|
Howrah–New Jalpaiguri Line
The Howrah–New Jalpaiguri line is a railway line connecting Howrah railway station to New Jalpaiguri Junction railway station in the Indian state of West Bengal. The line continues through North Bengal and western part of Assam to connect with Guwahati Junction railway station, Guwahati. The – link allows trains from another terminus in Kolkata to use this route. The line uses a major part of the Barharwa–Azimganj–Katwa loop. Many trains use an alternative line between and , via . Other parts of West Bengal and Bihar are well-connected to this line. It is under the administrative jurisdiction of Eastern Railway zone, Eastern Railway and Northeast Frontier Railway zone, Northeast Frontier Railway. Main Stations Sections The ) long trunk line, been treated in more detail in smaller sections: # Howrah–Bardhaman main line, Howrah–Bandel–Katwa section # Barharwa–Azimganj–Katwa loop # Barsoi–New Farakka section # Katihar–Siliguri line, Katihar–New Jalpaigu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Railways
Indian Railways is a state-owned enterprise that is organised as a departmental undertaking of the Ministry of Railways (India), Ministry of Railways of the Government of India and operates India's national railway system. , it manages the fourth List of countries by rail transport network size, largest national railway system by size with a track length of , running track length of and route length of . , 96.59% of the broad-gauge network is Railway electric traction, electrified. With more than 1.2 million employees, it is the world's List of companies by employees, ninth-largest employer and List of largest employers in India, India's second largest employer. In 1951, the Indian Railways was established by the amalgamation of 42 different railway companies operating in the country, spanning a total of . The railway network across the country was reorganized into six regional zones in 1951–52 for administrative purposes, which was gradually expanded to 18 zones over the ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barharwa–Azimganj–Katwa Loop
The Barharwa–Azimganj–Katwa loop is a railway line connecting Barharwa on the Sahibganj loop and Katwa. Together with the Bandel–Katwa line, which connects this line to Bandel Junction on the Howrah–Bardhaman main line, it is also known as the B.B Loop Line. This line is under the jurisdiction of Eastern Railway. The majority of this line passes through the Purba Bardhaman and Murshidabad districts, in the Indian state of West Bengal, and lies on the west bank of the Bhagirathi river. History In 1913, the Barharwa–Azimganj–Katwa Railway constructed the Barharwa–Azimganj–Katwa loop line. This line connected Barharwa Junction one the Sahibganj loop with the Katwa Junction in what was then the Hooghly–Katwa Railway. Nalhati–Azimganj branch line In 1863, the Indian Branch Railway Company, a private company constructed the Nalhati-Azimganj branch line. The line was long and was constructed with a unique rail gauge of . The Indian Branch Railway Compa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahibganj Loop
The Sahibganj loop is a railway line connecting Khana Junction and Kiul Junction. Originally a part of the Howrah–Delhi main line, it was opened to traffic in 1866. With the construction of a shorter railway line for a part of the route, the stretch was assigned a separate identity. History Railway transportation was introduced in India within 30 years of its maiden run in England. The East Indian Railway Company which was formed on 1 June 1845, completed its survey for a railway line from Kolkata, then called Calcutta, to Delhi via Mirzapur in 1846. The company initially became defunct on refusal of government guarantee, which was given in 1849. Thereafter, an agreement was signed between East Indian Railway Company and the East India Company, for the construction and operation of an "experimental" line between Kolkata and Rajmahal, which would later be extended to Delhi via Mirzapur. Construction began in 1851. On 15 August 1854, the first passenger train in the easter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
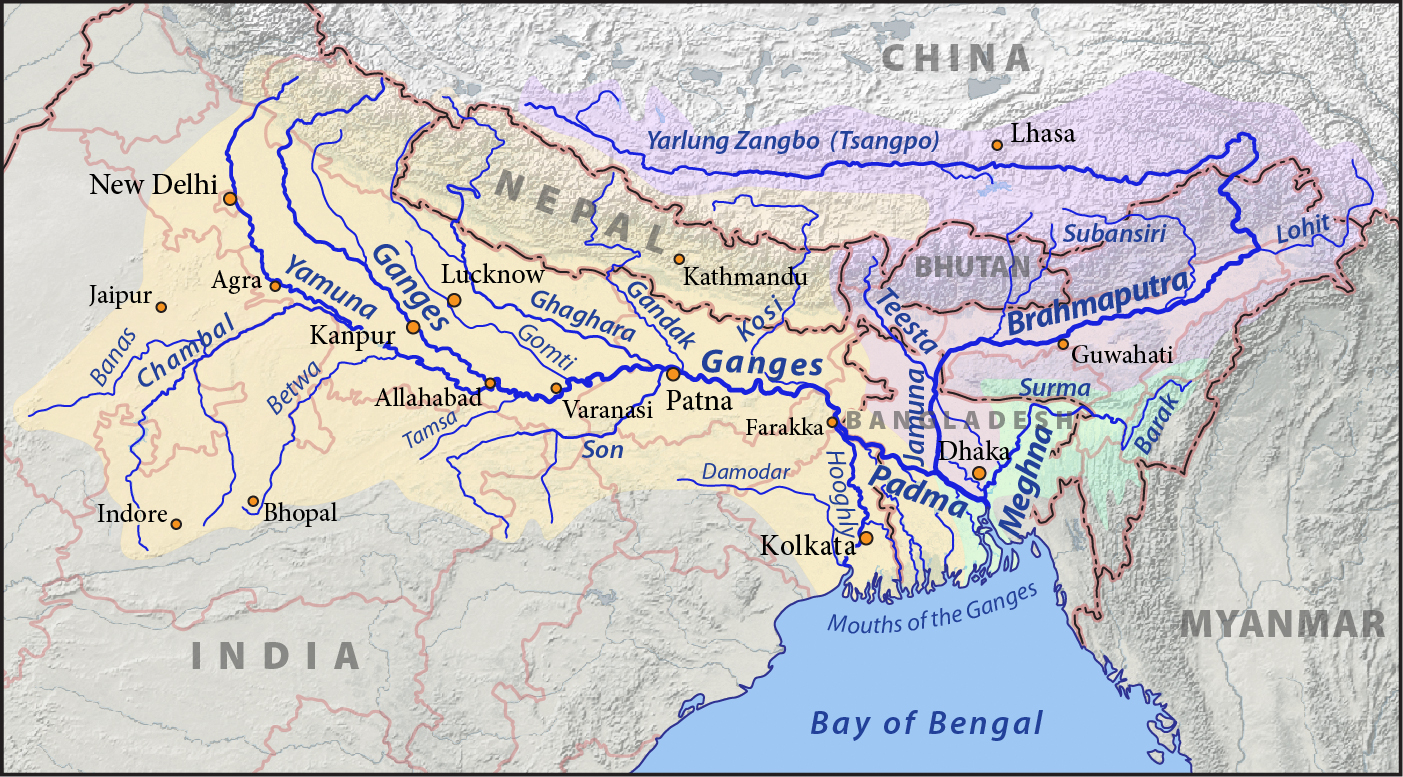
Ganges
The Ganges ( ; in India: Ganga, ; in Bangladesh: Padma, ). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international which goes through India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China." is a trans-boundary river of Asia which flows through India and Bangladesh. The river rises in the western Himalayas in the States and union territories of India, Indian state of Uttarakhand. It flows south and east through the Gangetic Plain, Gangetic plain of North India, receiving the right-bank tributary, the Yamuna, which also rises in the western Indian Himalayas, and several left-bank tributaries from Nepal that account for the bulk of its flow. In West Bengal state, India, a feeder canal taking off from its right bank diverts 50% of its flow southwards, artificially connecting it to the Hooghly River. The Ganges continues into Bangladesh, its name changing to the Padma River, Padma. It is then joined by the Jamuna River (Bangladesh), Jamuna, the lower str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siliguri Town Railway Station
Siliguri Town railway station serves Siliguri in Darjeeling district in the Indian state of West Bengal. The other important stations serving the metropolis are Siliguri Junction, Bagdogra, , , Matigara and New Jalpaiguri Junction. This is a small station consisting of three platforms, among them two broad-gauge platforms and one narrow-gauge platform. This station is located almost at the centre of the city. It opened in 1880. History In 1878, the railway line from Calcutta (later called Sealdah) station to Siliguri was in two stages – broad gauge from Calcutta to Damookeah Ghat, on the southern bank of the Padma, across the river in a ferry and then to Siliguri. In 1881, the narrow-gauge line from Siliguri to Darjeeling was added. In 1926, with the Hardinge Bridge in position, the entire Calcutta–Siliguri line was converted to broad gauge and in 1947, following the partition of India The partition of India in 1947 was the division of British India into tw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nilphamari Sadar Upazila
Nilphamari Sadar () is an upazila of Nilphamari District in the Division of Rangpur Division, Rangpur, Bangladesh. Nilphamari Sadar thana was established in 1870. It was under Daroani thana before 1870. It gradually turned into an Upazilla in 1984. Geography Nilphamari Sadar is located at . It has 97,088 households and total area 373.30 km2. It is bounded by Debiganj Upazila, Debiganj and Domar Upazila, Domar upazilas on the north, Jaldhaka Upazila, Jaldhaka and Kishoreganj Upazila, Kishoreganj upazilas on the east, Saidpur Upazila to the south and Khansama Upazila to the west. Demographics According to the 2011 Bangladesh census, 2011 Census of Bangladesh, Nilphamari Sadar Upazila had 97,088 households and a population of 435,162. 107,932 (24.80%) were under 10 years of age. Nilphamari Sadar had a literacy rate (age 7 and over) of 45.73%, compared to the national average of 51.8%, and a sex ratio of 986 females per 1000 males. 45,386 (10.43%) lived in urban areas. As of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parbatipur Railway Station
Parbatipur Junction railway station () is a railway junction in Dinajpur district of Rangpur Division in Bangladesh. History During the British period all railway connections to Assam and North Bengal were through the eastern part of Bengal. From 1878, the railway route from Kolkata, then called Calcutta, to Siliguri was in two laps. The first lap was a 185 km journey along the Eastern Bengal State Railway from Calcutta Station (later renamed Sealdah) to Damookdeah Ghat on the southern bank of the Padma River, then across the river in a ferry and the second lap of the train journey, which was a 336 km metre gauge line of the North Bengal Railway that linked Saraghat on the northern bank of the Padma to Siliguri. The 1.8 km long Hardinge Bridge across the Padma came up in 1912. In 1926 the metre-gauge section north of the bridge was converted to broad gauge, and so the entire Calcutta-Siliguri route became broad-gauge. Parbatipur came up as a station on the Calc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bheramara Upazila
Bheramara () is an upazila of Kushtia District in the Division of Khulna, Bangladesh. The upazila lies along the Padma River, and the important Hardinge Bridge crosses the river between Bheramara Upazila and Ishwardi Upazila of Pabna District. Geography Bheramara is located at . It has 47586 households and total area 153.71 km2. Bheramara sub-district is located within Kushtia district, Bangladesh and falls roughly within 23° 40′ – 24° 10′ N and 88° 45′ – 89° 20′ E. The town of Bheramara has an area of 3.26 km2 and a population of 20,676. Agriculture is the main occupation of the people, and the major crops are paddy, wheat, mustard, sweet potato, sunflower, onion, garlic, betel leaf, tobacco, and sugarcane. The survey was conducted in Bheramara town and its immediate vicinity.American-Eurasian Journal of Sustainable Agriculture, 3(3): 534-541, 2009 ISSN 1995-0748, American Eurasian Network for Scientific Information Demographics As of the 2011 Cens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asiatic Society Of Bangladesh
The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh is a non political and non profit research organisation registered under both Society Act of 1864 and NGO Affairs Bureau, Government of Bangladesh. The Asiatic Society of Bangladesh was established as the Asiatic Society of East Pakistan in Dhaka in 1952 by a number of Muslim leaders, and renamed in 1972. Ahmed Hasan Dani, a noted Muslim historian and archaeologist of Pakistan played an important role in founding this society. He was assisted by Muhammad Shahidullah, a Bengali linguist. The society is housed in Nimtali, walking distance from the Curzon Hall of Dhaka University, locality of Old Dhaka. History Asiatic Society of Bangladesh traces its origins to The Asiatic Society, which was founded by Sir William Jones in 1784. Some of scholars of the Asiatic Society moved to Dhaka, capital of East Bengal, after the Partition of India. Ahmad Hasan Dani, professor of history at the University of Dhaka, proposed the idea of establishing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hardinge Bridge
Hardinge Bridge is a steel railway truss bridge over the Padma River located at Ishwardi, Pabna and Bheramara, Kushtia in Bangladesh. It is named after Lord Hardinge, who was the Viceroy of India from 1910 to 1916. The bridge is long. Construction Construction of the through truss bridge began in 1910, though it was proposed at least 20 years earlier. It was constructed by Braithwaite and Kirk Company based on design of Sir Alexander Meadows Rendel. It was completed in 1912, and trains started moving on it in 1915. Lord Hardinge officially opened the bridge on 4 March of that year. Brief history The construction of a railway bridge over the Padma was proposed in 1889 by the Eastern Bengal Railway for easier communication between Calcutta and the then Eastern Bengal and Assam. In 1902, Sir FJE Spring prepared a report on the bridge. A technical committee reported that a bridge could be constructed at Sara crossing the lower Ganges between the Paksey and Bheramara Upazi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre-gauge
Metre-gauge railways ( US: meter-gauge railways) are narrow-gauge railways with track gauge of or 1 metre. Metre gauge is used in around of tracks around the world. It was used by several European colonial powers including France, Britain and Germany in their colonies. In Europe, large metre-gauge networks remain in use in Switzerland, Spain and many European towns with urban trams, but most metre-gauge local railways in France, Germany and Belgium closed down in the mid-20th century, although some still remain. With the revival of urban rail transport, metre-gauge light metros were built in some cities. The slightly-wider gauge is used in Sofia, Bulgaria. Another similar gauge is . __TOC__ Examples of metre-gauge See also * Italian metre gauge * Narrow-gauge railways A narrow-gauge railway (narrow-gauge railroad in the US) is a railway with a track gauge (distance between the rails) narrower than . Most narrow-gauge railways are between and . Since narrow-gaug ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Padma River
The Padma () is a major river in Bangladesh. It is the eastern and main distributary of the Ganges, flowing generally southeast for to its confluence with the Meghna River, near the Bay of Bengal. The city of Rajshahi is situated on the banks of the river.Hossain ML, Mahmud J, Islam J, Khokon ZH and Islam S (eds.) (2005) Padma, Tatthyakosh Vol. 1 and 2, Dhaka, Bangladesh, p. 182 . Since 1966, over 66,000 hectares of land have been lost to erosion of the Padma. History Etymology The Padma, Sanskrit for lotus flower, is mentioned in ancient Hindu scripts as a byname for the Goddess Lakshmi. Geographic effects Eighteenth-century geographer James Rennell referred to a former course of the Ganges north of its present channel, as follows: Murshidabad District Murshidabad District is situated on the western bank of the Padma. It flows dividing the Rajshahi and Murshidabad District of West Bengal and created a natural river border between India and Bangladesh. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |