|
Hexactinellid
Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed siliceous spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually classified along with other sponges in the phylum Porifera, but some researchers consider them sufficiently distinct to deserve their own phylum, Symplasma. Some experts believe that glass sponges are the longest-lived animals on earth; these scientists tentatively estimate a maximum age of up to 15,000 years. Biology Glass sponges are relatively uncommon and are mostly found at depths from below sea level. Although the species '' Oopsacas minuta'' has been found in shallow water, others have been found much deeper. They are found in all oceans of the world, although they are particularly common in Antarctic and Northern Pacific waters. They are more-or-less cup-shaped animals, ranging from in height, with sturdy skeletons made of glass-like silica spicules, fused to form a lattice. In some glass sponges such as member ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
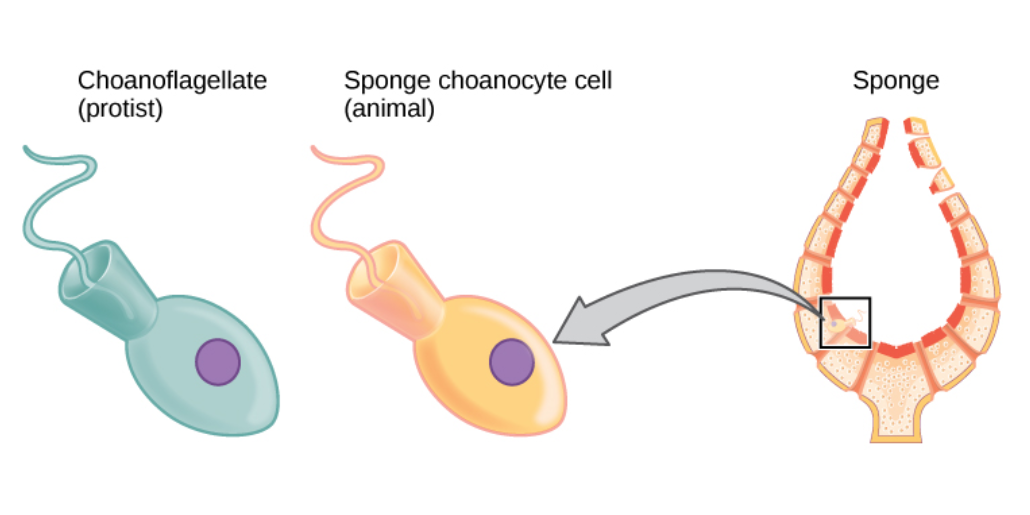
Sponge
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a basal clade and a sister taxon of the diploblasts. They are sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes, usually via flagella movements of the so-called " collar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porifera
Sponges or sea sponges are primarily marine invertebrates of the animal phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), a Basal (phylogenetics) , basal clade and a sister taxon of the Eumetazoa , diploblasts. They are sessility (motility) , sessile filter feeders that are bound to the seabed, and are one of the most ancient members of macrobenthos, with many historical species being important sponge reef , reef-building organisms. Sponges are multicellular organisms consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cell (biology) , cells, and usually have tube-like bodies full of pores and channels that allow water to circulate through them. They have unspecialized cells that can cellular differentiation , transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. They do not have complex nervous system , nervous, digestive system , digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spicule (sponge)
Spicules are structural elements found in most Sea sponge, sponges. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or Silicon dioxide, silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres or macroscleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy. Overview Sponges are a species-rich clade of the earliest-diverging (most Basal (phylogenetics), basal) animals. They are distributed globally, with diverse ecologies and functions, and a record spanning at least the entire Phanerozoic. Most sponges produce skeletons formed by spicules, structural elements that develop in a wide variety of sizes and three dimensional shapes. Among the four sub-clades of Porifera, three (Demospong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge Spicule
Spicules are structural elements found in most sponges. The meshing of many spicules serves as the sponge's skeleton and thus it provides structural support and potentially defense against predators. Sponge spicules are made of calcium carbonate or silica. Large spicules visible to the naked eye are referred to as megascleres or macroscleres, while smaller, microscopic ones are termed microscleres. The composition, size, and shape of spicules are major characters in sponge systematics and taxonomy. Overview Sponges are a species-rich clade of the earliest-diverging (most basal) animals. They are distributed globally, with diverse ecologies and functions, and a record spanning at least the entire Phanerozoic. Most sponges produce skeletons formed by spicules, structural elements that develop in a wide variety of sizes and three dimensional shapes. Among the four sub-clades of Porifera, three ( Demospongiae, Hexactinellida, and Homoscleromorpha) produce skeletons of am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oopsacas Minuta
''Oopsacas minuta'' is a species of glass sponge Hexactinellid sponges are sponges with a skeleton made of four- and/or six-pointed silica, siliceous spicule (sponge), spicules, often referred to as glass sponges. They are usually biological classification, classified along with other sponges i ... found in cold submarine caves in the Mediterranean. Unlike most glass sponges, ''O. minuta'' lives in shallow waters above 200 meters in depth. At this depth the temperature is low and constant, so silica metabolism is optimized. Description ''O. minuta'' has a elongated, cylindrical and a slightly flared shape. It can be between a few millimeters and 3.5 centimeters in size, and is supported by a siliceous skeleton like other glass sponges. These spindles partially block the top of the sponge. There are no obvious oscules. The sponge is anchored or suspended from the cave by silica fibers. ''O. minuta'' belongs to the order Lyssacinosida. Lyssacinosida are characterized by the pare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Flower Basket
The Venus' flower basket (''Euplectella aspergillum'') is a species of glass sponge found in the deep waters of the Pacific Ocean, usually at depths below . Like other glass sponges, they build their skeletons out of silica, which forms a unique lattice structure consisting of spicules. This body structure is of great interest in materials science as the optical and mechanical properties are in some ways superior to man-made materials. Like other sponges, they feed by filtering sea water to capture plankton and marine snow. Little is known regarding their reproductive habits, though the fluid dynamics of their body structure likely influence reproduction and it is hypothesized that they may be hermaphroditic. Taxonomy ''Euplectella aspergillum'' was described in 1841 by Sir Richard Owen. As the genus ''Euplectella'' was named to accommodate this species, it is the type of its genus. Owen describes it as "...one of the most singular and beautiful, as well as the rarest of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euplectella 01
''Euplectella'' is a genus of glass sponges which includes the well-known Venus' Flower Basket The Venus' flower basket (''Euplectella aspergillum'') is a species of glass sponge found in the deep waters of the Pacific Ocean, usually at depths below . Like other glass sponges, they build their skeletons out of silica, which forms a unique .... Glass sponges have a skeleton made up of silica spicules that can form geometric patterns. These animals are most commonly found on muddy sea bottoms in the Western Pacific and Indian Oceans. They are sessile organisms and do not move once attached to a rock. They can be found at depths between 100 m and 1000 m but are most commonly found at depths greater than 500 m. Anatomy ''Euplectella'' is a member of the class Sclerospongiae or glass sponges. The body shape of ''Euplectella'' is cylindrical and vase-like with a hole located at the top of the cylinder structure. This tubular shape is referred to as asconoid. The inner structure o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syncytium
A syncytium (; : syncytia; from Greek: σύν ''syn'' "together" and κύτος ''kytos'' "box, i.e. cell") or symplasm is a multinucleate cell that can result from multiple cell fusions of uninuclear cells (i.e., cells with a single nucleus), in contrast to a coenocyte, which can result from multiple nuclear divisions without accompanying cytokinesis. The muscle cell that makes up animal skeletal muscle is a classic example of a syncytium cell. The term may also refer to cells interconnected by specialized membranes with gap junctions, as seen in the heart muscle cells and certain smooth muscle cells, which are synchronized electrically in an action potential. The field of embryogenesis uses the word ''syncytium'' to refer to the coenocytic blastoderm embryos of invertebrates, such as ''Drosophila melanogaster''. Physiological examples Protists In protists, syncytia can be found in some rhizarians (e.g., chlorarachniophytes, plasmodiophorids, haplosporidians) and acellul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of most animals. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is a rigid outer shell that holds up an organism's shape; the endoskeleton, a rigid internal frame to which the organs and soft tissues attach; and the hydroskeleton, a flexible internal structure supported by the hydrostatic pressure of body fluids. Vertebrates are animals with an endoskeleton centered around an axial vertebral column, and their skeletons are typically composed of bones and cartilages. Invertebrates are other animals that lack a vertebral column, and their skeletons vary, including hard-shelled exoskeleton (arthropods and most molluscs), plated internal shells (e.g. cuttlebones in some cephalopods) or rods (e.g. ossicles in echinoderms), hydrostatically supported body cavities (most), and spicules (sponges). Cartilage is a rigid connective tissue that is found in the skeletal systems of vertebrates and invert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |