|
Hohmann Transfer Orbit
In astronautics, the Hohmann transfer orbit () is an orbital maneuver used to transfer a spacecraft between two orbits of different altitudes around a central body. For example, a Hohmann transfer could be used to raise a satellite's orbit from low Earth orbit to geostationary orbit. In the idealized case, the initial and target orbits are both circular orbit, circular and orbital plane, coplanar. The maneuver is accomplished by placing the craft into an elliptical orbit, elliptical transfer orbit that is tangential to both the initial and target orbits. The maneuver uses two impulse (physics), impulsive engine burns: the first establishes the transfer orbit, and the second adjusts the orbit to match the target. The Hohmann maneuver often uses the lowest possible amount of impulse (which consumes a proportional amount of delta-v, and hence propellant) to accomplish the transfer, but requires a relatively longer travel time than higher-impulse transfers. In some cases where one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two Planets
''Two Planets'' (, lit. ''On Two Planets'', 1897) is an influential science fiction novel by Kurd Lasswitz, postulating intelligent life on Mars. It was first published in hardcover by Felber in two volumes in 1897; there have been many editions since, including abridgements by the author's son Erich Lasswitz (Cassianeum, 1948) and Burckhardt Kiegeland and Martin Molitor (Verlag Heinrich Scheffler, 1969). The 1948 abridgement, with "incidental parts" of the text taken from the 1969 version, was the basis of the first translation into English by Hans H. Rudnick, published in hardcover by Southern Illinois University Press in 1971. A paperback edition followed from Popular Library in 1976. The story covers topics like colonization, mutually assured destruction and clash of civilizations many generations before these topics came into politics. Summary A group of Arctic explorers seeking the North Pole find a Martian base there. The Martians can only operate in a polar region not beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the form of energy that it possesses due to its motion. In classical mechanics, the kinetic energy of a non-rotating object of mass ''m'' traveling at a speed ''v'' is \fracmv^2.Resnick, Robert and Halliday, David (1960) ''Physics'', Section 7-5, Wiley International Edition The kinetic energy of an object is equal to the work, or force ( F) in the direction of motion times its displacement ( s), needed to accelerate the object from rest to its given speed. The same amount of work is done by the object when decelerating from its current speed to a state of rest. The SI unit of energy is the joule, while the English unit of energy is the foot-pound. In relativistic mechanics, \fracmv^2 is a good approximation of kinetic energy only when ''v'' is much less than the speed of light. History and etymology The adjective ''kinetic'' has its roots in the Greek word κίνησις ''kinesis'', meaning "motion". The dichoto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar System
The Solar SystemCapitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar System" and "solar system" structures in theinaming guidelines document. The name is commonly rendered in lower case ('solar system'), as, for example, in the ''Oxford English Dictionary'' an''Merriam-Webster's 11th Collegiate Dictionary''. is the gravitationally bound Planetary system, system of the Sun and the objects that orbit it. It Formation and evolution of the Solar System, formed about 4.6 billion years ago when a dense region of a molecular cloud collapsed, forming the Sun and a protoplanetary disc. The Sun is a typical star that maintains a hydrostatic equilibrium, balanced equilibrium by the thermonuclear fusion, fusion of hydrogen into helium at its stellar core, core, releasing this energy from its outer photosphere. As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apogee Kick Motor
An apogee kick motor (AKM) is a rocket motor that is regularly employed on artificial satellites to provide the final impulse to change the trajectory from the transfer orbit into its final orbit (most commonly circular). For a satellite launched from the Earth, the rocket firing is done at the highest point of the transfer orbit, known as the apogee. An apogee kick motor is used, for example, for satellites launched into a geostationary orbit. As the vast majority of geostationary satellite launches are carried out from spaceports at a significant distance away from Earth's equator, the carrier rocket often only launches the satellite into an orbit with a non-zero inclination approximately equal to the latitude of the launch site. This orbit is commonly known as a "geostationary transfer orbit" or a "geosynchronous transfer orbit". The satellite must then provide thrust to bring forth the needed delta v to reach a geostationary orbit. This is typically done with a fixed onbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Impulse Function
In mathematical analysis, the Dirac delta function (or distribution), also known as the unit impulse, is a generalized function on the real numbers, whose value is zero everywhere except at zero, and whose integral over the entire real line is equal to one. Thus it can be represented heuristically as \delta (x) = \begin 0, & x \neq 0 \\ , & x = 0 \end such that \int_^ \delta(x) dx=1. Since there is no function having this property, modelling the delta "function" rigorously involves the use of limits or, as is common in mathematics, measure theory and the theory of distributions. The delta function was introduced by physicist Paul Dirac, and has since been applied routinely in physics and engineering to model point masses and instantaneous impulses. It is called the delta function because it is a continuous analogue of the Kronecker delta function, which is usually defined on a discrete domain and takes values 0 and 1. The mathematical rigor of the delta function wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reversibility Of Orbits
Reversibility can refer to: * Time reversibility, a property of some mathematical or physical processes and systems for which time-reversed dynamics are well defined :* Reversible diffusion, an example of a reversible stochastic process * Reversible process (thermodynamics), a process or cycle such that the net change at each stage in the combined entropy of the system and its surroundings is zero * Reversible reaction, a chemical reaction for which the position of the chemical equilibrium is very sensitive to the imposed physical conditions; so the reaction can be made to run either forwards or in reverse by changing those conditions * Reversible computing, logical reversibility of a computation; a computational step for which a well-defined inverse exists * Reversible error, a legal mistake invalidating a trial * Reversible garment, a garment that can be worn two ways * Piaget's theory of cognitive development, in which mental reversibility is part of the concrete operational stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hohmann Transfer Orbit2
Hohmann may refer to: * Hohmann (surname) (article includes list of persons named Hohmann) * Hohmann transfer orbit, in orbital mechanics * Hohmann (crater) Hohmann is a Lunar craters, lunar impact crater that lies within the central basin of the Mare Orientale formation, on the Far side (Moon), farside of the Moon. It is located to the south of the crater Maunder (lunar crater), Maunder, and to the ..., a lunar crater * 9661 Hohmann (1996 FU13), an asteroid See also * Hohman * Homann * Homan (other) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apsis
An apsis (; ) is the farthest or nearest point in the orbit of a planetary body about its primary body. The line of apsides (also called apse line, or major axis of the orbit) is the line connecting the two extreme values. Apsides pertaining to orbits around different bodies have distinct names to differentiate themselves from other apsides. Apsides pertaining to geocentric orbits, orbits around the Earth, are at the farthest point called the ''apogee'', and at the nearest point the ''perigee'', like with orbits of satellites and the Moon around Earth. Apsides pertaining to orbits around the Sun are named ''aphelion'' for the farthest and ''perihelion'' for the nearest point in a heliocentric orbit. Earth's two apsides are the farthest point, ''aphelion'', and the nearest point, ''perihelion'', of its orbit around the host Sun. The terms ''aphelion'' and ''perihelion'' apply in the same way to the orbits of Jupiter and the other planets, the comets, and the asteroids of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
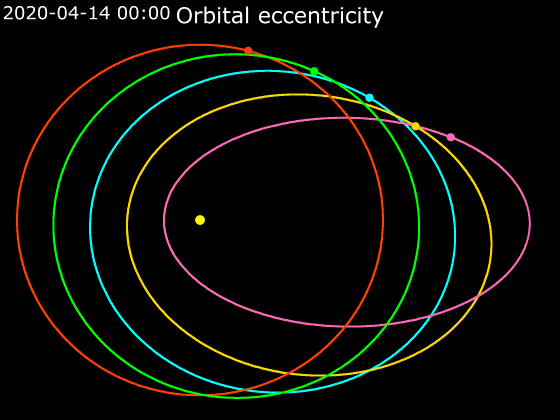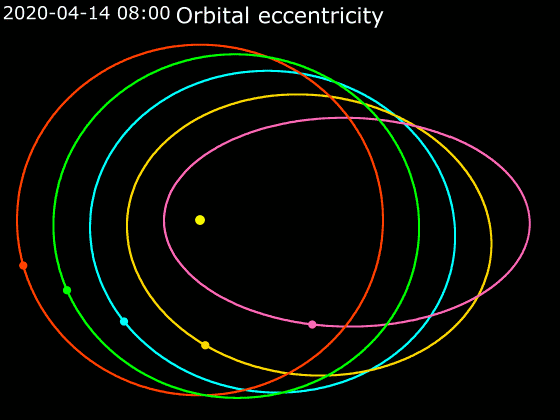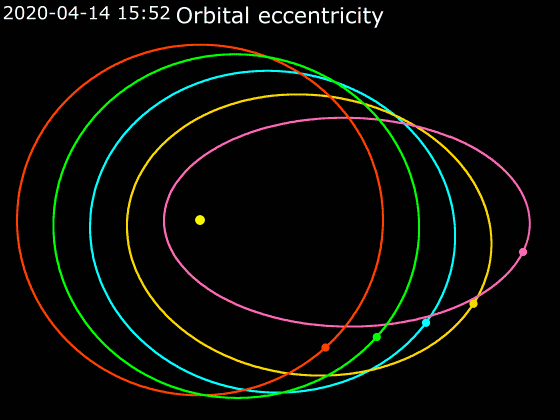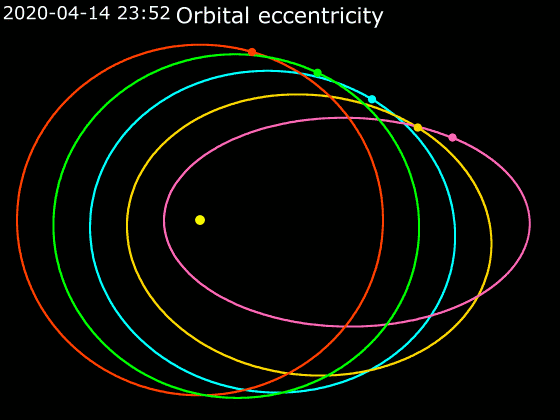
Elliptic Orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics, an elliptical orbit or eccentric orbit is an orbit with an eccentricity of less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to 0. Some orbits have been referred to as "elongated orbits" if the eccentricity is "high" but that is not an explanatory term. For the simple two body problem, all orbits are ellipses. In a gravitational two-body problem, both bodies follow similar elliptical orbits with the same orbital period around their common barycenter. The relative position of one body with respect to the other also follows an elliptic orbit. Examples of elliptic orbits include Hohmann transfer orbits, Molniya orbits, and tundra orbits. Velocity Under standard assumptions, no other forces acting except two spherically symmetrical bodies (m_1) and (m_2), the orbital speed (v\,) of one body traveling along an elliptical orbit can be computed from the vis-viva equation as: :v = \sqrt where: * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-energy Transfer
A low-energy transfer, or low-energy trajectory, is a route in space that allows spacecraft to change orbits using significantly less fuel than traditional transfers. These routes work in the Earth–Moon system and also in other systems, such as between the moons of Jupiter. The drawback of such trajectories is that they take longer to complete than higher-energy (more-fuel) transfers, such as Hohmann transfer orbits. Low-energy transfers are also known as Weak Stability Boundary trajectories, and include ballistic capture trajectories. Low-energy transfers follow special pathways in space, sometimes referred to as the Interplanetary Transport Network. Following these pathways allows for long distances to be traversed for little change in velocity, or . Example missions Missions that have used low-energy transfers include: * '' Hiten'', from JAXA * '' SMART-1'', from ESA * ''Genesis'', from NASA. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberth Effect
In astronautics, a powered flyby, or Oberth maneuver, is a maneuver in which a spacecraft falls into a gravitational well and then uses its engines to further accelerate as it is falling, thereby achieving additional speed. The resulting maneuver is a more efficient way to gain kinetic energy than applying the same impulse outside of a gravitational well. The gain in efficiency is explained by the Oberth effect, wherein the use of a reaction engine at higher speeds generates a greater change in mechanical energy than its use at lower speeds. In practical terms, this means that the most energy-efficient method for a spacecraft to burn its fuel is at the lowest possible orbital periapsis, when its orbital velocity (and so, its kinetic energy) is greatest. In some cases, it is even worth spending fuel on slowing the spacecraft into a gravity well to take advantage of the efficiencies of the Oberth effect. The maneuver and effect are named after the Transylvanian Saxon physicist an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |