|
Homestead Acts
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of government land or the public domain, typically called a homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of the total area of the United States, were given away free to 1.6 million homesteaders; most of the homesteads were west of the Mississippi River. An extension of the homestead principle in law, the Homestead Acts were an expression of the Free Soil policy of Northerners who wanted individual farmers to own and operate their own farms, as opposed to Southern slave owners who wanted to buy up large tracts of land and use slave labor, thereby shutting out free white farmers. For a number of years individual Congressmen put forward bills providing for homesteading, but it was not until 1862 that the first homestead act was passed. The Homestead Act of 1862 opened up millions of acres. Any adult who had never taken up arms against the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Privatization Of Public Land (United States)
In the United States, land owned and managed by governmental organizations is referred to as public land. As of 2020, the federal government owns roughly 640 million acres of land, the majority of which is concentrated in the Western US and Alaska. Privatization of public land involves the selling or auctioning of public lands to the private sector. The private sector can refer to private individuals, industry, or corporations. History The Homestead Act On May 20, 1862 President Lincoln signed the Homestead Act into law. This legislation allowed settlers to acquire 160 acres of federal land in the west, provided that they pay a filing fee and maintain residence on the parcel for five continuous years. This was intended to encourage western expansion and settlement into the interior. Between its passage in 1862 and 1900, 80 million acres of federal land had been claimed through the Homestead Act. The Sagebrush Rebellion In much of the west, public land is leased to ranchers a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Europe
Europe is a continent located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Eastern Hemisphere. It is bordered by the Arctic Ocean to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the west, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and Asia to the east. Europe shares the landmass of Eurasia with Asia, and of Afro-Eurasia with both Africa and Asia. Europe is commonly considered to be Boundaries between the continents#Asia and Europe, separated from Asia by the Drainage divide, watershed of the Ural Mountains, the Ural (river), Ural River, the Caspian Sea, the Greater Caucasus, the Black Sea, and the waterway of the Bosporus, Bosporus Strait. "Europe" (pp. 68–69); "Asia" (pp. 90–91): "A commonly accepted division between Asia and Europe ... is formed by the Ural Mountains, Ural River, Caspian Sea, Caucasus Mountains, and the Black Sea with its outlets, the Bosporus and Dardanelles." Europe covers approx. , or 2% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface (6.8% of Earth's land area), making it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Eric Foner
Eric Foner (; born February 7, 1943) is an American historian. He writes extensively on American political history, the history of freedom, the early history of the Republican Party, African American biography, the American Civil War, Reconstruction, and historiography, and has been a member of the faculty at the Columbia University Department of History since 1982. He is the author of several popular textbooks, such as the ''Give Me Liberty'' series for high school classrooms. According to the Open Syllabus Project, Foner is the most frequently cited author on college syllabi for history courses. Foner has published several books on the Reconstruction period, starting with '' Reconstruction: America's Unfinished Revolution, 1863–1877'' in 1988.Perman, Michael. "Eric Foner's Reconstruction: A Finished Revolution". ''Reviews in American History,'' Vol. 17, No. 1. (March 1989), pp. 73–78. His online courses on "The Civil War and Reconstruction", published in 2014, are avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Marginal Land
Marginal land is land that is of little agricultural or developmental value because crops produced from the area would be worth less than any rent paid for access to the area. Although the term ''marginal (other)#Economics, marginal'' is often used in a subjective sense for less-than-ideal lands, it is fundamentally an economic term that is defined by the local economic context. Thus what constitutes marginal land varies both with location and over time: for example, "a soil profile with a set of specific biophysical characteristics reported as “marginal” in the US corn belt may be one of the better soils available in another context". In the context of bioenergy, marginal land is often redefined to include land that is not only economically suboptimal but also constrained by poor biophysical conditions (e.g., shallow rooting depth, low fertility, drainage issues) or declining productivity trends. Such land may be underused in conventional agriculture but holds potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jeffersonian Democracy
Jeffersonian democracy, named after its advocate Thomas Jefferson, was one of two dominant political outlooks and movements in the United States from the 1790s to the 1820s. The Jeffersonians were deeply committed to American republicanism, which meant opposition to what they considered to be elitism, opposition to corruption, and insistence on virtue, with a priority for the " yeoman farmer", " planters", and the "plain folk".Wood, ''The American Revolution'', p. 100 They were antagonistic to the elitism of merchants, bankers, and manufacturers, distrusted factory work, and strongly opposed and were on the watch for supporters of the British Westminster system. They believed farmers made the best citizens and they welcomed opening up new low-cost farmland, especially the Louisiana Purchase of 1803. The term was commonly used to refer to the Democratic-Republican Party, formally named the "Republican Party", which Jefferson founded in opposition to the Federalist Party of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yeoman
Yeoman is a noun originally referring either to one who owns and cultivates land or to the middle ranks of Serfdom, servants in an Peerage of England, English royal or noble household. The term was first documented in Kingdom of England, mid-14th-century England. The 14th century witnessed the rise of the yeoman English longbow, longbow Archery, archers during the Hundred Years' War, and the yeoman outlaws celebrated in the Robin Hood ballads. Yeomen joined the English Navy during the Hundred Years' War as Sailor, seamen and archers. In the early 15th century, yeoman was the rank of chivalry between Page (servant), page and squire. By the late 17th century, yeoman became a rank in the Royal Navy for the common seamen who were in charge of ship's stores, such as foodstuffs, gunpowder, and sails. References to the emerging social stratum of wealthy land-owning commoners began to appear after 1429. In that year, the Parliament of England re-organized the House of Commons of Englan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Freeman Homestead-certificate
Freeman, free men, Freeman's or Freemans may refer to: Places United States * Freeman, Georgia, an unincorporated community * Freeman, Illinois, an unincorporated community * Freeman, Indiana, an unincorporated community * Freeman, South Dakota, a city * Freeman, Virginia, an unincorporated community * Freeman, Washington, an unincorporated community * Freeman, Wisconsin, a town * Freeman, Langlade County, Wisconsin, an unincorporated community * Freeman Island, an island in the state of Washington * Freeman Peak, a mountain in Idaho * Freeman Township, Michigan * Freeman Township, Freeborn County, Minnesota Norway * Freeman Strait (Freemansundet), a body of water People and fictional characters * Freeman (surname), includes a list of people and fictional characters * Freeman (given name), includes a list of people and fictional characters * A member of the Third Estate in medieval society (commoners) * Freeman, a member or an apprentice who has been granted freed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
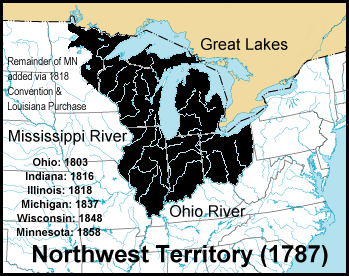
Organic Act
In United States law, an organic act is an act of the United States Congress that establishes an administrative agency or local government, for example, the laws that established territory of the United States and specified how they are to be governed, or established agency to manage certain federal lands. In the absence of organic law, the body of laws that define and establish a government, a territory is classified as unorganized. The first such act was the Northwest Ordinance, passed in 1787 by the U.S. Congress of the Confederation (under the Articles of Confederation, predecessor of the United States Constitution). The Northwest Ordinance created the Northwest Territory in the land west of Pennsylvania and northwest of the Ohio River and set the pattern of development that was followed for all subsequent territories. The Northwest Territory covered more than 260,000 square miles and included all of the modern states of Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, Wisconsin, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (PNW; ) is a geographic region in Western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Though no official boundary exists, the most common conception includes the U.S. states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, Idaho, and the Canadian province of British Columbia. Some broader conceptions reach north into Alaska and Yukon, south into Northern California, and east into western Montana. Other conceptions may be limited to the coastal areas west of the Cascade Mountains, Cascade and Coast Mountains, Coast mountains. The Northwest Coast is the coastal region of the Pacific Northwest, and the Northwest Plateau (also commonly known as "British Columbia Interior, the Interior" in British Columbia), is the inland region. The term "Pacific Northwest" should not be confused with the Northwest Territory (also known as the Great Northwest, a historical term in the United States) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Oregon, State of Oregon. Originally claimed by several countries (see Oregon Country), Spanish "El Orejón" was part of the Territorio de Nutca (1789–1795), later in the 19th century, the region was divided between the British North America, British Empire and the US in 1846. When established, the territory encompassed an area that included the current states of Oregon, Washington (state), Washington, and Idaho, as well as parts of Wyoming and Montana. The capital of the territory was first Oregon City, Oregon, Oregon City, then Salem, Oregon, Salem, followed briefly by Corvallis, Oregon, Corvallis, then back to Salem, which became the state capital upon Oregon's admission to the Union. Background Originally inhabited by Native Americans, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |