|
History Of Steam Road Vehicles
The history of steam road vehicles comprises the development of vehicles powered by a steam engine for use on land and independent of rails, whether for conventional road use, such as the steam car and steam waggon, or for agricultural or heavy haulage work, such as the traction engine. The first experimental vehicles were built in the 18th and 19th century, but it was not until after Richard Trevithick had developed the use of high-pressure steam, around 1800, that mobile steam engines became a practical proposition. The first half of the 19th century saw great progress in steam vehicle design, and by the 1850s it was viable to produce them on a commercial basis. This progress was dampened by legislation which limited or prohibited the use of steam-powered vehicles on roads. Nevertheless, the 1880s to the 1920s saw continuing improvements in vehicle technology and manufacturing techniques, and steam road vehicles were developed for many applications. In the 20th century, the ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steam Powered Road-locomotive From England
Steam is water vapor, often mixed with air or an aerosol of liquid water droplets. This may occur due to evaporation or due to boiling, where heat is applied until water reaches the enthalpy of vaporization. Saturated or superheated steam is invisible; however, wet steam, a visible mist or aerosol of water droplets, is often referred to as "steam". When liquid water becomes steam, it increases in volume by 1,700 times at standard temperature and pressure; this change in volume can be converted into mechanical work by steam engines such as reciprocating piston type engines and steam turbines, which are a sub-group of steam engines. Piston type steam engines played a central role in the Industrial Revolution and modern steam turbines are used to generate more than 80% of the world's electricity. If liquid water comes in contact with a very hot surface or depressurizes quickly below its vapour pressure, it can create a steam explosion. Types of steam and conversions Steam is trad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthew Boulton
Matthew Boulton ( ; 3 September 172817 August 1809) was an English businessman, inventor, mechanical engineer, and silversmith. He was a business partner of the Scottish engineer James Watt. In the final quarter of the 18th century, the partnership installed hundreds of Boulton and Watt, Boulton & Watt steam engines, which were a great advance on the state of the art, making possible the mechanisation of factories and mills. Boulton applied modern techniques to the minting of coins, striking millions of pieces for Britain and other countries, and supplying the Royal Mint with up-to-date equipment. Born in Birmingham, he was the son of a Birmingham manufacturer of small metal products who died when Boulton was 31. By then Boulton had managed the business for several years, and thereafter expanded it considerably, consolidating operations at the Soho Manufactory, built by him near Birmingham. At Soho, he adopted the latest techniques, branching into silver plate, ormolu ("gilt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connecting Rod
A connecting rod, also called a 'con rod', is the part of a reciprocating engine, piston engine which connects the piston to the crankshaft. Together with the crank (mechanism), crank, the connecting rod converts the reciprocating motion of the piston into the rotation of the crankshaft. The connecting rod is required to transmit the compressive and tensile forces from the piston. In its most common form, in an internal combustion engine, it allows pivoting on the piston end and rotation on the shaft end. The predecessor to the connecting rod is a mechanic linkage used by water mills to convert rotating motion of the water wheel into reciprocating motion. The most common usage of connecting rods is in internal combustion engines or on steam engines. __TOC__ Origins A connecting rod crank has been found in the Celtic Oppida at Paule in Brittany, dated to 69 BC. The predecessor to the connecting length is the Linkage (mechanical), mechanical linkage used by List of Roman wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trevithick Road Loco 01
Trevithick ( ) is a Cornish surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Francis Trevithick (1812–1877), one of the first locomotive engineers of the London and North Western Railway * Jonathan Trevethick (1864–1939), New Zealand politician * Paul Trevithick (born 1959), American inventor, engineer and entrepreneur * Richard Trevithick Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He ... (1771–1833), British inventor, mining engineer and builder of the first working railway steam locomotive * William Edward Trevithick (1899–1958), Irish botanical illustrator {{surname Cornish-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Symington
William Symington (1764–1831) was a Scottish engineer and inventor during the Georgian era. He is most well known as the builder of the first practical steamboat, the Charlotte Dundas. The engine has been described as ''"without doubt the most compact and efficient marine steam engine up to that time"'' and its design would influence later steamboat and steamship engine designs. While Symington died in poverty after failing to commercialise his steam engine designs, he is still credited as one of the great inventors of the early Industrial Revolution. Early life Symington was born in Leadhills, South Lanarkshire, Scotland, to a family he described as being "respectable but not wealthy." His father worked as a practical mechanic at the Leadhills mines. Although his parents intended for him to enter the ministry, he intended to use his good education to make a career as an engineer. So, in 1785, he joined his brother George in his attempts to build a steam engine at Wanlockhea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tiller
A tiller or till is a lever used to steer a vehicle. The mechanism is primarily used in watercraft, where it is attached to an outboard motor, rudder post, rudder post or stock to provide leverage in the form of torque for the helmsman to turn the rudder. A tiller may also be used in vehicles outside of water, and was seen in early automobiles. On vessels, a tiller can be used by the helmsman directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using tiller lines or a ship's wheel. Rapid or excessive movement of the tiller results in an increase in drag and will result in braking or slowing the boat. Description A tiller is a lever used to steer a vehicle. It provides leverage in the form of torque to turn the device that changes the direction of the vehicle, such as a rudder on a watercraft or the surface wheels on a wheeled vehicle. A tiller can be used by directly pulling or pushing it, but it may also be moved remotely using a whipstaff, tiller lines, or a sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tricycle
A tricycle, sometimes abbreviated to trike, is a Human-powered transport, human-powered (or gasoline or electric motor powered or assisted, or gravity powered) Three-wheeler, three-wheeled vehicle. Some tricycles, such as cycle rickshaws (for passenger transport) and freight trikes, are used for commercial purposes, especially in the developing world, particularly Africa and Asia. In the West, adult-sized tricycles are used primarily for recreation, shopping, and exercise. Tricycles are favoured by children, the disabled, and senior adults for their apparent stability versus a bicycle; however a Three-wheeler#Two rear, conventional trike may exhibit poor dynamic lateral stability, and the rider should exercise appropriate operating caution when cornering (e.g., with regard to speed, rate of turn, slope of surface) and operating technique (e.g., leaning the body 'into' the turn) to avoid tipping the trike over. Designs such as recumbents or others which place the rider lower relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
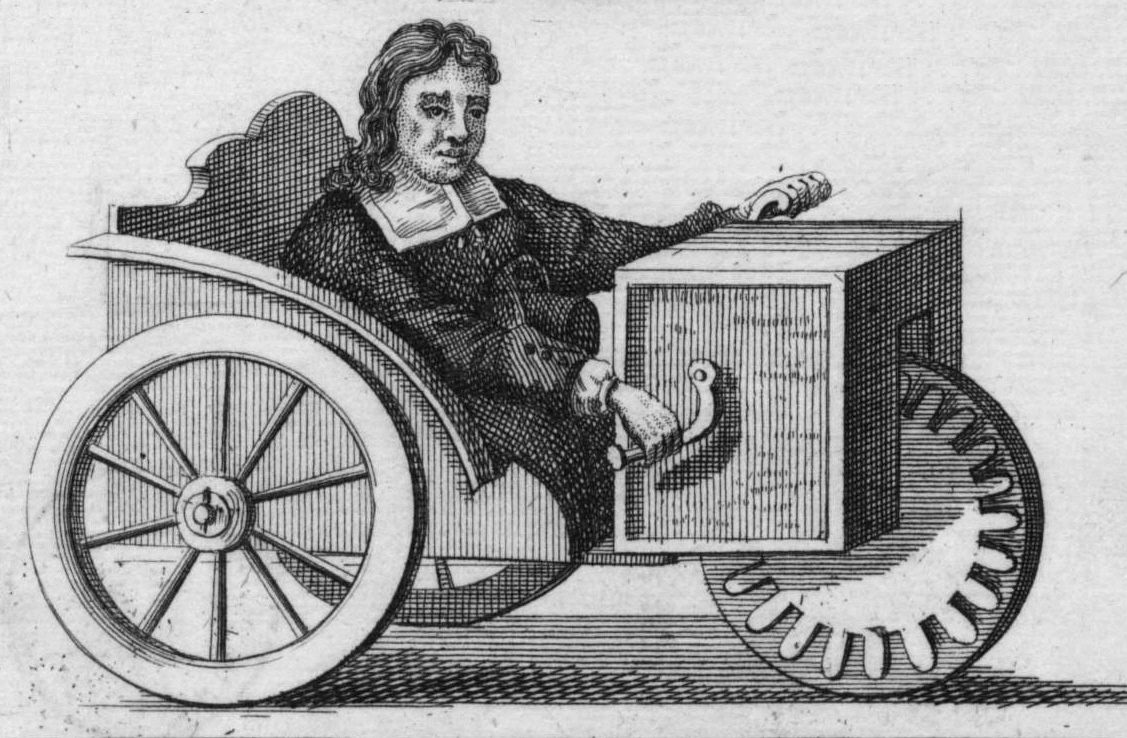
Steam Wagon
A steam wagon (or steam lorry, steam waggon or steamtruck) is a Steam power, steam-powered truck for carrying freight. It was the earliest form of lorry (truck) and came in two basic forms: ''overtype'' and ''undertype'', the distinction being the position of the steam engine, engine relative to the boiler. Manufacturers tended to concentrate on one form or the other. Steam wagons were a widespread form of powered road traction for commercial haulage in the early part of the twentieth century, although they were a largely British phenomenon, with few manufacturers outside Great Britain. Competition from internal-combustion engine, internal-combustion-powered vehicles and adverse legislation meant that few remained in commercial use beyond the Second World War. Although the majority of steam wagons have been scrapped, a significant number have been preserved in working order and may be seen in operation at steam fairs, particularly in the UK. Design features The steam wagon came ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot (26 February 1725 – 2 October 1804) was a French inventor who built the world's first full-size and working self-propelled mechanical land-vehicle, the "Fardier à vapeur" – effectively the world's first automobile. Background He was born in Void-Vacon, Lorraine, (now ' of Meuse), France. He trained as a military engineer. In 1765, he began experimenting with working models of steam-engine-powered vehicles for the French Army, intended for transporting cannons. First self-propelled vehicle French Army captain Cugnot was one of the first to successfully employ a device for converting the reciprocating motion of a steam piston into a rotary motion by means of a ratchet arrangement. A small version of his three-wheeled ''fardier à vapeur'' ("steam dray") was made and used in 1769 (a ''fardier'' was a massively built two-wheeled horse-drawn cart for transporting very heavy equipment, such as cannon barrels) In 1770, a full-size version of the ''f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Verbiest
Ferdinand Verbiest, (9 October 1623 – 28 January 1688) was a Flemish Jesuit missionary in China during the Qing dynasty. He was born in Pittem near Tielt in the County of Flanders (now part of Belgium). He is known as Nan Huairen () in Chinese. He was an accomplished mathematician and astronomer and proved to the court of the Kangxi Emperor that European astronomy was more accurate than Chinese astronomy. He then corrected the Chinese calendar and was later asked to rebuild and re-equip the Beijing Ancient Observatory, being given the roles of Head of the Mathematical Board and Director of the Observatory. He became close friends with the Kangxi Emperor, who frequently requested his instruction in geometry, philosophy and music. Verbiest worked as a diplomat, cartographer, and translator; he spoke Latin, German, Dutch, Spanish, Hebrew, Italian and Manchu. He wrote more than thirty books. During the 1670s, Verbiest designed what some claim to be the first ever self-propell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |