|
History Of Malaysia
Malaysia is a modern concept, created in the second half of the 20th century. However, contemporary Malaysia regards the entire history of Malaya and Borneo, spanning thousands of years back to prehistoric times, as its own history. Significant events in Malaysia's modern history include the formation of the federation, the separation of Singapore, the racial riots, Mahathir Mohamad's era of industrialisation and privatisation, and the nation's political upheavals of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. The first evidence of archaic human occupation in the region dates back at least 1.83 million years, while the earliest remnants of anatomically modern humans are approximately 40,000 years old. The ancestors of the present-day population of Malaysia entered the area in multiple waves during prehistoric and historical times. Hinduism and Buddhism from India and China dominated early regional history, reaching their peak from the 7th to the 13th centuries during the reign of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KITLV - 105898 - Lambert & Co
The KITLV/Royal Netherlands Institute of Southeast Asian and Caribbean Studies (, abbreviated as KITLV) at Leiden was founded in 1851. Its objective is the advancement of the study of the anthropology, linguistics, social sciences, and history of Southeast Asia, the Pacific Area, and the Caribbean. Special emphasis is laid on the former Dutch colonies of the Dutch East Indies (now Indonesia), Suriname, and the Dutch West Indies (the Netherlands Antilles and Aruba). Its unique collection of books, manuscripts, prints and photographs attracts visiting scholars from all over the world. On July 1, 2014, the management of the collection was taken over by Leiden University Libraries. Jakarta In 1969, a KITLV office was started by Hans Ras in Jakarta ("KITLV-Jakarta"), as a part of an agreement with the Indonesian Institute of Sciences. Here, publications from Indonesia, Malaysia and Singapore are bought and given a place in the library of the institute, publications of the institute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sultanate Of Malacca
The Malacca Sultanate (; Jawi script: ) was a Malays (ethnic group), Malay sultanate based in the modern-day state of Malacca, Malaysia. Conventional historical thesis marks as the founding year of the sultanate by King of Singapura, Parameswara of Malacca, Parameswara, also known as Iskandar Shah, although earlier dates for its founding have been proposed. At the height of the sultanate's power in the 15th century, its capital grew into one of the most important entrepôt, transshipment ports of its time, with territory covering much of the Malay Peninsula, the Riau Islands and part of the central eastern coast of Sumatra in present-day Indonesia. As a bustling international trading port, Malacca emerged as a centre for Islamic learning and dissemination, and encouraged the development of the Malay language, Malaysian literature, literature and arts. It heralded the Golden Age, golden age of Malay sultanates in the archipelago, in which Classical Malay became the ''lingua fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania, between the Indian Ocean, Indian and Pacific Ocean, Pacific oceans. Comprising over List of islands of Indonesia, 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guinea, Indonesia is the world's largest archipelagic state and the List of countries and dependencies by area, 14th-largest country by area, at . With over 280 million people, Indonesia is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fourth-most-populous country and the most populous Islam by country, Muslim-majority country. Java, the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, is home to more than half of the country's population. Indonesia operates as a Presidential system, presidential republic with an elected People's Consultative Assembly, legislature and consists of Provinces of Indonesia, 38 provinces, nine of which have Autonomous administrative divisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
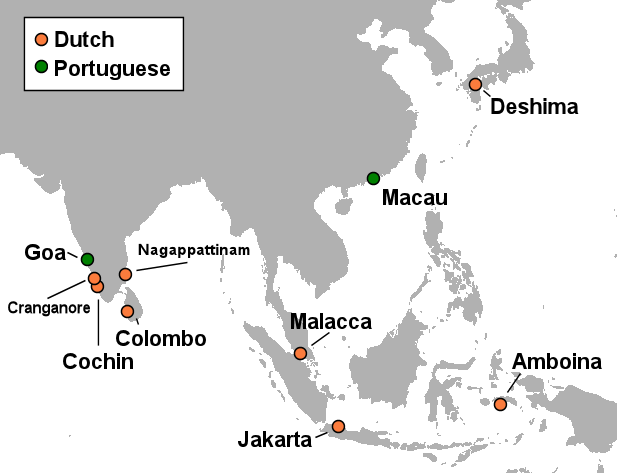
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies (; ), was a Dutch Empire, Dutch colony with territory mostly comprising the modern state of Indonesia, which Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, declared independence on 17 August 1945. Following the Indonesian National Revolution, Indonesian War of Independence, Indonesia and the Netherlands Dutch–Indonesian Round Table Conference, made peace in 1949. In the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, the Dutch ceded the governorate of Dutch Malacca to Britain, leading to its eventual incorporation into Malacca, Malacca (state) of modern Malaysia. The Dutch East Indies was formed from the nationalised Factory (trading post), trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Batavian Republic, Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch fought Royal Netherlands East Indies Army, many wars against indigenous rulers and peoples, which caused hundreds of thousands of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British Empire, British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. Unlike the term "British Raj, British India", which excludes the Indian princely states, British Malaya is often used to refer to the Federated Malay States, Federated and the Unfederated Malay States, which were British protectorates with their own local rulers, as well as the Straits Settlements, which were under the sovereignty and direct rule of the British Crown, after a period of control by the East India Company. Before the formation of the Malayan Union in 1946, the territories were not placed under a single unified administration, with the exception of the immediate post-war period when a British military officer became the temporary administrator of Malaya. Instead, British Malaya comprised the Straits Settlements, the Federated Malay State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anglo-Dutch Treaty Of 1824
The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, also known as the Treaty of London (), was a treaty signed between the United Kingdom and the Netherlands in London on 17 March 1824. The treaty was to resolve disputes arising from the execution of the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814. For the Dutch, it was signed by Hendrik Fagel and Anton Reinhard Falck, and for the British, George Canning and Charles Williams-Wynn (1775–1850), Charles Williams-Wynn. History The Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1824, designed to solve issues arising from British occupation of Dutch colonial possessions during the Napoleonic Wars, as well as trading rights existing for hundreds of years in the Spice Islands between the two nations, addressed a wide array of issues but did not clearly describe limitations of expansion by either side in maritime Southeast Asia. The Founding years of modern Singapore, British establishment of Singapore on the Malay Peninsula in 1819 by Sir Stamford Raffles exacerbated tensions between the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Empire
The British Empire comprised the dominions, Crown colony, colonies, protectorates, League of Nations mandate, mandates, and other Dependent territory, territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the English overseas possessions, overseas possessions and trading posts established by Kingdom of England, England in the late 16th and early 17th centuries, and colonisation attempts by Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland during the 17th century. At its height in the 19th and early 20th centuries, it became the List of largest empires, largest empire in history and, for a century, was the foremost global power. By 1913, the British Empire held sway over 412 million people, of the world population at the time, and by 1920, it covered , of the Earth's total land area. As a result, Westminster system, its constitutional, Common law, legal, English language, linguistic, and Culture of the United Kingdom, cultural legacy is widespread. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Malacca (1641)
The siege of Malacca (3 August 1640 – 14 January 1641) was initiated by the Dutch East India Company and their local ally, Johor, against Portuguese Malacca. It ended with a Portuguese surrender and, according to Portugal, the deaths of thousands of Portuguese individuals. The roots of the conflict began in the late 16th century when the Dutch arrived in the vicinity of Malacca. From there, they launched occasional attacks against the Portuguese colony, including multiple failed sieges. In August 1640, the Dutch commenced their final siege, which took a heavy toll on both sides, with disease and starvation rampant. Finally, after the loss of several major commanders and numerous troops, the Dutch stormed the citadel, completely ending Portugal's control of the city. Ultimately, the new colony was of little importance to the Dutch compared to their previously existing local territory, Batavia. Background Malacca, established by the Malays in the 1400s, was a significant hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:Category:Sultanates In Malaysia
* in — current and sultanates based in territory of present-day Malaysia. {{portal, Malaysia Feudalism in Malaysia Former countries in Malaysian history Monarchies of Malaysia Malaysia Malaysia is a country in Southeast Asia. Featuring the Tanjung Piai, southernmost point of continental Eurasia, it is a federation, federal constitutional monarchy consisting of States and federal territories of Malaysia, 13 states and thre ... Subdivisions of Malaysia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Colonial Empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Dutch East India Company (1602–1799) and Dutch West India Company (1621–1792)—and subsequently governed by the Dutch Republic (1581–1795) and modern Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1975). Following the ''de facto'' independence of the Dutch Republic from the Spanish Empire in the late 16th century, various trading companies known as '' voorcompagnie'' led maritime expeditions overseas in search of commercial opportunities. By 1600, Dutch traders and mariners had penetrated the lucrative Asian spice trade but lacked the capital or manpower to secure or expand their ventures; this prompted the States General in 1602 to consolidate several trading enterprises into the semi-state-owned Dutch East India Company (, VOC), which was gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perak Sultanate
The Sultan of Perak (, Jawi: ) is the constitutional monarch and head of state of the Malaysian state of Perak. It is one of the oldest hereditary seats among the Malay states. The current Sultan of Perak, Sultan Nazrin Muizzuddin Shah, has been in office since 29 May 2014. When the Malacca Sultanate fell to Portugal in 1511, Sultan Mahmud Shah retreated to Kampar, Sumatra, and died there in 1528. He left behind two princes, Alauddin Riayat Shah II and Muzaffar Shah. The former established the Sultanate of Johor. Muzaffar Shah was invited to rule Perak, of which he became the first sultan. Line of succession to the Perak throne In contrast to the other Malay sultanates, the ruling dynasty of Perak utilises a somewhat complex order of succession. The reigning sultan appoints princes in the male line of descent from a sultan to certain high princely titles. They are arranged in an order of precedence indicating the order of succession to the throne. As per ruling of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johor Sultanate
The Johor Sultanate ( or ; also called the Sultanate of Johor, Johor-Pahang-Riau-Lingga, or the Johor Empire) was founded by Sultan of Malacca Mahmud Shah of Malacca, Mahmud Shah's son, Alauddin Riayat Shah II of Johor, Alauddin Riayat Shah II in 1528. Prior to being a sultanate of its own right, Johor had been part of the Malacca Sultanate, Malaccan Sultanate before the Portuguese Empire, Portuguese Capture of Malacca (1511), captured its capital in 1511. At its height, the sultanate controlled territory in what is now modern-day Johor, Pahang, Terengganu, territories stretching from the rivers of Klang River, Klang to the Linggi River, Linggi and Tanjung Tuan, situated respectively in Selangor, Negeri Sembilan and Malacca (as an exclave), Singapore, Pulau Tinggi and other islands off the east coast of the Malay Peninsula, the Karimun Regency, Karimun Islands, the islands of Bintan, Bulang, Lingga Islands, Lingga and Bunguran Islands, Bunguran, and Bengkalis, Kampar Regency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |