|
Hiwinui
Hiwinui is a settlement in Manawatū District, in the Manawatū-Whanganui region in New Zealand's central North Island. "Hiwinui" means "big ridge" in the Māori language. History The Hiwinui area was originally settled by the Rangitāne iwi. Land was purchased by the government in the 1860s and resold to pākehā settlers, who converted the forest to farmland. Demographics Hiwinui is defined by Statistics New Zealand as a rural settlement. It covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. It is part of the larger Taonui statistical area. Hiwinui had a population of 336 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 93 people (38.3%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 162 people (93.1%) since the 2006 census. There were 105 households, comprising 171 males and 165 females, giving a sex ratio of 1.04 males per female, with 93 people (27.7%) aged under 15 years, 39 (11.6%) aged 15 to 29, 180 (53.6%) aged 30 to 64, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colyton, New Zealand
Colyton is a community in the Manawatū District and Manawatū-Whanganui region in New Zealand's central North Island. Colyton has the postcode of 4775. Demographics Colyton is in an SA1 statistical area which covers . The SA1 area is part of the larger Taonui statistical area. The SA1 area had a population of 159 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 9 people (6.0%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 48 people (43.2%) since the 2006 census. There were 57 households, comprising 81 males and 78 females, giving a sex ratio of 1.04 males per female. The median age was 43.3 years (compared with 37.4 years nationally), with 30 people (18.9%) aged under 15 years, 21 (13.2%) aged 15 to 29, 81 (50.9%) aged 30 to 64, and 27 (17.0%) aged 65 or older. Ethnicities were 92.5% European/Pākehā, 7.5% Māori, and 3.8% Asian. People may identify with more than one ethnicity. Although some people chose not to answer the census's question about religious affiliation, 62.3% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 New Zealand Census
The New Zealand Census of Population and Dwellings () is a national population and housing census conducted by Statistics New Zealand, a government department, every five years. There have been 34 censuses since 1851 New Zealand census, 1851. In addition to providing detailed information about national demographics, the results of the census play an important part in the calculation of resource allocation to local service providers. The 2023 New Zealand census, 2023 census held on 7 March 2023 was the most recent, with the results being released from 29 May 2024 to August 2025. Census date Since 1926, the census has always been held on a Tuesday and since 1966, the census always occurs in March. These are statistically the month and weekday on which New Zealanders are least likely to be travelling. The census forms have to be returned by midnight on census day for them to be valid. Conducting the census Until 2018, census forms were hand-delivered by census workers during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education Review Office
The Education Review Office (ERO; ) is the public service department of New Zealand charged with reviewing and publicly reporting on the quality of education and care of students in all New Zealand schools and early childhood services. Leadership and structure Led by a Chief Review Officer - the department's chief executive - the Office has approximately 150 designated review officers located in five regions. These regions are: Northern, Waikato/Bay of Plenty, Central, Southern, and Te Uepū ā-Motu (ERO's Māori review services unit). The Education Review Office and the Ministry of Education are two separate public service departments. The functions and powers of the office are set out in Part 28 (sections 323–328) of the Education Act 1989. In May 2023, the Independent Children's Monitor was transferred from the Ministry of Social Development, and reconstituted as a departmental agency of the Education Review Office. The Children's Monitor oversees the entire Oranga Ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ministry Of Education (New Zealand)
The Ministry of Education () is the public service department of New Zealand charged with overseeing the New Zealand education system. The Ministry was formed in 1989 when the former, all-encompassing Department of Education was broken up into six separate agencies. History Picot report The Ministry was established as a result of the Picot task force set up by the Labour government in July 1987 to review the New Zealand education system. The members were Brian Picot, a businessman, Peter Ramsay, an associate professor of education at the University of Waikato, Margaret Rosemergy, a senior lecturer at the Wellington College of Education, Whetumarama Wereta, a social researcher at the Department of Maori Affairs and Colin Wise, another businessman. The task force was assisted by staff from the Treasury and the State Services Commission (SSC), who may have applied pressure on the task force to move towards eventually privatizing education, as had happened with other governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion Of Māori People
The Māori people, Māori people have a Polynesian mythology, Polynesian religion that, prior to the introduction of Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity to New Zealand was the main religious belief for Māori. By 1845, more than half of the Māori population attended church and Christianity remains the largest religion for Māori. Very few Māori still follow traditional Māori religion, although many elements of it are still observed. Several Māori religious movements have been born out of Christianity, such as the Ratana movement. Traditional Māori religion Traditional Māori religion, that is, the pre-European belief-system of the Māori people , Māori, differed little from that of their perceived homeland, Hawaiki, Hawaiki Nui, aka Raʻiātea or Raiatea, conceiving of everything – including natural elements and all living things – as connected by common descent through whakapapa or genealogy. Accordingly, Māori regarded all things as possessing a life force ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhism In New Zealand
Buddhism is New Zealand's third-largest religion after Christianity and Hinduism standing at 1.5% of the population of New Zealand. Buddhism originates in Asia and was introduced to New Zealand by immigrants from East Asia. History The first Buddhists in New Zealand were Chinese diggers in the Otago goldfields in the mid-1860s. Their numbers were small, and the 1926 census, the first to include Buddhism, recorded only 169. Buddhism grew significantly as a religion in New Zealand during the 1970s and 1980s with the arrival of Southeast Asian immigrants and refugees, coinciding with increased interest in Buddhist teaching from Western communities. Buddhist associations began forming, such as the Zen Society of New Zealand in 1972 (originally known as the Denkyo-ji Society), often fundraising to organise In the 1970s travel to Asian countries and visits by Buddhist teachers sparked an interest in the religious traditions of Asia, and significant numbers of New Zealanders adopte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
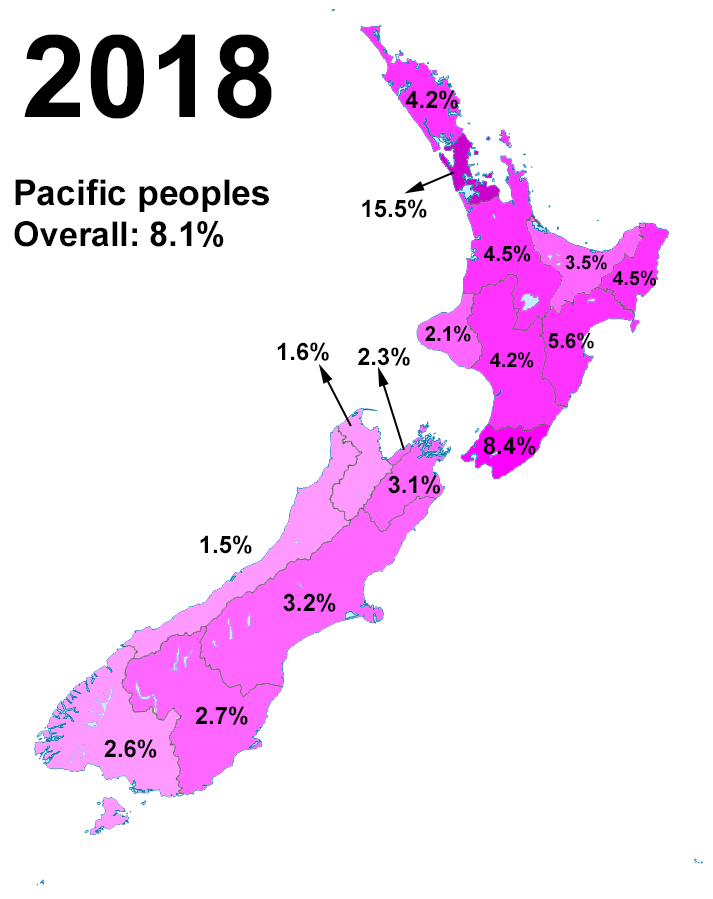
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
Māori () are the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, indigenous Polynesians, Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand. Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of Māori migration canoes, canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed Māori culture, a distinct culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Early contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, Treaty of Waitangi/Te Tiriti o Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
''Pākehā'' (or ''Pakeha''; ; ) is a Māori language, Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesians, Polynesian New Zealanders, New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zealanders, European New Zealander. It is not a legal term and has no definition under New Zealand law. ''Papa'a'' has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Etymology and history The etymology of is uncertain. The most likely sources are the Māori words or , which refer to an oral tale of a "mythical, human like being, with fair skin and hair who possessed canoes made of reeds which changed magically into sailing vessels". When Europeans first arrived they rowed to shore in longboats, facing backwards: In traditional Māori canoes or , paddlers face the direction of travel. This is supposed to have led to the belief by some, that the sailors were ''patupaiarehe'' (supernatural beings). There have been several dubious interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |