|
Historic Villages Of Shirakawa-gō And Gokayama
The Historic Villages of Shirakawa-gō and Gokayama are one of Japan's UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The cultural property consists of three historic mountain villages over an area of in the remote Shogawa river valley, stretching across the border of Gifu Prefecture, Gifu and Toyama Prefectures in central Japan. Shirakawa-gō (白川郷, "White River Old-District") is located in the village of Shirakawa, Gifu (village), Shirakawa in Gifu Prefecture. The Gokayama (五箇山, "Five Mountains") area is divided between the former villages of Kamitaira and Taira in Nanto, Toyama, Nanto, Toyama Prefecture. The valley is in a mountain region with considerable snowfall, and these villages are well known for their clusters of farmhouses, constructed in the architectural style known as minka, gasshō-zukuri (合掌造り), which are designed to easily shed snow from their steep roofs. Geography The three villages are situated in a remote valley, surrounded by high and rugged mountains wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirakawa, Gifu (village)
is a village located in Ōno District, Gifu Prefecture, Japan. It is best known for being the site of Shirakawa-gō, a small, traditional village showcasing a building style known as '' gasshō-zukuri''. Together with Gokayama in Nanto, Toyama, it is one of UNESCO's World Heritage Sites. , the village had an estimated population of 1,630 in 588 households and a population density of 4.6 persons per km2. The total area of the village was . Geography Shirakawa is a mountain village located in far northern Gifu Prefecture, bordering Ishikawa Prefecture and Toyama Prefecture on the Ryōhaku Mountains. Mount Hakusan is the highest elevation at . The village's area is 95.7% mountainous forests, and its steep places are characteristic. In between the mountains flows the Shō River, which continues to the north into Nanto, Toyama. Most of the population is in its river valley. Since the opening of Hida Tunnel, Shirakawa can be reached within 50 minutes from Takayama, Gifu comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buckwheat
Buckwheat (''Fagopyrum esculentum'') or common buckwheat is a flowering plant in the knotweed family Polygonaceae cultivated for its grain-like seeds and as a cover crop. Buckwheat originated around the 6th millennium BCE in the region of what is now Yunnan, Yunnan Province in southwestern China. The name "buckwheat" is used for several other species, such as ''Fagopyrum tataricum'', a domesticated food plant raised in Asia. Despite its name, buckwheat is not closely related to wheat. Buckwheat is not a cereal, nor is it a member of the Poaceae, grass family. It is related to sorrel, Polygonum, knotweed, and rhubarb. Buckwheat is considered a pseudocereal because the high starch content of the seeds enables buckwheat to be cooked and consumed like a cereal. Etymology The name "buckwheat" or "beech wheat" comes from its tetrahedral seeds, which resemble the much larger seeds of the beech nut from the beech, beech tree, and the fact that it is used like wheat. The word may be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Period
The , also known as the , is the period between 1600 or 1603 and 1868 in the history of Japan, when the country was under the rule of the Tokugawa shogunate and some 300 regional ''daimyo'', or feudal lords. Emerging from the chaos of the Sengoku period, the Edo period was characterized by prolonged peace and stability, urbanization and economic growth, strict social order, Isolationism, isolationist foreign policies, and popular enjoyment of Japanese art, arts and Culture of Japan, culture. In 1600, Tokugawa Ieyasu prevailed at the Battle of Sekigahara and established hegemony over most of Japan, and in 1603 was given the title ''shogun'' by Emperor Go-Yōzei. Ieyasu resigned two years later in favor of his son Tokugawa Hidetada, Hidetada, but maintained power, and defeated the primary rival to his authority, Toyotomi Hideyori, at the Siege of Osaka in 1615 before his death the next year. Peace generally prevailed from this point on, making samurai largely redundant. Tokugawa sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ogimachi Village-02
{{disambig ...
Ogimachi may refer to: *Emperor Ōgimachi, the 106th Emperor of Japan *Ōgimachi Station (Osaka), a station of the Sakaisuji Line of Osaka Municipal Subway *Ōgimachi Station (Kanagawa), a station of the JR Tsurumi Line *Ogimachi Village, included in Historic Villages of Shirakawa-gō and Gokayama The Historic Villages of Shirakawa-gō and Gokayama are one of Japan's UNESCO World Heritage Sites. The cultural property consists of three historic mountain villages over an area of in the remote Shogawa river valley, stretching across the borde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potassium Nitrate
Potassium nitrate is a chemical compound with a sharp, salty, bitter taste and the chemical formula . It is a potassium salt of nitric acid. This salt consists of potassium cations and nitrate anions , and is therefore an alkali metal nitrate. It occurs in nature as a mineral, niter (or ''nitre'' outside the United States). It is a source of nitrogen, and nitrogen was named after niter. Potassium nitrate is one of several nitrogen-containing compounds collectively referred to as saltpetre (or saltpeter in the United States). Major uses of potassium nitrate are in fertilizers, tree stump removal, rocket propellants and fireworks. It is one of the major constituents of traditional gunpowder (black powder). In processed meats, potassium nitrate reacts with hemoglobin and myoglobin generating a red color. Etymology Nitre, or potassium nitrate, because of its early and global use and production, has many names. As for nitrate, Egyptian and Hebrew words for it had the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
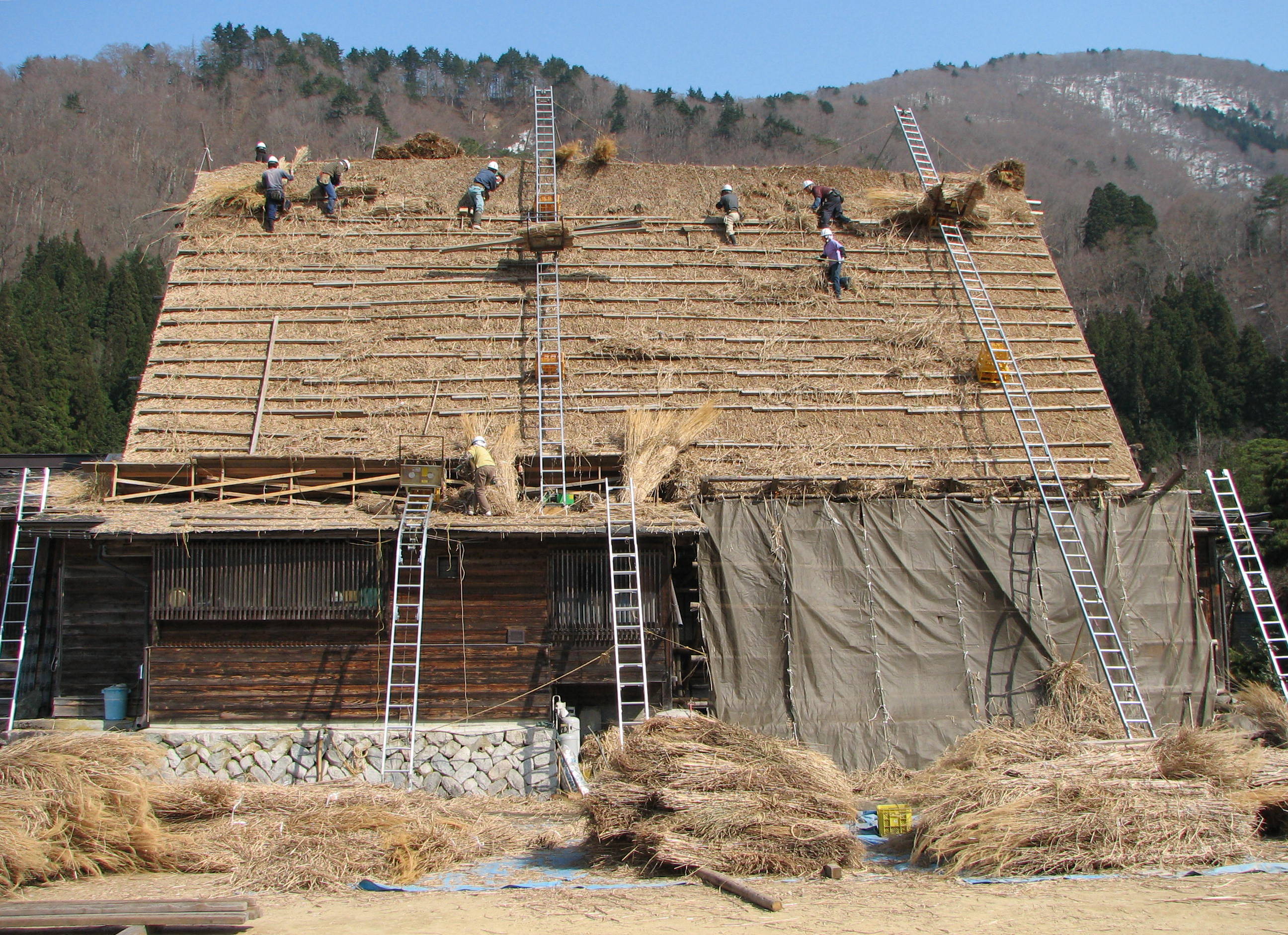
Thatching
Thatching is the craft of building a roof with dry vegetation such as straw, water reed, sedge ('' Cladium mariscus''), rushes, heather, or palm branches, layering the vegetation so as to shed water away from the inner roof. Since the bulk of the vegetation stays dry and is densely packed—trapping air—thatching also functions as insulation. It is a very old roofing method and has been used in both tropical and temperate climates. Thatch is still employed by builders in developing countries, usually with low-cost local vegetation. By contrast, in some developed countries it is the choice of some affluent people who desire a rustic look for their home, would like a more ecologically friendly roof, or who have purchased an originally thatched abode. History Thatching methods have traditionally been passed down from generation to generation and numerous descriptions of the materials and methods used in Europe over the past three centuries survive in archives and early publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gassho-zukuri Farmhouse-03
are Vernacular architecture, vernacular houses constructed in any one of several traditional Japanese architecture, Japanese building styles. In the context of the four divisions of society, were the dwellings of farmers, artisans, and merchants (i.e., the three non-samurai castes).Nishi & Hozumi (1996), p82 This connotation no longer exists in the modern Japanese language, and any traditional Japanese-style residence of appropriate age could be referred to as . are characterized by their basic structure, their roof structure, and their roof shape. developed through history with distinctive styles emerging in the Edo period. Types come in a wide range of styles and sizes, largely as a result of differing geographic and climatic conditions as well as the lifestyle of the inhabitants. They generally fall into one of four classifications: farmhouses town houses , fishermen's dwellings and mountain dwellings . Unlike other forms of Japanese architecture (such as those of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gassho-zukuri Farmhouse-02
are vernacular houses constructed in any one of several traditional Japanese building styles. In the context of the four divisions of society, were the dwellings of farmers, artisans, and merchants (i.e., the three non-samurai castes).Nishi & Hozumi (1996), p82 This connotation no longer exists in the modern Japanese language, and any traditional Japanese-style residence of appropriate age could be referred to as . are characterized by their basic structure, their roof structure, and their roof shape. developed through history with distinctive styles emerging in the Edo period. Types come in a wide range of styles and sizes, largely as a result of differing geographic and climatic conditions as well as the lifestyle of the inhabitants. They generally fall into one of four classifications: farmhouses town houses , fishermen's dwellings and mountain dwellings . Unlike other forms of Japanese architecture (such as those of the style), it is the structure rather than t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
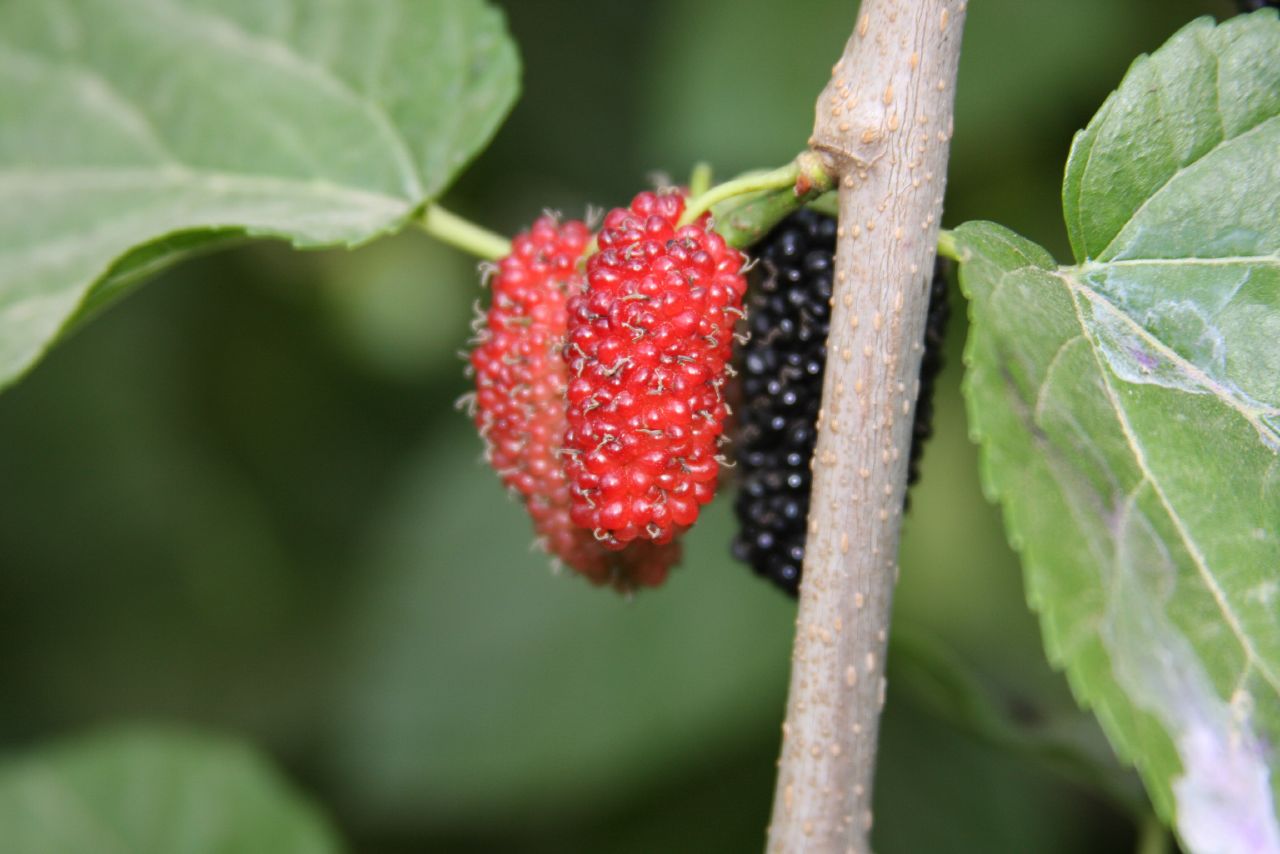
Mulberry
''Morus'', a genus of flowering plants in the family Moraceae, consists of 19 species of deciduous trees commonly known as mulberries, growing wild and under cultivation in many temperate world regions. Generally, the genus has 64 subordinate taxa, though the three most common are referred to as white, red, and black, originating from the color of their dormant buds and not necessarily the fruit color (''Morus alba'', '' M. rubra'', and '' M. nigra'', respectively), with numerous cultivars and some taxa currently unchecked and awaiting taxonomic scrutiny. ''M. alba'' is native to South Asia, but is widely distributed across Europe, Southern Africa, South America, and North America. ''M. alba'' is also the species most preferred by the silkworm. It is regarded as an invasive species in Brazil, the United States and some states of Australia. The closely related genus '' Broussonetia'' is also commonly known as mulberry, notably the paper mulberry (''Brouss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silkworm
''Bombyx mori'', commonly known as the domestic silk moth, is a moth species belonging to the family Bombycidae. It is the closest relative of '' Bombyx mandarina'', the wild silk moth. Silkworms are the larvae of silk moths. The silkworm is of particular economic value, being a primary producer of silk. The silkworm's preferred food are the leaves of white mulberry, though they may eat other species of mulberry, and even leaves of other plants like the Osage orange. Domestic silk moths are entirely dependent on humans for reproduction, as a result of millennia of selective breeding. Wild silk moths, which are other species of ''Bombyx'', are not as commercially viable in the production of silk. Sericulture, the practice of breeding silkworms for the production of raw silk, has existed for at least 5,000 years in China, whence it spread to India, Korea, Nepal, Japan, and then the West. The conventional process of sericulture kills the silkworm in the pupal stage. The domestic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sericulture
Sericulture, or silk farming, is the cultivation of silkworms to produce silk. Although there are several commercial species of silkworms, the caterpillar of the Bombyx mori, domestic silkmoth is the most widely used and intensively studied silkworm. This species of silkmoth is no longer found in the wild as they have been modified through selective breeding, rendering most flightless and without defense against predators. Silk is believed to have first been produced in China as early as the Neolithic period. Sericulture has become an important Putting-out system#Cottage industry, cottage industry in countries such as Brazil, China, France, India, Italy, Japan, Korea, Russia, and Thailand. Today, China and India are the two main producers, with more than 60% of the world's annual production. History According to Confucius, Confucian text, the discovery of silk production dates to about 2700 BCE, although archaeological records point to silk cultivation as early as the Yangshao ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |