|
History Of Pizza
The history of pizza began in Ancient history, antiquity, as various ancient cultures produced flatbreads with several toppings. Pizza today is an Italian dish with a flat dough-based base and toppings, with significant Italian roots in history. A precursor of pizza was probably the focaccia, a flatbread known to the Romans as , to which toppings were then added. Modern pizza evolved from similar flatbread dishes in Naples, Italy, between the 16th and mid-18th century. The word ''pizza'' was first documented in 997 CE in GaetaSalvatore Riciniello (1987) ''Codice Diplomatico Gaetano'', Vol. I, La Poligrafica. and successively in different parts of Central Italy, central and Southern Italy, southern Italy. Furthermore, the '':it:Vocabolario etimologico della lingua italiana, Etymological Dictionary of the Italian Language'' explains the word ''pizza'' as coming from dialectal ''pinza'', 'clamp', as in modern Italian ''pinze'', 'pliers, pincers, tongs, forceps'. Their origin is fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece () was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity (), that comprised a loose collection of culturally and linguistically related city-states and communities. Prior to the Roman period, most of these regions were officially unified only once under the Kingdom of Macedon from 338 to 323 BC. In Western history, the era of classical antiquity was immediately followed by the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine period. Three centuries after the decline of Mycenaean Greece during the Bronze Age collapse, Greek urban poleis began to form in the 8th century BC, ushering in the Archaic period and the colonization of the Mediterranean Basin. This was followed by the age of Classical Greece, from the Greco-Persian Wars to the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC, and which included the Golden Age of Athens and the Peloponnesian War. The u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pita
Pita ( or ; ) or pitta (British English), also known as Arabic bread (, ), as Lebanese bread and as kmaj (from the Persian ''kumaj''), is a family of yeast- leavened round flatbreads baked from wheat flour, common in the Mediterranean, Levant, and neighboring areas. It includes the widely known version with an interior pocket. In the United Kingdom, the term is used for pocket versions such as the Greek pita, used for barbecue Barbecue or barbeque (often shortened to BBQ worldwide; barbie or barby in Australia and New Zealand) is a term used with significant regional and national variations to describe various cooking methods that employ live fire and smoke to coo ...s as a souvlaki wrap. The Western world, Western name ''pita'' may sometimes be used to refer to various other types of flatbreads that have different names in their local languages, such as numerous styles of Arab ''khubz'' (). Etymology The first mention of the word in English cited in the Oxford English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balearic Islands
The Balearic Islands are an archipelago in the western Mediterranean Sea, near the eastern coast of the Iberian Peninsula. The archipelago forms a Provinces of Spain, province and Autonomous communities of Spain, autonomous community of Spain, with Palma de Mallorca being its capital and largest city. Formerly part of the Kingdom of Majorca, Kingdom of Mallorca, the islands were made a province in the 19th century provincial division, which in 1983 received a Statute of Autonomy of the Balearic Islands, Statute of Autonomy. In its later reform of 2007, the Statute designates the Balearic Islands as one of the ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationalities'' of Spain. The official Languages of Spain, languages of the Balearic Islands are Catalan language, Catalan and Spanish language, Spanish. The archipelago islands are further grouped in western Pityusic Islands, Pytiuses (the largest being Ibiza and Formentera), and eastern Gymnesian Islands, Gymnesians (the largest bein ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Valencia
Valencia ( , ), officially València (), is a provinces of Spain, province of Spain, in the central part of the autonomous Valencian Community. Of the province's 2.7 million people (2024), almost one-third live in the capital, Valencia, which is also the capital of the autonomous community and the list of metropolitan areas in Spain, 3rd biggest city in Spain, with a metropolitan area of 2,522,383 people it is also one of the most populated cities of Southern Europe. There are 265 List of municipalities in Valencia, municipalities in the province. History Although the Spanish Constitution of 1812 loosely created the province of València, a stable administrative entity does not arise until the territorial division of Spain in 1833, remaining today without major changes. The Provincial Council of Valencia dates from that period. After the Valencian Statute of Autonomy of 1982, the province became part of the Valencian Community. Valencian language, Valencian and Spanish langua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationalities and regions of Spain, nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy of Catalonia of 2006, Statute of Autonomy. Most of its territory (except the Val d'Aran) is situated on the northeast of the Iberian Peninsula, to the south of the Pyrenees mountain range. Catalonia is administratively divided into four Provinces of Spain, provinces or eight Vegueries of Catalonia, ''vegueries'' (regions), which are in turn divided into 43 Comarques of Catalonia, ''comarques''. The capital and largest city, Barcelona, is the second-most populous Municipalities in Spain, municipality in Spain and the fifth-most populous List of metropolitan areas in Europe, urban area in the European Union. > > > ''Catalonia'' theoretically derived. During the Middle Ages, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine chroniclers claimed that ''Catalania'' derives from the local medley of Goths with Alans, initially constituting a ''Goth-Alania''. Othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coca (pastry)
The coca (), coc or fogassa, is a pastry typically made and consumed in Catalonia,Eliana Thibaut i Comalada, ''Les Coques Catalanes'', Proa, Barcelona 1995. the Aragonese Strip, most of Valencia, the Balearic Islands, Andorra and in French Catalonia. All around the Mediterranean there are similar typical dishes. Etymology The word ''coca''—plural ''coques''—comes from Dutch during the Carolingian Empire, and shares the same roots as the English "cake" and the German "Kuchen". Similarities There are many diverse cocas, with four main varieties: sweet, savoury, closed and open. All of them use dough as the main ingredient, which is then decorated. This dough can be sweet or savoury. If it is sweet, eggs and sugar are added, and if it is savoury, yeast and salt. As regards the topping or filling, fish and vegetables are usual at the coast whilst inland they prefer fruit, nuts, cheese and meat. Some cocas can be both sweet and savoury (typically mixing meat and frui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Levant
The Levant ( ) is the subregion that borders the Eastern Mediterranean, Eastern Mediterranean sea to the west, and forms the core of West Asia and the political term, Middle East, ''Middle East''. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is equivalent to Cyprus and a stretch of land bordering the Mediterranean Sea in Western AsiaGasiorowski, Mark (2016). ''The Government and Politics of the Middle East and North Africa''. p. 5: "... today the term ''Levantine'' can describe shared cultural products, such as Levantine cuisine or Levantine archaeology". .Steiner & Killebrew, p9: "The general limits ..., as defined here, begin at the Plain of 'Amuq in the north and extend south until the Wâdī al-Arish, along the northern coast of Sinai. ... The western coastline and the eastern deserts set the boundaries for the Levant ... The Euphrates and the area around Jebel el-Bishrī mark the eastern boundary of the northern Levant, as d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
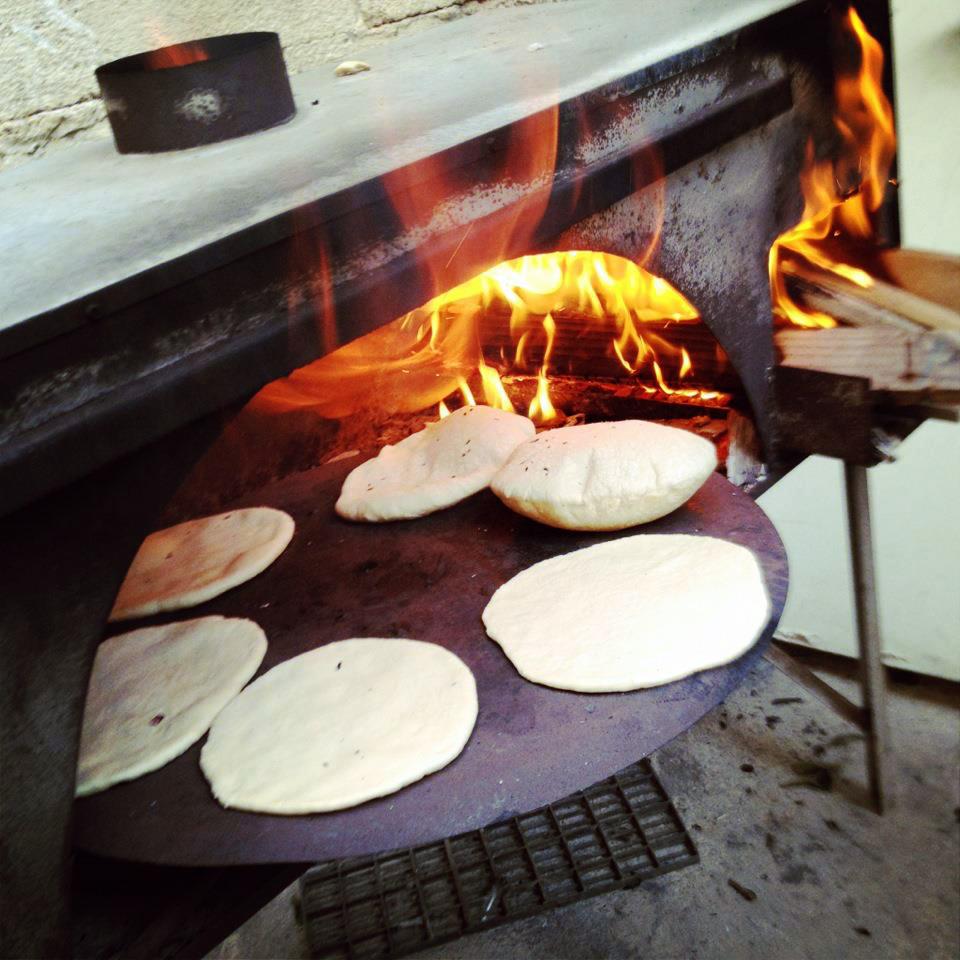
Manakish
Manakish (), or in singular form man'ousheh (), or other spellings, is a popular Lebanese food consisting of dough topped with za'atar, cheese, or ground meat. It can be sliced or folded, and it can be served either for breakfast or lunch. Traditionally, women would bake dough in a communal oven in the morning, to provide their family with their daily bread needs, and would prepare smaller portions of dough with different toppings for breakfast at this time. Manakish are popular across the Levant, and can also be found in neighboring regions, and centers of Levantine emigration. In 2023, manakish was inscribed to the UNESCO Intangible Cultural Heritage Lists as an emblematic culinary practice in Lebanon. Etymology The word ''manaqish'' is the plural of the Arabic word ''manqūshah'' (from the root verb ''naqasha'' 'to sculpt, carve out' or engrave), meaning that after the dough has been rolled flat, it is pressed by the fingertips to create little dips for the topping to li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization ( ) was an ancient civilization created by the Etruscans, a people who inhabited Etruria in List of ancient peoples of Italy, ancient Italy, with a common language and culture, and formed a federation of city-states. After adjacent lands had been conquered its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughly what is now Tuscany, western Umbria and northern Lazio, as well as what are now the Po Valley, Emilia-Romagna, south-eastern Lombardy, southern Veneto and western Campania. A large body of literature has flourished on the origins of the Etruscans, but the consensus among modern scholars is that the Etruscans were an indigenous population. The earliest evidence of a culture that is identifiably Etruscan dates from about 900 BC. This is the period of the Iron Age Villanovan culture, considered to be the earliest phase of Etruscan civilization, which itself developed from the previous late Bronze Age Proto-Villanovan culture in the same region, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moretum And Roman Bread (14971169175)
Moretum is an herb cheese spread that the Ancient Romans ate with bread. A typical moretum was made of herbs, cheese (typically ricotta), salt, oil, and vinegar. Optionally, different kinds of nuts could be added. The ingredients were crushed together in a mortar, for which the dish is named. Recipes A recipe for Moretum was handed down in a Latin poem of 122 dactylic hexameters attributed to Virgil under the title ''Moretum'' in the so-called ''Appendix Vergiliana''. It describes, as a parody of the exaggerated praise of rural life how a simple farmer begins his day's work; the centrepiece is the preparation of moretum for breakfast. Moretum is also mentioned in Columella's ''De re rustica'' (XII 59, 1-4). In it, Columella mentions a variant in which walnuts are used instead of cheese, as well as alternatives with roasted sesame seeds, with pine nuts or almond kernels, as well as mixtures with dried herbs. The variant with pine nuts is considered to be a precursor of pesto. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pompeii
Pompeii ( ; ) was a city in what is now the municipality of Pompei, near Naples, in the Campania region of Italy. Along with Herculaneum, Stabiae, and Villa Boscoreale, many surrounding villas, the city was buried under of volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD. Largely preserved under the ash, Pompeii offers a unique snapshot of Culture of ancient Rome, Roman life, frozen at the moment it was buried, as well as insight into ancient urban planning. It was a wealthy town of 10,000 to 20,000 residents at the time it was destroyed. It hosted many fine public buildings and luxurious private houses with lavish decorations, furnishings and artworks, which were the main attractions for early excavators; subsequent excavations have found hundreds of private homes and businesses reflecting various architectural styles and social classes, as well as numerous public buildings. Organic remains, including wooden objects and human bodies, were interred in the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |