|
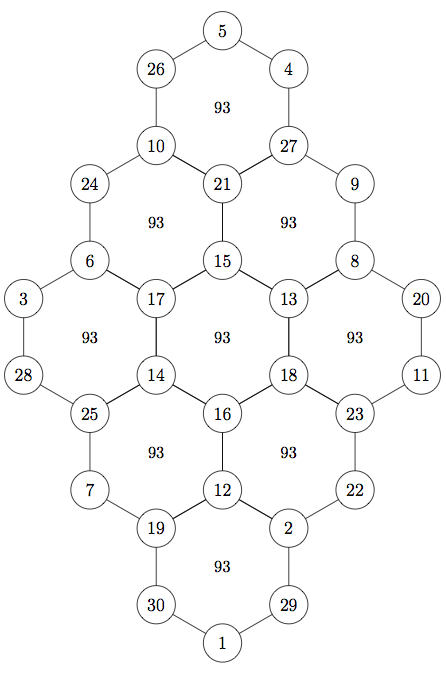
Hexagonal Tortoise Problem
The hexagonal tortoise problem () was invented by Korean aristocrat and mathematician Choi Seok-jeong (1646–1715). It is a mathematical problem that involves a hexagonal lattice, like the hexagonal pattern on some tortoises' shells, to the (''N'') vertices of which must be assigned integers (from 1 to ''N'') in such a way that the sum of all integers at the vertices of each hexagon is the same. The problem has apparent similarities to a magic square In recreational mathematics, a square array of numbers, usually positive integers, is called a magic square if the sums of the numbers in each row, each column, and both main diagonals are the same. The 'order' of the magic square is the number ... although it is a vertex-magic format rather than an edge-magic form or the more typical rows-of-cells form. His book, ''Gusuryak'', contains many mathematical discoveries. References Sources used * Recreational mathematics Magic shapes {{numtheory-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Choi Seok-jeong
Choi Seok-jeong (; 1646–1715) was a Korean politician and mathematician in the Joseon period of Korea. He published the ''Gusuryak'' () in 1700, the first known literature on Latin squares, predating Leonhard Euler Leonhard Euler ( , ; 15 April 170718 September 1783) was a Swiss mathematician, physicist, astronomer, geographer, logician and engineer who founded the studies of graph theory and topology and made pioneering and influential discoveries in ma ... by at least 67 years. He also invented the hexagonal tortoise problem. Choi was a member of the Jeonju Choe clan. Choi Seok-jeong Award The Choi Seok-jeong Award was created in 2021 to recognize those who develop or spread mathematics. Spelling of laureates' names matches their Wikipedia page, if it exists, the remainder used Revised Romanization of Korean with thKorean Romanization Converterof Al Lab and Narainfotech. References Korean mathematicians 1646 births 1715 deaths 18th-century Korean math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertex (geometry)
In geometry, a vertex (in plural form: vertices or vertexes) is a point (geometry), point where two or more curves, line (geometry), lines, or edge (geometry), edges meet. As a consequence of this definition, the point where two lines meet to form an angle and the corners of polygons and polyhedron, polyhedra are vertices. Definition Of an angle The ''vertex'' of an angle is the point where two Line (mathematics)#Ray, rays begin or meet, where two line segments join or meet, where two lines intersect (cross), or any appropriate combination of rays, segments, and lines that result in two straight "sides" meeting at one place. :(3 vols.): (vol. 1), (vol. 2), (vol. 3). Of a polytope A vertex is a corner point of a polygon, polyhedron, or other higher-dimensional polytope, formed by the intersection (Euclidean geometry), intersection of Edge (geometry), edges, face (geometry), faces or facets of the object. In a polygon, a vertex is called "convex set, convex" if the internal an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magic Square
In recreational mathematics, a square array of numbers, usually positive integers, is called a magic square if the sums of the numbers in each row, each column, and both main diagonals are the same. The 'order' of the magic square is the number of integers along one side (''n''), and the constant sum is called the ' magic constant'. If the array includes just the positive integers 1,2,...,n^2, the magic square is said to be 'normal'. Some authors take magic square to mean normal magic square. Magic squares that include repeated entries do not fall under this definition and are referred to as 'trivial'. Some well-known examples, including the Sagrada Família magic square and the Parker square are trivial in this sense. When all the rows and columns but not both diagonals sum to the magic constant this gives a ''semimagic square (sometimes called orthomagic square). The mathematical study of magic squares typically deals with their construction, classification, and enumeration. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recreational Mathematics
Recreational mathematics is mathematics carried out for recreation (entertainment) rather than as a strictly research and application-based professional activity or as a part of a student's formal education. Although it is not necessarily limited to being an endeavor for amateurs, many topics in this field require no knowledge of advanced mathematics. Recreational mathematics involves mathematical puzzles and games, often appealing to children and untrained adults, inspiring their further study of the subject. The Mathematical Association of America (MAA) includes recreational mathematics as one of its seventeen Special Interest Groups, commenting: Mathematical competitions (such as those sponsored by mathematical associations) are also categorized under recreational mathematics. Topics Some of the more well-known topics in recreational mathematics are Rubik's Cubes, magic squares, fractals, logic puzzles and mathematical chess problems, but this area of mathematics incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |