|
Hypotension
Hypotension, also known as low blood pressure, is a cardiovascular condition characterized by abnormally reduced blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood and is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number), which are the maximum and minimum blood pressures within the cardiac cycle, respectively. A systolic blood pressure of less than 90 millimeters of mercury (mmHg) or diastolic of less than 60 mmHg is generally considered to be hypotension. Different numbers apply to children. However, in practice, blood pressure is considered too low only if noticeable symptoms are present. Symptoms may include dizziness, lightheadedness, confusion, feeling tired, weakness, headache, blurred vision, nausea, neck or back pain, an irregular heartbeat or feeling that the heart is skipping beats or fluttering, sweating, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a signs and symptoms, symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself. Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions including autoimmune disease, organ failure, chronic pain conditions, mood disorders, heart disease, infectious diseases, and post-infectious-disease states. However, fatigue is complex and in up to a third of primary care cases no medical or psychiatric diagnosis is found. Fatigue (in the general usage sense of normal tiredness) often follows prolonged physical or mental activity. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of Cognition, cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ability, can manifest as sleepiness, lethargy, or directed attention fatigue, and can also impair physical performance. Definition Fatigue in a medica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blurred Vision
Blurred vision is an ocular symptom where vision becomes less precise and there is added difficulty to resolve fine details. Temporary blurred vision may involve dry eyes, eye infections, alcohol poisoning, hypoglycemia, or low blood pressure. Other medical conditions may include refractive errors such as myopia, high hypermetropia, and astigmatism, amblyopia, presbyopia, pseudomyopia, diabetes, cataract, pernicious anemia, vitamin B12 deficiency, thiamine deficiency, glaucoma, retinopathy, hypervitaminosis A, migraine, sjögren's syndrome, floater, macular degeneration, and can be a sign of stroke or brain tumor. __TOC__ Causes There are many causes of blurred vision: * Refractive errors: Uncorrected refractive errors like myopia, high hypermetropia, and astigmatism will cause distance vision blurring. It is one of the leading cause of visual impairment worldwide. Unless there is no associated amblyopia, visual blur due to refractive errors can be corrected to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lightheadedness
Lightheadedness is a common and typically unpleasant sensation of dizziness or a feeling that one may faint. The sensation of lightheadedness can be short-lived, prolonged, or, rarely, recurring. In addition to dizziness, the individual may feel as though their head is weightless. The individual may also feel as though the room is "spinning" or moving (vertigo). Most causes of lightheadedness are not serious and either cure themselves quickly or are easily treated. Keeping a sense of balance requires the brain to process a variety of information received from the eyes, the nervous system, and the inner ears. If the brain is unable to process these signals, such as when the messages are contradictory, or if the sensory systems are improperly functioning, an individual may experience lightheadedness or dizziness. Lightheadedness is very similar to pre-syncope. Pre-syncope is the immediate stage before syncope (fainting), particularly in cases of temporary visual field loss (i.e. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malnourishment
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients which adversely affects the body's tissues and form. Malnutrition is a category of diseases that includes undernutrition and overnutrition. Undernutrition is a lack of nutrients, which can result in stunted growth, wasting, and being underweight. A surplus of nutrients causes overnutrition, which can result in obesity or toxic levels of micronutrients. In some developing countries, overnutrition in the form of obesity is beginning to appear within the same communities as undernutrition. Most clinical studies use the term 'malnutrition' to refer to undernutrition. However, the use of 'malnutrition' instead of 'undernutrition' makes it impossible to distinguish between undernutrition and overnutrition, a less acknowledged form of malnutrition. Accordingly, a 2019 report by The Lance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, clinical examination, or medical checkup, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a Disease, medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the patient's medical history followed by an examination based on the reported symptoms. Together, the medical history and the physical examination help to determine a medical diagnosis, diagnosis and devise the treatment plan. These data then become part of the medical record. Types Routine The ''routine physical'', also known as ''general medical examination'', ''periodic health evaluation'', ''annual physical'', ''comprehensive medical exam'', ''general health check'', ''preventive health examination'', ''medical check-up'', or simply ''medical'', is a physical examination performed on an asymptomatic patient for medical screening purposes. These are normally performed by a pediatrician, family practice physician, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Fluid
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consump ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cardiovascular Condition
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by high blood pressure, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of exercise, obesity, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, among other things. High blood pressure is estimated to account for approximately 13% of CVD deaths, while tobacco accounts for 9%, diabetes 6%, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
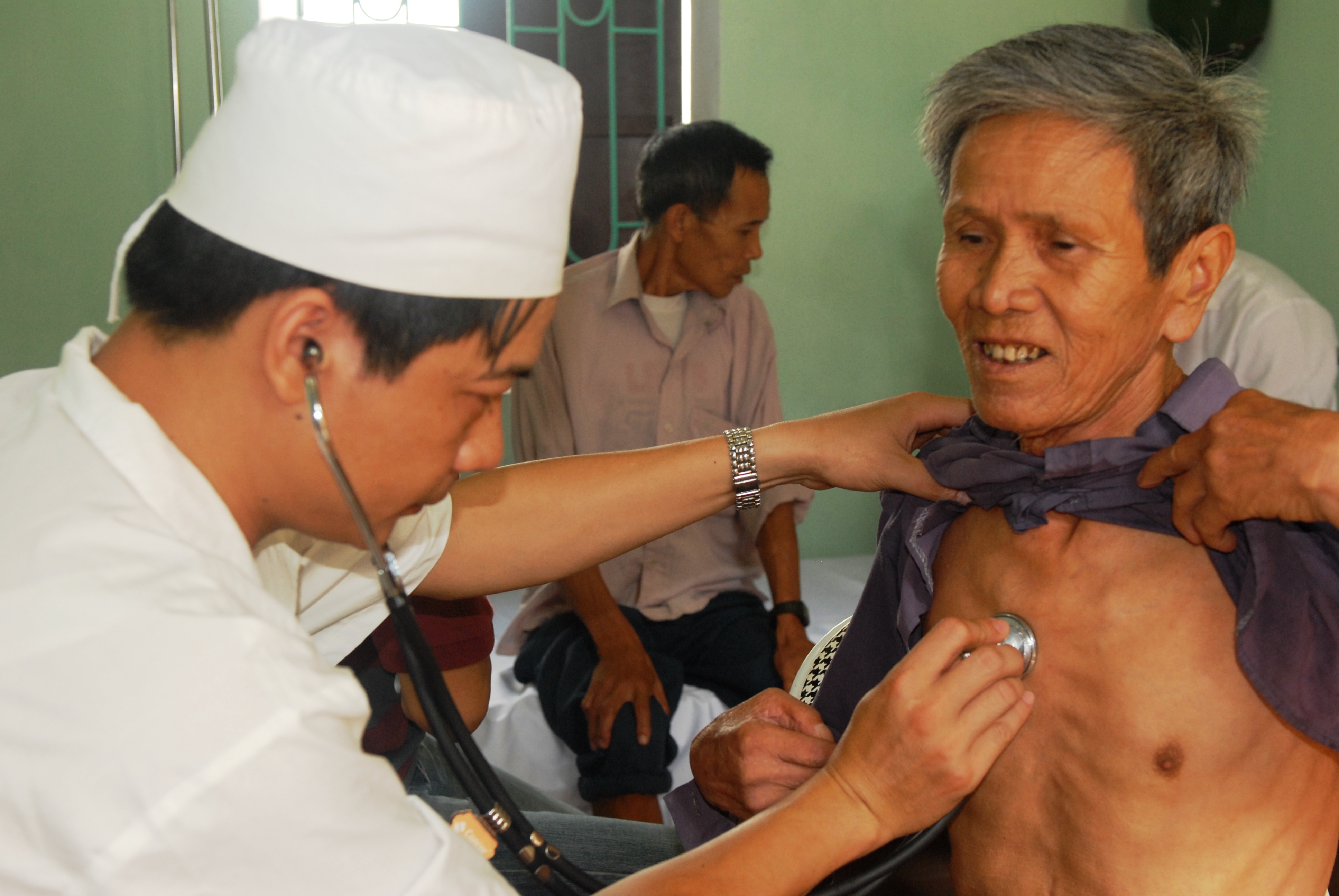
Depiction Of A Hypotension (low Blood Pressure) Patient Getting Her Blood Pressure Checked
Depiction is reference conveyed through pictures. A picture refers to its object through a non-linguistic two-dimensional scheme, and is distinct from writing or notation. A depictive two-dimensional scheme is called a picture plane and may be constructed according to descriptive geometry, where they are usually divided between ''projections'' (orthogonal and various oblique angles) and ''perspectives'' (according to number of vanishing points). Pictures are made with various materials and techniques, such as painting, drawing, or prints (including photography and movies) mosaics, tapestries, stained glass, and collages of unusual and disparate elements. Occasionally, picture-like features may be recognised in simple inkblots, accidental stains, peculiar clouds or a glimpse of the moon, but these are special cases, and it is controversial whether they count as genuine instances of depiction. Similarly, sculpture and theatrical performances are sometimes said to depict, but this req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
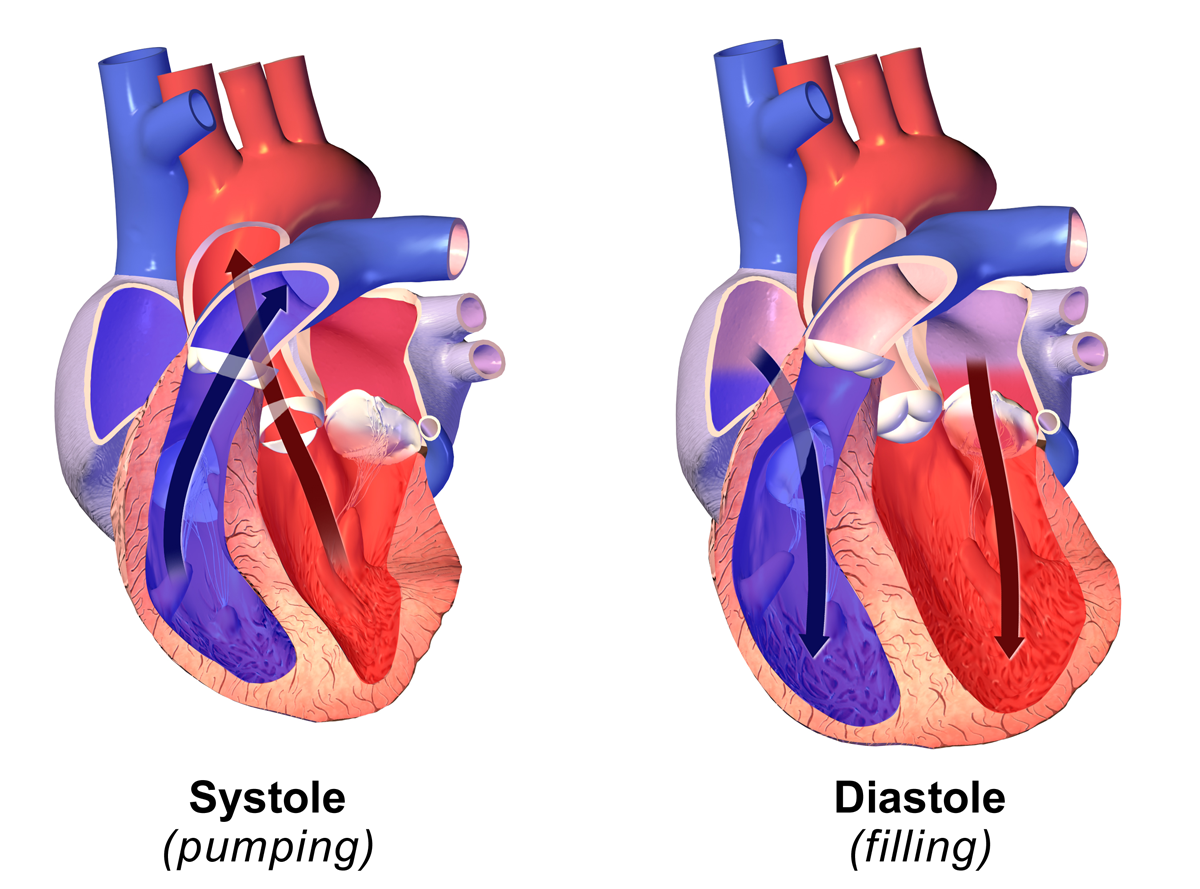
Systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. Its contrasting phase is diastole, the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. Etymology The term originates, via Neo-Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ''sun'' 'together' + ''stéllein'' 'to send'), and is similar to the use of the English term ''to squeeze''. Terminology, general explanation The mammalian heart has four chambers: the left atrium above the left ventricle (lighter pink, see graphic), which two are connected through the mitral (or bicuspid) valve; and the right atrium above the right ventricle (lighter blue), connected through the tricuspid valve. The atria are the receiving blood chambers for the circulation of blood and the ventricles are the discharging chambers. In late ventricular diastole, the atrial chambers contract and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fainting
Syncope , commonly known as fainting or passing out, is a loss of consciousness and muscle strength characterized by a fast onset, short duration, and spontaneous recovery. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain, typically from low blood pressure. There are sometimes symptoms before the loss of consciousness such as lightheadedness, sweating, pale skin, blurred vision, nausea, vomiting, or feeling warm. Syncope may also be associated with a short episode of muscle twitching. Psychiatric causes can also be determined when a patient experiences fear, anxiety, or panic; particularly before a stressful event, usually medical in nature. When consciousness and muscle strength are not completely lost, it is called presyncope. It is recommended that presyncope be treated the same as syncope. Causes range from non-serious to potentially fatal. There are three broad categories of causes: heart or blood vessel related; reflex, also known as neurally mediated; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diastolic
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles. The term originates from the Greek word (''diastolē''), meaning "dilation", from (''diá'', "apart") + (''stéllein'', "to send"). Role in cardiac cycle A typical heart rate is 75 beats per minute (bpm), which means that the cardiac cycle that produces one heartbeat, lasts for less than one second. The cycle requires 0.3 sec in ventricular systole (contraction)—pumping blood to all body systems from the two ventricles; and 0.5 sec in diastole (dilation), re-filling the four chambers of the heart, for a total of 0.8 sec to complete the cycle. Early ventricular diastole During early ventricular diastole, pressure in the two ventricles begins to drop from the peak reached during systole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |