|
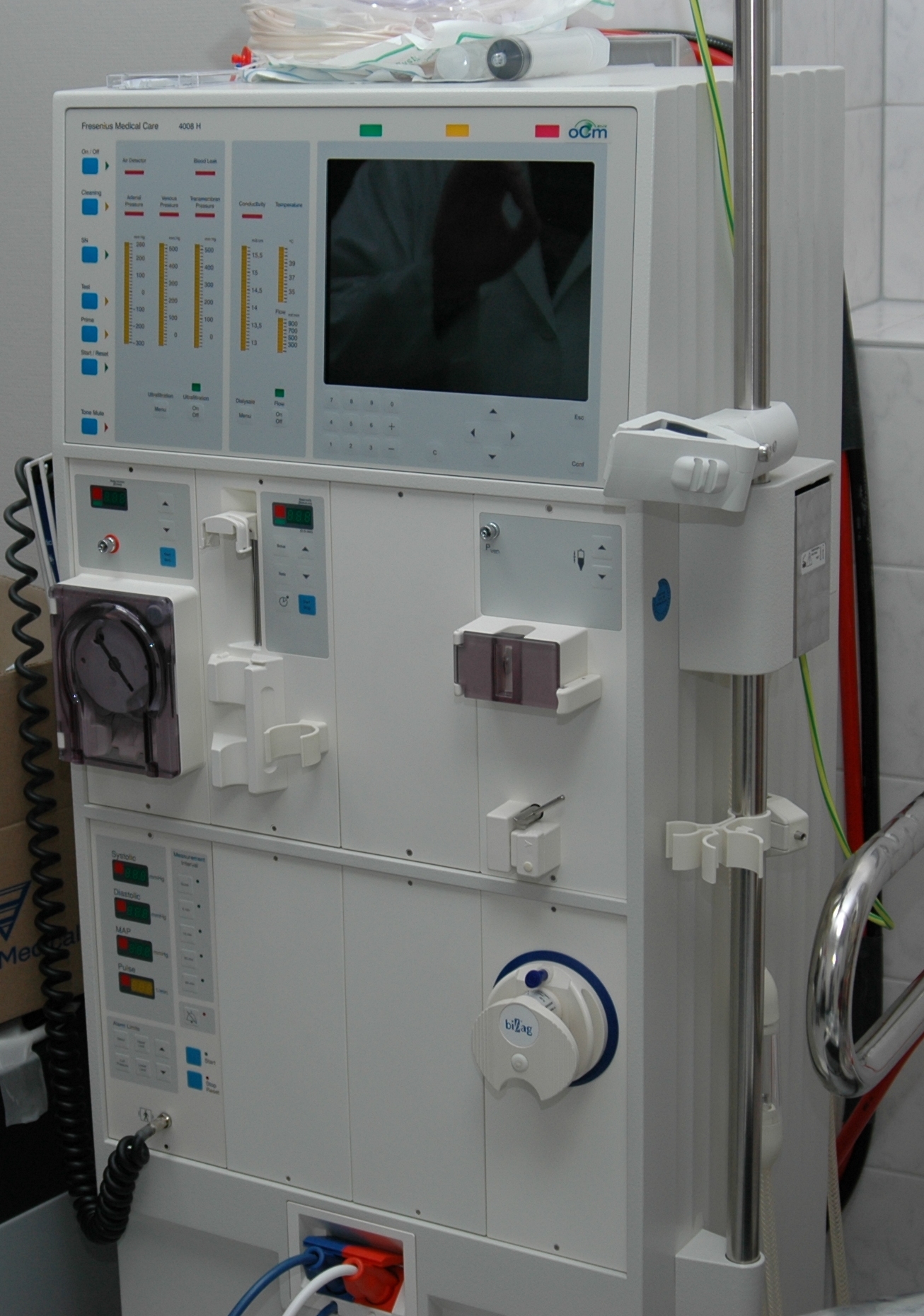
Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, American and British English spelling differences#ae and oe, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply ''"'dialysis'"'', is a process of filtering the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of Kidney dialysis, dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinine and urea and free water from the blood when the kidneys are in a state of kidney failure. Hemodialysis is one of three renal replacement therapy, renal replacement therapies (the other two being kidney transplant and peritoneal dialysis). An alternative method for extracorporeal separation of blood components such as plasma or cells is apheresis. Hemodialysis can be an outpatient or inpatient therapy. Routine hemodialysis is conducted in a dialysis outpatient facility, either a purpose-built room in a hospital or a dedicated, stand-alone clinic. Less frequently hemodialysis is done at home hemodialysis, home. Dialysis treatments in a clinic are initiated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney Dialysis
Kidney dialysis is the process of removing excess water, solutes, and toxins from the blood in people whose kidneys can no longer perform these functions naturally. Along with kidney transplantation, it is a type of renal replacement therapy. Dialysis may need to be initiated when there is a sudden rapid loss of kidney function, known as acute kidney injury (previously called acute renal failure), or when a gradual decline in kidney function, chronic kidney failure, reaches stage 5. Stage 5 chronic renal failure is reached when the glomerular filtration rate is less than 15% of the normal, creatinine clearance is less than 10 mL per minute, and uremia is present. Dialysis is used as a temporary measure in either acute kidney injury or in those awaiting kidney transplant and as a permanent measure in those for whom a transplant is not Indication (medicine), indicated or not possible.Pendse S, Singh A, Zawada E. "Initiation of Dialysis". In: ''Handbook of Dialysis''. 4th ed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Hemodialysis
Home hemodialysis (HHD) is the provision of hemodialysis to purify the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally, in their own home. One advantage to doing dialysis at home is that it can be done more frequently and slowly, which reduces the "washed out" feeling and other symptoms caused by rapid ultrafiltration, and it can often be done at night, while the person is sleeping. People on home hemodialysis are followed by a nephrologist who writes the dialysis prescription and they rely on the support of a dialysis unit for back-up treatments and case management. Studies show that HHD improves patients' sense of well-being; the more they know about and control their own treatment the better they are likely to do on dialysis. HHD was introduced in the 1960s as a way to conserve scarce healthcare resources. Schedules There are three basic schedules of HHD and these are differentiated by the length and frequency of dialysis and the time of day the dialysis is carried o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Failure
Kidney failure, also known as renal failure or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), is a medical condition in which the kidneys can no longer adequately filter waste products from the blood, functioning at less than 15% of normal levels. Kidney failure is classified as either acute kidney failure, which develops rapidly and may resolve; and chronic kidney failure, which develops slowly and can often be irreversible. Symptoms may include edema, leg swelling, feeling tired, vomiting, loss of appetite, and confusion. Complications of acute and chronic failure include uremia, hyperkalemia, and volume overload. Complications of chronic failure also include heart disease, high blood pressure, and anaemia. Causes of acute kidney failure include low blood pressure, blockage of the urinary tract, certain medications, muscle breakdown, and hemolytic uremic syndrome. Causes of chronic kidney failure include diabetic nephropathy, diabetes, high blood pressure, nephrotic syndrome, and polycyst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
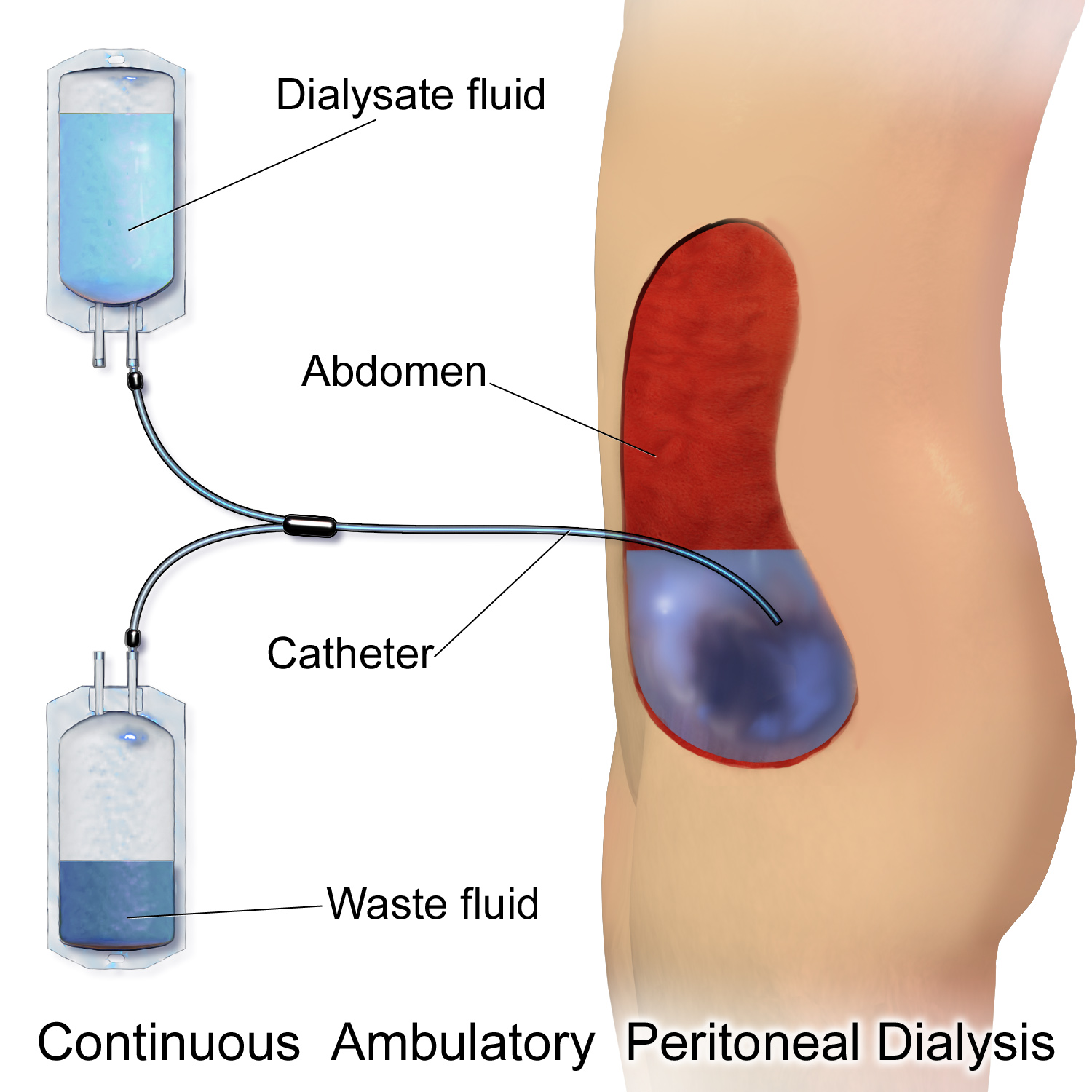
Peritoneal Dialysis
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of kidney dialysis, dialysis that uses the peritoneum in a person's abdomen as the membrane through which fluid and dissolved substances are exchanged with the blood. It is used to remove excess fluid, correct electrolyte problems, and remove toxins in those with kidney failure. Peritoneal dialysis has better outcomes than hemodialysis during the first two years. Other benefits include greater flexibility and better tolerability in those with significant heart disease. Side effects Complications may include peritonitis, infections within the abdomen, hernias, high blood sugar, bleeding in the abdomen, and blockage of the catheter. Peritoneal dialysis is not possible in those with significant prior abdominal surgery or inflammatory bowel disease. It requires some degree of technical skill to be done properly. Mechanism In peritoneal dialysis, a specific solution is introduced and then removed through a permanent tube in the lower abdomen. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renal Replacement Therapy
Renal replacement therapy (RRT) is therapy that replaces the normal blood-filtering function of the kidneys. It is used when the kidneys are not working well, which is called kidney failure and includes acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. Renal replacement therapy includes dialysis (hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis), hemofiltration, and hemodiafiltration, which are various ways of filtration of blood with or without machines. Renal replacement therapy also includes kidney transplantation, which is the ultimate form of replacement in that the old kidney is replaced by a donor kidney. These treatments are not truly cures for kidney disease. In the context of chronic kidney disease, they are more accurately viewed as life-extending treatments, although if chronic kidney disease is managed well with dialysis and a compatible graft is found early and is successfully transplanted, the clinical course can be quite favorable, with life expectancy of many years. Likew ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. It can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of the throat. Over 30 definitions of nausea were proposed in a 2011 book on the topic. Nausea is a non-specific symptom, which means that it has many possible causes. Some common causes of nausea are gastroenteritis and other gastrointestinal disorders, food poisoning, motion sickness, dizziness, migraine, fainting, low blood sugar, anxiety, hyperthermia, dehydration and lack of sleep. Nausea is a side effect of many medications including chemotherapy, or morning sickness in early pregnancy. Nausea may also be caused by disgust and depression. Medications taken to prevent and treat nausea and vomiting are called antiemetics. The most commonly prescribed antiemetics in the US are promethazine, metoclopramide, and the newer ondansetron. The word na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultrafiltration (renal)
In renal physiology, ultrafiltration occurs at the barrier between the blood and the filtrate in the glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule) in the kidneys. As in nonbiological examples of ultrafiltration, pressure (in this case blood pressure) and concentration gradients lead to a separation through a semipermeable membrane (provided by the podocytes). The Bowman's capsule contains a dense capillary network called the glomerulus. Blood flows into these capillaries through the afferent arterioles and leaves through the efferent arterioles. The high hydrostatic pressure forces small molecules in the tubular fluid such as water, glucose, amino acids, sodium chloride and urea through the filter, from the blood in the glomerular capsule across the basement membrane of the Bowman's capsule and into the renal tubules. This process is called ultrafiltration; the resulting fluid, virtually free of large proteins and blood cells, is referred to as glomerular filtrate, or ultrafiltr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of Circulatory system, circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" refers to the pressure in a brachial artery, where it is most commonly measured. Blood pressure is usually expressed in terms of the systolic pressure (maximum pressure during one Cardiac cycle, heartbeat) over diastolic pressure (minimum pressure between two heartbeats) in the cardiac cycle. It is measured in Millimetre of mercury, millimetres of mercury (mmHg) above the surrounding atmospheric pressure, or in Pascal (unit), kilopascals (kPa). The difference between the systolic and diastolic pressures is known as pulse pressure, while the average pressure during a cardiac cycle is known as mean arterial pressure. Blood pressure is one of the vital signs—together with respiratory rate, heart rate, Oxygen saturation (me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (physical)
Fatigue is a state of tiredness (which is not sleepiness), exhaustion or loss of energy. It is a symptom of any of various diseases; it is not a disease in itself. Fatigue (in the medical sense) is sometimes associated with medical conditions including autoimmune disease, organ failure, chronic pain conditions, mood disorders, heart disease, infectious diseases, and post-infectious-disease states. However, fatigue is complex and in up to a third of primary care cases no medical or psychiatric diagnosis is found. Fatigue (in the general usage sense of normal tiredness) often follows prolonged physical or mental activity. Physical fatigue results from muscle fatigue brought about by intense physical activity. Mental fatigue results from prolonged periods of cognitive activity which impairs cognitive ability, can manifest as sleepiness, lethargy, or directed attention fatigue, and can also impair physical performance. Definition Fatigue in a medical context is used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American And British English Spelling Differences
Despite the various list of dialects of English, English dialects spoken from country to country and within different regions of the same country, there are only slight regional variations in English orthography, the two most notable variations being British and American spelling. Many of Comparison of American and British English, the differences between American English, American and British English, British or English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English date back to a time before spelling standards were developed. For instance, some spellings seen as "American" today were once commonly used in Britain, and some spellings seen as "British" were once commonly used in the United States. A "British standard" began to emerge following the 1755 publication of Samuel Johnson's ''A Dictionary of the English Language'', and an "American standard" started following the work of Noah Webster and, in particular, his ''Webster's Dictionary, An American Dictionary of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Headaches
A headache, also known as cephalalgia, is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches. Headaches can occur as a result of many conditions. There are a number of different classification systems for headaches. The most well-recognized is that of the International Headache Society, which classifies it into more than 150 types of primary and secondary headaches. Causes of headaches may include dehydration; fatigue; sleep deprivation; stress; the effects of medications (overuse) and recreational drugs, including withdrawal; viral infections; loud noises; head injury; rapid ingestion of a very cold food or beverage; and dental or sinus issues (such as sinusitis). Treatment of a headache depends on the underlying cause, but commonly involves pain medication (especially in case of migraine or cluster headaches). A headache is one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |