model was originally formally propounded by James T. Reason of the University of Manchester, and has since gained widespread acceptance. It is sometimes called the "cumulative act effect". Although the Swiss cheese model is respected and considered to be a useful method of relating concepts, it has been subjec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
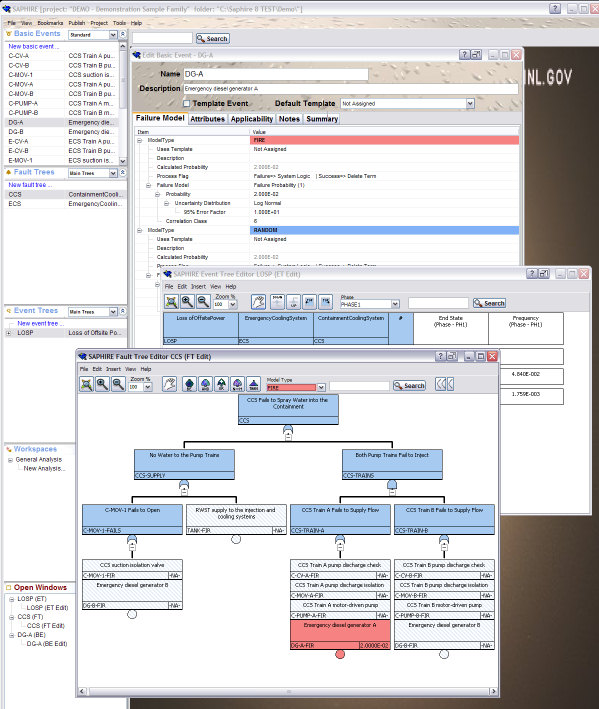
SAPHIRE
{{primary sources, date=March 2015 SAPHIRE is a probabilistic risk and reliability assessment software tool. SAPHIRE stands for ''Systems Analysis Programs for Hands-on Integrated Reliability Evaluations''. The system was developed for the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) by the Idaho National Laboratory. Development began in the mid-1980s when the NRC began exploring two notions: 1) that Probabilistic Risk Assessment (PRA) information could be displayed and manipulated using the emerging microcomputer technology of the day and 2) the rapid advancement of PRA technology required a relatively inexpensive and readily available platform for teaching PRA concepts to students. The history of SAPHIRE 1987 Version 1 of the code called IRRAS (now known as SAPHIRE) introduced an innovative way to draw, edit, and analyze graphical fault trees. 1989 Version 2 is released incorporating the ability to draw, edit, and analyze graphical event trees. 1990 Analysis improvements to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault Tree
Fault tree analysis (FTA) is a type of failure analysis in which an undesired state of a system is examined. This analysis method is mainly used in safety engineering and reliability engineering to understand how systems can fail, to identify the best ways to reduce risk and to determine (or get a feeling for) event rates of a safety accident or a particular system level (functional) failure. FTA is used in the aerospace, nuclear power, chemical and process, pharmaceutical, petrochemical and other high-hazard industries; but is also used in fields as diverse as risk factor identification relating to social service system failure. FTA is also used in software engineering for debugging purposes and is closely related to cause-elimination technique used to detect bugs. In aerospace, the more general term "system failure condition" is used for the "undesired state" / top event of the fault tree. These conditions are classified by the severity of their effects. The most severe condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazop
A hazard and operability study (HAZOP) is a structured and systematic examination of a complex plan or operation in order to identify and evaluate problems that may represent risks to personnel or equipment. The intention of performing a HAZOP is to review the design to pick up design and engineering issues that may otherwise not have been found. The technique is based on breaking the overall complex design of the process into a number of simpler sections called 'nodes' which are then individually reviewed. It is carried out by a suitably experienced multi-disciplinary team (HAZOP) during a series of meetings. The HAZOP technique is qualitative, and aims to stimulate the imagination of participants to identify potential hazards and operability problems. Structure and direction are given to the review process by applying standardised guide-word prompts to the review of each node. The relevant international standard calls for team members to display 'intuition and good judgement' and f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Failure Mode And Effects Analysis
Failure mode and effects analysis (FMEA; often written with "failure modes" in plural) is the process of reviewing as many components, assemblies, and subsystems as possible to identify potential failure modes in a system and their causes and effects. For each component, the failure modes and their resulting effects on the rest of the system are recorded in a specific FMEA worksheet. There are numerous variations of such worksheets. An FMEA can be a qualitative analysis, but may be put on a quantitative basis when mathematical failure rate models are combined with a statistical failure mode ratio database. It was one of the first highly structured, systematic techniques for failure analysis. It was developed by reliability engineers in the late 1950s to study problems that might arise from malfunctions of military systems. An FMEA is often the first step of a system reliability study. A few different types of FMEA analyses exist, such as: * Functional * Design * Process Sometime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance, repair and operations, maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety engineering. Safety engineering assures that a life-critical system behaves as needed, even when components fail. Analysis techniques Analysis techniques can be split into two categories: qualitative and quantitative methods. Both approaches share the goal of finding causal dependencies between a hazard on system level and failures of individual components. Qualitative approaches focus on the question "What must go wrong, such that a system hazard may occur?", while quantitative methods aim at providing estimations about probabilities, rates and/or severity of consequences. The complexity of the technical systems such as Improvements of Design and Materials, Planned Inspections, Fool-proof design, and Backup Redundancy decreases risk and increases the cost. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Technique For Human Error Rate Prediction
The technique for human error-rate prediction (THERP) is a technique used in the field of human reliability assessment (HRA), for the purposes of evaluating the probability of a human error occurring throughout the completion of a specific task. From such analyses measures can then be taken to reduce the likelihood of errors occurring within a system and therefore lead to an improvement in the overall levels of safety. There exist three primary reasons for conducting an HRA: error identification, error quantification and error reduction. As there exist a number of techniques used for such purposes, they can be split into one of two classifications: first-generation techniques and second-generation techniques. First-generation techniques work on the basis of the simple dichotomy of ‘fits/doesn’t fit’ in matching an error situation in context with related error identification and quantification. Second generation techniques are more theory-based in their assessment and quantifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Task Analysis
Task analysis is the analysis of how a task is accomplished, including a detailed description of both manual and mental activities, task and element durations, task frequency, task allocation, task complexity, environmental conditions, necessary clothing and equipment, and any other unique factors involved in or required for one or more people to perform a given task. Information from a task analysis can then be used for many purposes, such as personnel selection and training, tool or equipment design, procedure design (e.g., design of checklists, or decision support systems) and automation. Though distinct, task analysis is related to user analysis. Safety Critical Task Analysis Safety Critical Task Analysis (SCTA) focuses on how tasks that are critical to major accident risk are performed. SCTA is a crucial assessment designed to predict and understand the role that human error plays in major accidents. This is a type or workshop conducted to support Major Accident Hazard (MA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Decomposition
In mathematics, functional decomposition is the process of resolving a functional relationship into its constituent parts in such a way that the original function can be reconstructed (i.e., recomposed) from those parts by function composition. This process of decomposition may be undertaken to gain insight into the identity of the constituent components which may reflect individual physical processes of interest. Also functional decomposition may result in a compressed representation of the global function, a task which is feasible only when the constituent processes possess a certain level of ''modularity'' (i.e., independence or non-interaction). between the components are critical to the function of the collection. All interactions may not be , but possibly deduced through repetitive , synthesis, validation and verification of composite behavior. Basic mathematical definition For a multivariate function y = f(x_1,x_2,\dots,x_n), functional decomposition generally refers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |