|
History Of Geology
The history of geology is concerned with the development of the natural science of geology. Geology is the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth. Antiquity Some of the first geological thoughts were about the origin of Earth. Ancient Greece developed some primary geological concepts concerning the origin of the earth. Additionally, in the 4th century BC Aristotle made critical observations of the slow rate of geological change. He observed the composition of the land and formulated a theory where the earth changes at a slow rate and that these changes cannot be observed during one person's lifetime. Aristotle developed one of the first evidence-based concepts connected to the geological realm regarding the rate at which the earth physically changes. However, it was his successor at the Lyceum, the philosopher Theophrastus, who made the greatest progress in antiquity in his work ''On Stones''. He described many minerals and ores both from local m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology
Geology () is a branch of natural science concerned with Earth and other astronomical objects, the features or rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change over time. Modern geology significantly overlaps all other Earth sciences, including hydrology, and so is treated as one major aspect of integrated Earth system science and planetary science. Geology describes the structure of the Earth on and beneath its surface, and the processes that have shaped that structure. It also provides tools to determine the relative and absolute ages of rocks found in a given location, and also to describe the histories of those rocks. By combining these tools, geologists are able to chronicle the geological history of the Earth as a whole, and also to demonstrate the age of the Earth. Geology provides the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and the Earth's past climates. Geologists broadly study the properties and processes of E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' Naturalis Historia'' (''Natural History''), which became an editorial model for encyclopedias. He spent most of his spare time studying, writing, and investigating natural and geographic phenomena in the field. His nephew, Pliny the Younger, wrote of him in a letter to the historian Tacitus: Among Pliny's greatest works was the twenty-volume work ''Bella Germaniae'' ("The History of the German Wars"), which is no longer extant. ''Bella Germaniae'', which began where Aufidius Bassus' ''Libri Belli Germanici'' ("The War with the Germans") left off, was used as a source by other prominent Roman historians, including Plutarch, Tacitus and Suetonius. Tacitus—who many scholars agree had never travelled in Germania—used ''Bella Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific problems. In Western Europe, the first work to use the term polymathy in its title () was published in 1603 by Johann von Wowern, a Hamburg philosopher. Von Wowern defined polymathy as "knowledge of various matters, drawn from all kinds of studies ... ranging freely through all the fields of the disciplines, as far as the human mind, with unwearied industry, is able to pursue them". Von Wowern lists erudition, literature, philology, philomathy, and polyhistory as synonyms. The earliest recorded use of the term in the English language is from 1624, in the second edition of '' The Anatomy of Melancholy'' by Robert Burton; the form ''polymathist'' is slightly older, first appearing in the ''Diatribae upon the first part of the late Histo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avicenna
Ibn Sina ( fa, ابن سینا; 980 – June 1037 CE), commonly known in the West as Avicenna (), was a Persian polymath who is regarded as one of the most significant physicians, astronomers, philosophers, and writers of the Islamic Golden Age, and the father of early modern medicine. Sajjad H. Rizvi has called Avicenna "arguably the most influential philosopher of the pre-modern era". He was a Muslim Peripatetic philosopher influenced by Greek Aristotelian philosophy. Of the 450 works he is believed to have written, around 240 have survived, including 150 on philosophy and 40 on medicine. His most famous works are '' The Book of Healing'', a philosophical and scientific encyclopedia, and '' The Canon of Medicine'', a medical encyclopedia which became a standard medical text at many medieval universities and remained in use as late as 1650. Besides philosophy and medicine, Avicenna's corpus includes writings on astronomy, alchemy, geography and geology, psycholo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian Ocean from the Himalayas. Geopolitically, it includes the countries of Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka."Indian subcontinent". ''Oxford Dictionary of English, New Oxford Dictionary of English'' () New York: Oxford University Press, 2001; p. 929: "the part of Asia south of the Himalayas which forms a peninsula extending into the Indian Ocean, between the Arabian Sea and the Bay of Bengal. Historically forming the whole territory of Greater India, the region is now divided into three countries named Bangladesh, India and Pakistan." The terms ''Indian subcontinent'' and ''South Asia'' are often used interchangeably to denote the region, although the geopolitical term of South Asia frequently includes Afghanist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
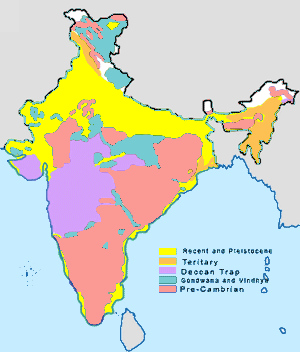
Geological History Of India
The geology of India is diverse. Different regions of India contain rocks belonging to different geologic periods, dating as far back as the Eoarchean Era. Some of the rocks are very deformed and altered. Other deposits include recently deposited alluvium that has yet to undergo diagenesis. Mineral deposits of great variety are found in the Indian subcontinent in huge quantities. Even India's fossil record is impressive in which stromatolites, invertebrates, vertebrates and plant fossils are included. India's geographical land area can be classified into the Deccan Traps, Gondwana and Vindhyan. The Deccan Traps covers almost all of Maharashtra, a part of Gujarat, Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh and Andhra Pradesh marginally. During its journey northward after breaking off from the rest of Gondwana, the Indian Plate passed over a geologic hotspot, the Réunion hotspot, which caused extensive melting underneath the Indian Craton. The melting broke through the surface of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamic Geography
Medieval Islamic geography and cartography refer to the study of geography and cartography in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age (variously dated between the 8th century and 16th century). Muslim scholars made advances to the map-making traditions of earlier cultures, particularly the Hellenistic geographers Ptolemy and Marinus of Tyre, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Islamic geography had three major fields: exploration and navigation, physical geography, and cartography and mathematical geography. Islamic geography reached its apex with Muhammad al-Idrisi in the 12th century. History Islamic geography began in the 8th century, influenced by Hellenistic geography, combined with what explorers and merchants learned in their travels across the Old World (Afro-Eurasia). Muslim scholars engaged in extensive exploration and navigation during the 9th-12th centuries, including journeys across the Musli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abū Al-Rayhān Al-Bīrūnī
Abu Rayhan Muhammad ibn Ahmad al-Biruni (973 – after 1050) commonly known as al-Biruni, was a Khwarazmian Iranian in scholar and polymath during the Islamic Golden Age. He has been called variously the "founder of Indology", "Father of Comparative Religion", "Father of modern geodesy", and the first anthropologist. Al-Biruni was well versed in physics, mathematics, astronomy, and natural sciences, and also distinguished himself as a historian, chronologist, and linguist. He studied almost all the sciences of his day and was rewarded abundantly for his tireless research in many fields of knowledge. Royalty and other powerful elements in society funded Al-Biruni's research and sought him out with specific projects in mind. Influential in his own right, Al-Biruni was himself influenced by the scholars of other nations, such as the Greeks, from whom he took inspiration when he turned to the study of philosophy. A gifted linguist, he was conversant in Khwarezmian, Persian, Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, but diamond is metastable and converts to it at a negligible rate under those conditions. Diamond has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any natural material, properties that are used in major industrial applications such as cutting and polishing tools. They are also the reason that diamond anvil cells can subject materials to pressures found deep in the Earth. Because the arrangement of atoms in diamond is extremely rigid, few types of impurity can contaminate it (two exceptions are boron and nitrogen). Small numbers of defects or impurities (about one per million of lattice atoms) color diamond blue (boron), yellow (nitrogen), brown (defects), green (radiation exposure), purple, pink, orange, or red. Diamond also has a ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Octahedron
In geometry, an octahedron (plural: octahedra, octahedrons) is a polyhedron with eight faces. The term is most commonly used to refer to the regular octahedron, a Platonic solid composed of eight equilateral triangles, four of which meet at each vertex. A regular octahedron is the dual polyhedron of a cube. It is a rectified tetrahedron. It is a square bipyramid in any of three orthogonal orientations. It is also a triangular antiprism in any of four orientations. An octahedron is the three-dimensional case of the more general concept of a cross polytope. A regular octahedron is a 3-ball in the Manhattan () metric. Regular octahedron Dimensions If the edge length of a regular octahedron is ''a'', the radius of a circumscribed sphere (one that touches the octahedron at all vertices) is :r_u = \frac a \approx 0.707 \cdot a and the radius of an inscribed sphere (tangent to each of the octahedron's faces) is :r_i = \frac a \approx 0.408\cdot a while the midradius, which t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystallography
Crystallography is the experimental science of determining the arrangement of atoms in crystalline solids. Crystallography is a fundamental subject in the fields of materials science and solid-state physics ( condensed matter physics). The word "crystallography" is derived from the Greek word κρύσταλλος (''krystallos'') "clear ice, rock-crystal", with its meaning extending to all solids with some degree of transparency, and γράφειν (''graphein'') "to write". In July 2012, the United Nations recognised the importance of the science of crystallography by proclaiming that 2014 would be the International Year of Crystallography. denote a direction vector (in real space). * Coordinates in ''angle brackets'' or ''chevrons'' such as <100> denote a ''family'' of directions which are related by symmetry operations. In the cubic crystal system for example, would mean 00 10 01/nowiki> or the negative of any of those directions. * Miller indices in ''parentheses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resin
In polymer chemistry and materials science, resin is a solid or highly viscous substance of plant or synthetic origin that is typically convertible into polymers. Resins are usually mixtures of organic compounds. This article focuses on naturally occurring resins. Plants secrete resins for their protective benefits in response to injury. The resin protects the plant from insects and pathogens. Resins confound a wide range of herbivores, insects, and pathogens, while the volatile phenolic compounds may attract benefactors such as parasitoids or predators of the herbivores that attack the plant. Composition Most plant resins are composed of terpenes. Specific components are alpha-pinene, beta-pinene, delta-3 carene, and sabinene, the monocyclic terpenes limonene and terpinolene, and smaller amounts of the tricyclic sesquiterpenes, longifolene, caryophyllene, and delta-cadinene. Some resins also contain a high proportion of resin acids. Rosins on the other hand are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |








.jpg)