|
Holographic Associative Memory
For holographic data storage, holographic associative memory (HAM) is an information storage and retrieval system based on the principles of holography. Holograms are made by using two beams of light, called a "reference beam" and an "object beam". They produce a pattern on the film that contains them both. Afterwards, by reproducing the reference beam, the hologram recreates a visual image of the original object. In theory, one could use the object beam to do the same thing: reproduce the original reference beam. In HAM, the pieces of information act like the two beams. Each can be used to retrieve the other from the pattern. It can be thought of as an artificial neural network which mimics the way the brain uses information. The information is presented in abstract form by a complex vector which may be expressed directly by a waveform possessing frequency and magnitude. This waveform is analogous to electrochemical impulses believed to transmit information between biological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holographic Data Storage
Holographic data storage is a potential technology in the area of high-capacity data storage. While magnetic and optical data storage devices rely on individual bits being stored as distinct magnetic or optical changes on the surface of the recording medium, holographic data storage records information throughout the volume of the medium and is capable of recording multiple images in the same area utilizing light at different angles. Additionally, whereas magnetic and optical data storage records information a bit at a time in a linear fashion, holographic storage is capable of recording and reading millions of bits in parallel, enabling data transfer rates greater than those attained by traditional optical storage. Recording data Holographic data storage contains information using an optical interference pattern within a thick, photosensitive optical material. Light from a single laser beam is divided into two, or more, separate optical patterns of dark and light pixels. By ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Riemann Surface
In mathematics, particularly in complex analysis, a Riemann surface is a connected one-dimensional complex manifold. These surfaces were first studied by and are named after Bernhard Riemann. Riemann surfaces can be thought of as deformed versions of the complex plane: locally near every point they look like patches of the complex plane, but the global topology can be quite different. For example, they can look like a sphere or a torus or several sheets glued together. Examples of Riemann surfaces include Graph of a function, graphs of Multivalued function, multivalued functions such as √''z'' or log(''z''), e.g. the subset of pairs with . Every Riemann surface is a Surface (topology), surface: a two-dimensional real manifold, but it contains more structure (specifically a Complex Manifold, complex structure). Conversely, a two-dimensional real manifold can be turned into a Riemann surface (usually in several inequivalent ways) if and only if it is orientable and Metrizabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short-term Memory
Short-term memory (or "primary" or "active memory") is the capacity for holding a small amount of information in an active, readily available state for a short interval. For example, short-term memory holds a phone number that has just been recited. The duration of short-term memory (absent rehearsal or active maintenance) is estimated to be on the order of seconds. The commonly cited capacity of 7 items, found in Miller's Law, has been superseded by 4±1 items. In contrast, long-term memory holds information indefinitely. Short-term memory is not the same as working memory, which refers to structures and processes used for temporarily storing and manipulating information. Stores The idea of separate memories for short-term and long-term storage originated in the 19th century. A model of memory developed in the 1960s assumed that all memories are formed in one store and transfer to other stores after a small period of time. This model is referred to as the "modal model", mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Signal
An analog signal (American English) or analogue signal (British and Commonwealth English) is any continuous-time signal representing some other quantity, i.e., ''analogous'' to another quantity. For example, in an analog audio signal, the instantaneous signal voltage varies continuously with the pressure of the sound waves. In contrast, a digital signal represents the original time-varying quantity as a sampled sequence of quantized values. Digital sampling imposes some bandwidth and dynamic range constraints on the representation and adds quantization noise. The term ''analog signal'' usually refers to electrical signals; however, mechanical, pneumatic, hydraulic, and other systems may also convey or be considered analog signals. Representation An analog signal uses some property of the medium to convey the signal's information. For example, an aneroid barometer uses rotary position as the signal to convey pressure information. In an electrical signal, the voltage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Distribution
In probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or Gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real number, real-valued random variable. The general form of its probability density function is f(x) = \frac e^\,. The parameter is the Mean#Mean of a probability distribution, mean or expected value, expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode (statistics), mode), while the parameter \sigma^2 is the variance. The standard deviation of the distribution is (sigma). A random variable with a Gaussian distribution is said to be normally distributed, and is called a normal deviate. Normal distributions are important in statistics and are often used in the natural science, natural and social sciences to represent real-valued random variables whose distributions are not known. Their importance is partly due to the central limit theorem. It states that, under some conditions, the average of many samples (observations) of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigmoid Function
A sigmoid function is any mathematical function whose graph of a function, graph has a characteristic S-shaped or sigmoid curve. A common example of a sigmoid function is the logistic function, which is defined by the formula :\sigma(x) = \frac = \frac = 1 - \sigma(-x). Other sigmoid functions are given in the #Examples, Examples section. In some fields, most notably in the context of artificial neural networks, the term "sigmoid function" is used as a synonym for "logistic function". Special cases of the sigmoid function include the Gompertz curve (used in modeling systems that saturate at large values of ''x'') and the ogee curve (used in the spillway of some dams). Sigmoid functions have domain of all real numbers, with return (response) value commonly monotonically increasing but could be decreasing. Sigmoid functions most often show a return value (''y'' axis) in the range 0 to 1. Another commonly used range is from −1 to 1. A wide variety of sigmoid functions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthogonal
In mathematics, orthogonality (mathematics), orthogonality is the generalization of the geometric notion of ''perpendicularity''. Although many authors use the two terms ''perpendicular'' and ''orthogonal'' interchangeably, the term ''perpendicular'' is more specifically used for lines and planes that intersect to form a right angle, whereas ''orthogonal'' is used in generalizations, such as ''orthogonal vectors'' or ''orthogonal curves''. ''Orthogonality'' is also used with various meanings that are often weakly related or not related at all with the mathematical meanings. Etymology The word comes from the Ancient Greek ('), meaning "upright", and ('), meaning "angle". The Ancient Greek (') and Classical Latin ' originally denoted a rectangle. Later, they came to mean a right triangle. In the 12th century, the post-classical Latin word ''orthogonalis'' came to mean a right angle or something related to a right angle. Mathematics Physics Optics In optics, polarization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
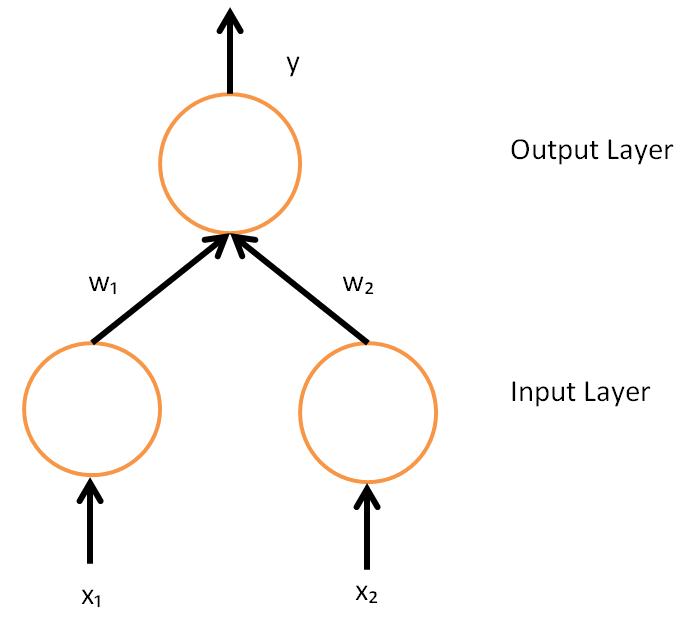
Connectionism
Connectionism is an approach to the study of human mental processes and cognition that utilizes mathematical models known as connectionist networks or artificial neural networks. Connectionism has had many "waves" since its beginnings. The first wave appeared 1943 with Warren Sturgis McCulloch and Walter Pitts both focusing on comprehending neural circuitry through a formal and mathematical approach, and Frank Rosenblatt who published the 1958 paper "The Perceptron: A Probabilistic Model For Information Storage and Organization in the Brain" in ''Psychological Review'', while working at the Cornell Aeronautical Laboratory. The first wave ended with the 1969 book about the limitations of the original perceptron idea, written by Marvin Minsky and Seymour Papert, which contributed to discouraging major funding agencies in the US from investing in connectionist research. With a few noteworthy deviations, most connectionist research entered a period of inactivity until the mid-1980 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backpropagation
In machine learning, backpropagation is a gradient computation method commonly used for training a neural network to compute its parameter updates. It is an efficient application of the chain rule to neural networks. Backpropagation computes the gradient of a loss function with respect to the weights of the network for a single input–output example, and does so efficiently, computing the gradient one layer at a time, iterating backward from the last layer to avoid redundant calculations of intermediate terms in the chain rule; this can be derived through dynamic programming. Strictly speaking, the term ''backpropagation'' refers only to an algorithm for efficiently computing the gradient, not how the gradient is used; but the term is often used loosely to refer to the entire learning algorithm – including how the gradient is used, such as by stochastic gradient descent, or as an intermediate step in a more complicated optimizer, such as Adaptive Moment Estimation. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phasor
In physics and engineering, a phasor (a portmanteau of phase vector) is a complex number representing a sinusoidal function whose amplitude and initial phase are time-invariant and whose angular frequency is fixed. It is related to a more general concept called analytic representation,Bracewell, Ron. ''The Fourier Transform and Its Applications''. McGraw-Hill, 1965. p269 which decomposes a sinusoid into the product of a complex constant and a factor depending on time and frequency. The complex constant, which depends on amplitude and phase, is known as a phasor, or complex amplitude, and (in older texts) sinor or even complexor. A common application is in the steady-state analysis of an electrical network powered by time varying current where all signals are assumed to be sinusoidal with a common frequency. Phasor representation allows the analyst to represent the amplitude and phase of the signal using a single complex number. The only difference in their analytic rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holography
Holography is a technique that allows a wavefront to be recorded and later reconstructed. It is best known as a method of generating three-dimensional images, and has a wide range of other uses, including data storage, microscopy, and interferometry. In principle, it is possible to make a hologram for any type of Holography#Non-optical holography, wave. A hologram is a recording of an Wave interference, interference pattern that can reproduce a 3D light field using diffraction. In general usage, a hologram is a recording of any type of wavefront in the form of an interference pattern. It can be created by capturing light from a real scene, or it can be generated by a computer, in which case it is known as a computer-generated hologram, which can show virtual objects or scenes. Optical holography needs a laser light to record the light field. The reproduced light field can generate an image that has the depth and parallax of the original scene. A hologram is usually unintelligi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered, it would be impossible for language, relationships, or personal identity to develop. Memory loss is usually described as forgetfulness or amnesia. Memory is often understood as an informational processing system with explicit and implicit functioning that is made up of a sensory processor, short-term (or working) memory, and long-term memory. This can be related to the neuron. The sensory processor allows information from the outside world to be sensed in the form of chemical and physical stimuli and attended to various levels of focus and intent. Working memory serves as an encoding and retrieval processor. Information in the form of stimuli is encoded in accordance with explicit or implicit functions by the working memory p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |