|
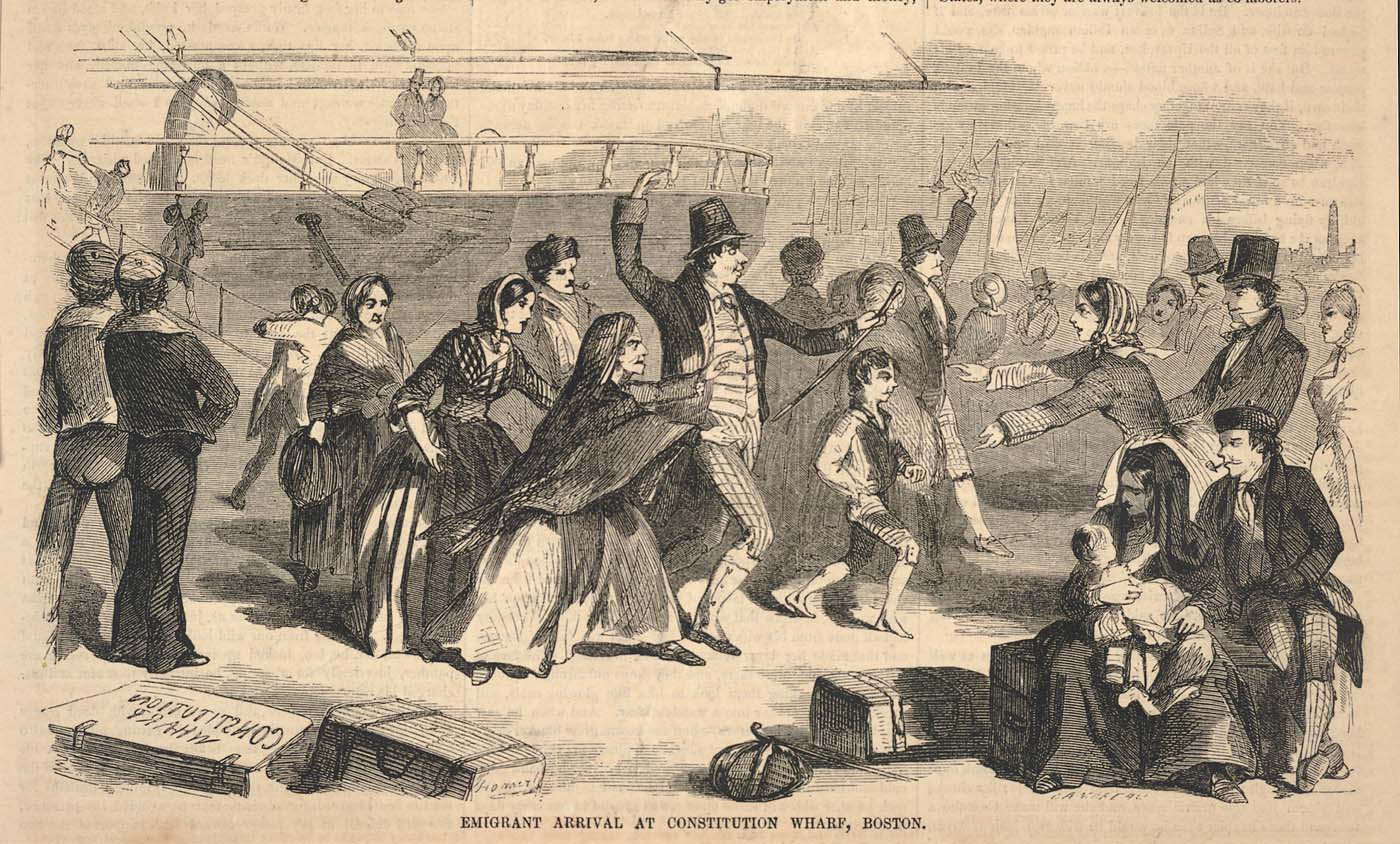
History Of Irish Americans In Boston
People of Irish descent form the largest single ethnic group in Massachusetts, and one of the largest in Boston. Once a Puritan stronghold, Boston changed dramatically in the 19th century with the arrival of immigrants from other parts of the world. The Irish dominated the first wave of newcomers during this period, especially following the Great Irish Famine. Their arrival transformed Boston from an Anglo-Saxon, Protestant city into one that has become progressively more diverse. These people hired Irish as workers and servants, but there was little social interaction. In the 1840s and 50s, the anti-Catholic, anti-immigrant Know Nothing movement targeted Irish Catholics in Boston. In the 1860s, many Irish immigrants fought for the Union in the American Civil War, a display of patriotism that helped to dispel much of the prejudice against them. With an expanding population, group loyalty, and block-by-block political organization, the Irish took political control of the city, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ann Glover
Goody Ann Glover (died November 16, 1688) was an Irish former indentured servant and the last person to be hanged in Boston as a witch, although the Salem witch trials in nearby Salem, Massachusetts, occurred mainly in 1692. Early life and accounts The trial of Ann Glover cannot be found in official records perhaps because it occurred during the brief and controversial Dominion of New England under the royally appointed governor Edmund Andros. There are four primary contemporary sources for the accusations against Glover and her execution: * 1 - Cotton Mather's ''Memorable Providences'' (1689) Mather's book is the most extensive treatment of the trial and includes a " Notandum" at the end written after the execution of Glover and Mather reports that the children Glover had supposedly bewitched continued to suffer "renewal of their afflictions." But Mather concludes that the meaning of this is "not to disappoint our expectations of their deliverance, but for the ''detection' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
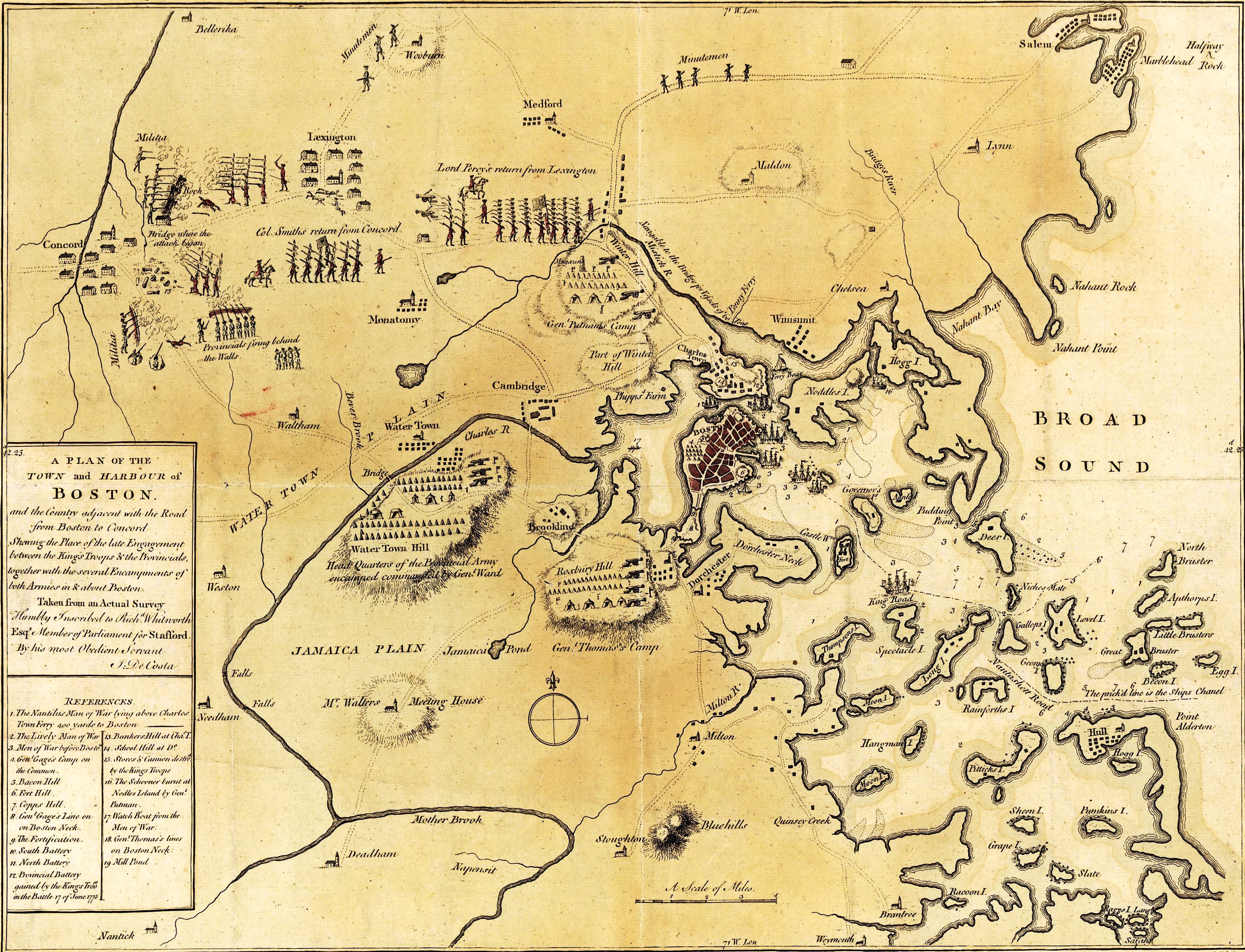
Battle Of Bunker Hill
The Battle of Bunker Hill was fought on June 17, 1775, during the Siege of Boston in the first stage of the American Revolutionary War. The battle is named after Bunker Hill in Charlestown, Boston, Charlestown, Massachusetts, which was peripherally involved. It was the original objective of both the colonial and British troops, though the majority of combat took place on the adjacent hill, which became known as Breed's Hill. On June 13, 1775, the leaders of the colonial forces besieging Boston learned that the British were planning to send troops out from the city to fortify the unoccupied hills surrounding the city, which would give them control of Boston Harbor. In response, 1,200 colonial troops under the command of William Prescott stealthily occupied Bunker Hill and Breed's Hill. They constructed a strong redoubt on Breed's Hill overnight, as well as smaller fortified lines across the Charlestown Peninsula. By daybreak of June 17, the British became aware of the presen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was the armed conflict that comprised the final eight years of the broader American Revolution, in which American Patriot (American Revolution), Patriot forces organized as the Continental Army and commanded by George Washington defeated the British Army during the American Revolutionary War, British Army. The conflict was fought in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. The war's outcome seemed uncertain for most of the war. However, Washington and the Continental Army's decisive victory in the Siege of Yorktown in 1781 led King George III and the Kingdom of Great Britain to negotiate an end to the war in the Treaty of Paris (1783), Treaty of Paris two years later, in 1783, in which the British monarchy acknowledged the independence of the Thirteen Colonies, leading to the establishment of the United States as an independent and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thirteen Colonies
The Thirteen Colonies were the British colonies on the Atlantic coast of North America which broke away from the British Crown in the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783), and joined to form the United States of America. The Thirteen Colonies in their traditional groupings were: the New England Colonies (New Hampshire, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut); the Middle Colonies ( New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware); and the Southern Colonies (Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia). These colonies were part of British America, which also included territory in The Floridas, the Caribbean, and what is today Canada. The Thirteen Colonies were separately administered under the Crown, but had similar political, constitutional, and legal systems, and each was dominated by Protestant English-speakers. The first of the colonies, Virginia, was established at Jamestown, in 1607. Maryland, Pennsylvania, and the New England Colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charitable Irish Society Of Boston
The Charitable Irish Society of Boston was founded in 1737 and is the oldest Irish organization in North America. Its early charitable efforts focused around providing temporary loans and assistance in finding work to Irish immigrants. The society was incorporated in 1809 and established a constitution in 1810. Involvement in the first St. Patrick's Day The society organized the first observance of St. Patrick's Day in the Thirteen Colonies. Surprisingly, the celebration was not Catholic in nature, Irish immigration to the colonies having been dominated by Protestants. The society's purpose in gathering was simply to honour its homeland, and although they continued to meet annually to coordinate charitable works for the Irish community in Boston, they did not meet on 17 March again until 1794. During the observance of the day, individuals attended a service of worship and a special dinner. The list of members names are available here Despite being protestant a large amount have I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Irish Slaves Myth
The Irish slaves myth is a fringe pseudohistorical narrative that conflates the penal transportation and indentured servitude of Irish people during the 17th and 18th centuries, with the hereditary chattel slavery experienced by the forebears of the African diaspora. Some white nationalists, and others who want to minimize the effects of hereditary chattel slavery on Africans and their descendants, have used this false equivalence to deny racism against African Americans or claim that African Americans are too vocal in seeking justice for historical grievances. It also can hide the facts around Irish involvement in the transatlantic slave trade. The myth has been in circulation since at least the 1990s and has been disseminated in online memes and social media debates. According to historians Jerome S. Handler and Matthew C. Reilly, "it is misleading, if not erroneous, to apply the term 'slave' to Irish and other indentured servants in early Barbados". In 2016, academi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Boston News-Letter
''The Boston News-Letter'', first published on April 24, 1704, is regarded as the first continuously published newspaper in the colony of Massachusetts. It was heavily subsidized by the British government, with a limited circulation. All copies were approved by the Royal governor before publication. The colonies’ first newspaper was '' Publick Occurrences Both Forreign and Domestick'', which published its first and only issue on September 25, 1690. The '' Weekly Jamaica Courant'' followed in Kingston, Jamaica from 1718. In 1726 the '' Boston Gazette'' began publishing with Bartholomew Green, Jr., as printer. History The ''News-Letter''’s first editor was John Campbell, a bookseller and postmaster of Boston. Campbell had been actively writing and sending "newsletters" of European occurrences to New England governors for a year or more and thought it would save trouble to print them for all. The ''News-Letter'' was originally issued weekly as a half sheet, a single page print ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Derry, New Hampshire
Derry is a town in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 34,317 at the 2020 census. Although it is a town and not a city, Derry is the most populous community in Rockingham County and the 4th most populous in the state. The town's nickname, "Spacetown", derives from the fact that Derry is the birthplace of Alan Shepard, the first astronaut from the United States in space. Derry was also for a time the home of the poet Robert Frost and his family. The Derry census-designated place, with a 2020 population of 22,879, occupies the central part of the town, extending from Derry's downtown in the west to the town of Hampstead in the east. The town also includes the village of East Derry. History The area was first settled by Scots-Irish families in 1719 as part of the town of Londonderry, as were present-day Windham and portions of Manchester, Salem and Hudson. The town of Derry was formed in 1827 from the eastern portion of Londonderry and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Londonderry, New Hampshire
Londonderry is a town in western Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. It sits between Manchester and Derry, the largest and fourth-largest communities in the state. The population was 25,826 at the 2020 census. Londonderry is known for its apple orchards and is home to the headquarters of Stonyfield Farm and part of Manchester–Boston Regional Airport. The more densely settled portion of town, where 11,645 people lived at the 2020 census, is defined as the Londonderry census-designated place (CDP) and roughly occupies the southeastern and southern parts of town, around New Hampshire Route 102. History Early history Londonderry lies in an area that was first known as "Nutfield" because of the dense woods with nut trees. A petition for the town was submitted to the General Court of the Province of New Hampshire on September 23, 1719. That petition stated that the petitioners had settled "at Nutfield about the Eleventh of Aprile last"—i.e. April 11, 1719. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Belfast, Maine
Belfast is a city in Waldo County, Maine, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the city population was 6,938. Located at the mouth of the Passagassawakeag River estuary on Belfast Bay (Maine), Belfast Bay and Penobscot Bay. Belfast is the county seat of Waldo County. Its Port, seaport has a wealth of historic architecture in several historic districts, and remains popular with tourists. History The area was once territory of the Penobscot people, Penobscot tribe of the Abenaki people, Abenaki people, which each summer visited the seashore to hunt for fish, shellfish and seafowl. In 1630, it became part of the Muscongus Patent, which granted rights for English trading posts with the Indigenous peoples of the Americas, Native Americans, especially for the lucrative fur trading, fur trade. About 1720, General Samuel Waldo of Boston, Massachusetts, Boston bought the Muscongus Patent, which had evolved into outright ownership of the land, and was there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |