|
Henry's Fork Caldera
The Henry's Fork Caldera in eastern Idaho is a caldera located in an area known as Island Park, west of Yellowstone National Park. The caldera was formed by an eruption 1.3 million years ago of the Yellowstone hotspot. The eruption distributed at least 280 cubic kilometers of ash known as the Mesa Falls Tuff, covering a region including all of Wyoming and most of Colorado, Nebraska, and Kansas. The Henry's Fork Caldera is nested inside of the Island Park Caldera, and the calderas share a rim on the western side. The earlier Island Park Caldera is much larger and more oval and extends well into Yellowstone Park. Although much smaller than the Island Park Caldera, the Henry's Fork Caldera is still sizeable at long and wide and its curved rim is plainly visible from many locations in the Island Park area. Of the many calderas formed by the Yellowstone hotspot, including the later Yellowstone Caldera, the Henry's Fork Caldera is the only one that is currently clearly visi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Park Caldera
The Island Park Caldera, in the U.S. states of Idaho and Wyoming, is one of the world's largest calderas, with approximate dimensions of 80 by 65 km. Its ashfall is the source of the Huckleberry Ridge Tuff that is found from southern California to the Mississippi River near St. Louis. This super-eruption of approximately occurred 2.1 Ma (million years ago) and produced 2,500 times as much ash as the 1980 eruption of Mount St. Helens. Island Park Caldera has the smaller and younger Henry's Fork Caldera nested inside it. The caldera clearly visible today is the later Henry's Fork Caldera, which is the source of the Mesa Falls Tuff. It was formed 1.3 Ma in an eruption of more than . The two nested calderas share the same rim on their western sides, but the older Island Park Caldera is much larger and more oval and extends well into Yellowstone National Park.Newhall and Daniel Dzurisin, 1988, "Historical Unrest at Large Calderas of the World", ''U.S. Geological Survey B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snake River
The Snake River is a major river of the greater Pacific Northwest region in the United States. At long, it is the largest tributary of the Columbia River, in turn, the largest North American river that empties into the Pacific Ocean. The Snake River rises in western Wyoming, then flows through the Snake River Plain of southern Idaho, the rugged Hells Canyon on the Oregon–Idaho border and the rolling Palouse Hills of Washington, emptying into the Columbia River at the Tri-Cities in the Columbia Basin of Eastern Washington. The Snake River drainage basin encompasses parts of six U.S. states (Idaho, Washington, Oregon, Utah, Nevada, and Wyoming) and is known for its varied geologic history. The Snake River Plain was created by a volcanic hotspot which now lies underneath the Snake River headwaters in Yellowstone National Park. Gigantic glacial-retreat flooding episodes during the previous Ice Age carved out canyons, cliffs, and waterfalls along the middle and lower Snake ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pleistocene Calderas
The Pleistocene ( , often referred to as the ''Ice age'') is the geological epoch that lasted from about 2,580,000 to 11,700 years ago, spanning the Earth's most recent period of repeated glaciations. Before a change was finally confirmed in 2009 by the International Union of Geological Sciences, the cutoff of the Pleistocene and the preceding Pliocene was regarded as being 1.806 million years Before Present (BP). Publications from earlier years may use either definition of the period. The end of the Pleistocene corresponds with the end of the last glacial period and also with the end of the Paleolithic age used in archaeology. The name is a combination of Ancient Greek grc, label=none, πλεῖστος, pleīstos, most and grc, label=none, καινός, kainós (latinized as ), 'new'. At the end of the preceding Pliocene, the previously isolated North and South American continents were joined by the Isthmus of Panama, causing a faunal interchange between the two reg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landforms Of Fremont County, Idaho
A landform is a natural or anthropogenic land feature on the solid surface of the Earth or other planetary body. Landforms together make up a given terrain, and their arrangement in the landscape is known as topography. Landforms include hills, mountains, canyons, and valleys, as well as shoreline features such as bays, peninsulas, and seas, including submerged features such as mid-ocean ridges, volcanoes, and the great ocean basins. Physical characteristics Landforms are categorized by characteristic physical attributes such as elevation, slope, orientation, stratification, rock exposure and soil type. Gross physical features or landforms include intuitive elements such as berms, mounds, hills, ridges, cliffs, valleys, rivers, peninsulas, volcanoes, and numerous other structural and size-scaled (e.g. ponds vs. lakes, hills vs. mountains) elements including various kinds of inland and oceanic waterbodies and sub-surface features. Mountains, hills, plateaux, and plains are the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanoes Of Idaho
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plates slide pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calderas Of Idaho
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is gone. The ground surface then collapses into the emptied or partially emptied magma chamber, leaving a large depression at the surface (from one to dozens of kilometers in diameter). Although sometimes described as a crater, the feature is actually a type of sinkhole, as it is formed through subsidence and collapse rather than an explosion or impact. Compared to the thousands of volcanic eruptions that occur each century, the formation of a caldera is a rare event, occurring only a few times per century. Only seven caldera-forming collapses are known to have occurred between 1911 and 2016. More recently, a caldera collapse occurred at Kīlauea, Hawaii in 2018. Etymology The term ''caldera'' comes from Spanish ', and Latin ', meaning "co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanism Of Idaho
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a vent. It includes all phenomena resulting from and causing magma within the crust or mantle of the body, to rise through the crust and form volcanic rocks on the surface. Magmas, that reach the surface and solidify, form extrusive landforms. Volcanic processes Magma from the mantle or lower crust rises through the crust towards the surface. If magma reaches the surface, its behavior depends on the viscosity of the molten constituent rock. Viscous (thick) magma produces volcanoes characterised by explosive eruptions, while non-viscous (runny) magma produce volcanoes characterised by effusive eruptions pouring large amounts of lava onto the surface. In some cases, rising magma can cool and solidify without reaching the surface. Instead, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wyoming
Wyoming () is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. It is bordered by Montana to the north and northwest, South Dakota and Nebraska to the east, Idaho to the west, Utah to the southwest, and Colorado to the south. With a population of 576,851 in the 2020 United States census, Wyoming is the least populous state despite being the 10th largest by area, with the second-lowest population density after Alaska. The state capital and most populous city is Cheyenne, which had an estimated population of 63,957 in 2018. Wyoming's western half is covered mostly by the ranges and rangelands of the Rocky Mountains, while the eastern half of the state is high-elevation prairie called the High Plains. It is drier and windier than the rest of the country, being split between semi-arid and continental climates with greater temperature extremes. Almost half of the land in Wyoming is owned by the federal government, generally protected for public uses. The stat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
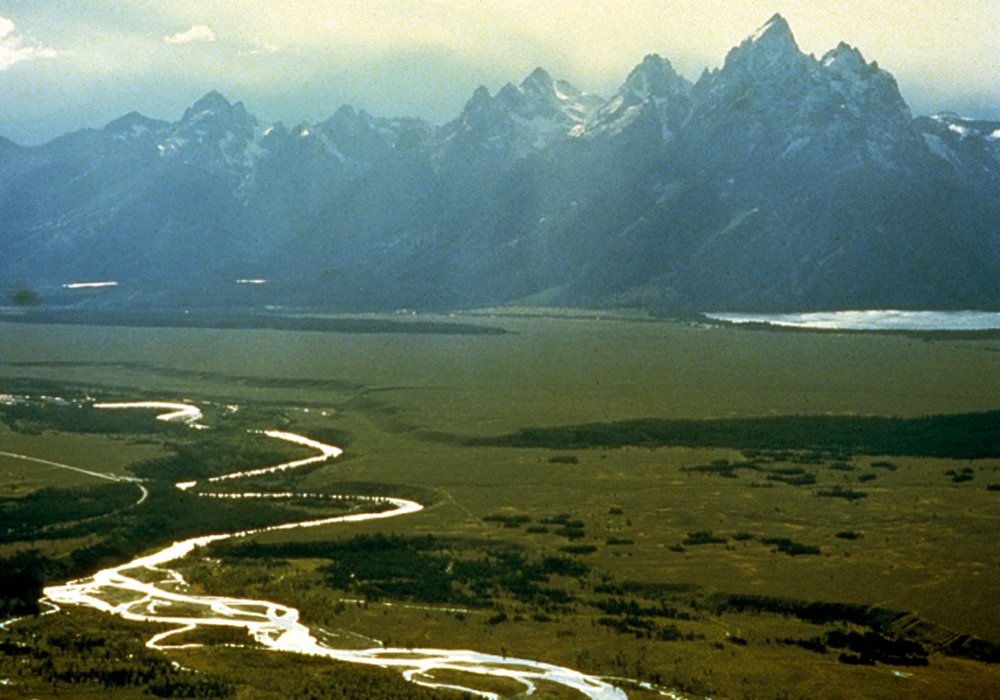
Teton Range
The Teton Range is a mountain range of the Rocky Mountains in North America. It extends for approximately in a north–south direction through the U.S. state of Wyoming, east of the Idaho state line. It is south of Yellowstone National Park and most of the east side of the range is within Grand Teton National Park. One theory says the early French voyageurs named the range ' ("the three nipples") after the breast-like shapes of its peaks. Another theory says the range is named for the Teton Sioux (from Thítȟuŋwaŋ), also known as the Lakota people.Ullrich, Jan. (2008). ''New Lakota Dictionary''. Lakota Language Consortium. It is likely that the local Shoshone people once called the whole range ', meaning "many pinnacles". The principal summits of the central massif, sometimes referred to as the Cathedral Group, are Grand Teton (), Mount Owen (), Teewinot (), Middle Teton () and South Teton (). Other peaks in the range include Mount Moran (), Mount Wister (), Buck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harriman State Park (Idaho)
Harriman State Park is a public recreation area located on the Harriman Wildlife Refuge in Fremont County, south of Island Park in eastern Idaho, United States. The state park is within the Henry's Fork Caldera in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem. It is home to an abundance of elk, moose, sandhill cranes, trumpeter swans, and the occasional black or grizzly bear. Two-thirds of the trumpeter swans that winter in the contiguous United States spend the season in Harriman State Park. History The park's acreage was owned by Union Pacific Railroad investors from 1902 to 1977, serving as a cattle ranch and private retreat for the Harriman and Guggenheim families. It was deeded to Idaho for free in 1977 by Roland and W. Averell Harriman, whose insistence that the state have a professional park managing service helped prompt the creation of the Idaho Department of Parks and Recreation in 1965. The park opened to the public in 1982. Support group Friends of Harriman State ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
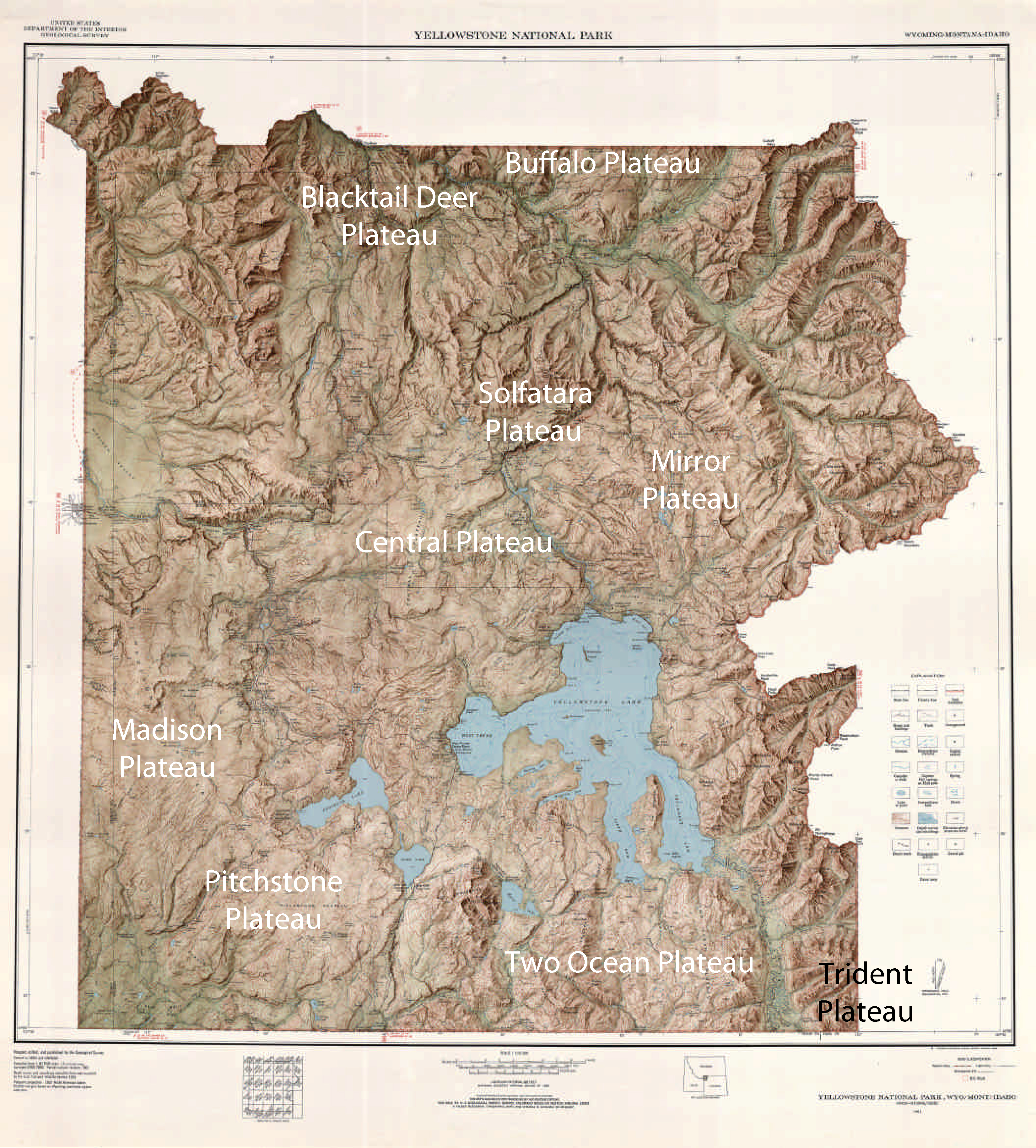
Madison Plateau
There are nine named plateaus in Yellowstone National Park. These plateaus are part of the much larger Yellowstone Plateau and dominate areas in the park south and west of the Gallatin and Absaroka mountain ranges. Four of the plateaus are from rhyolite lava flows that occurred between 110,000 and 70,000 years ago. * Blacktail Deer Plateau , ** Traversed by the Mammoth to Tower section of the Grand Loop Road, Blacktail Deer Plateau is one of the most accessible plateaus in the park. Blacktail Deer Plateau takes its name from Blacktail Deer Creek which flows off the plateau. Named by prospectors well before the park's creation in 1872, the name is probably attributable to the then prevalent Blacktail deer of the area. * Buffalo Plateau , ** The Buffalo Plateau straddles the Montana-Wyoming border north of the Lamar Valley and west of Slough Creek in the park's northern range. Named in 1870, before the park's creation, by prospectors Bart Henderson, James Gourley, Ada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)