|
Hayward Fault Zone
The Hayward Fault Zone is a right-lateral strike-slip geologic fault zone capable of generating destructive earthquakes. The fault was first named in the Lawson Report of the 1906 San Francisco Earthquake in recognition of its involvement in the earthquake of 1868. This fault is about long, situated mainly along the western base of the hills on the east side of San Francisco Bay. It runs through densely populated areas, including Richmond, El Cerrito, Berkeley, Oakland, San Leandro, Castro Valley, Hayward, Union City, Fremont, and San Jose. The Hayward Fault is parallel to the San Andreas Fault, which lies offshore and through the San Francisco Peninsula. To the east of the Hayward Fault lies the Calaveras Fault. In 2007, the Hayward Fault was discovered to have merged with the Calaveras Fault east of San Jose at a depth of , with the potential of creating earthquakes much larger than previously anticipated. Some geologists have suggested that the Southern Calaveras should ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
122-38HaywardFault
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural number, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calaveras Fault
The Calaveras Fault is a major branch of the San Andreas Fault System that is located in northern California in the San Francisco Bay Area. Activity on the different segments of the fault includes moderate and large earthquakes as well as aseismic creep. The last large event was the magnitude 6.2 1984 Morgan Hill event. The most recent moderate earthquakes were the magnitude 5.1 event on 25 October 2022, and the magnitude 5.6 2007 Alum Rock event. It is believed to link with the Hayward fault, as well as the West Napa Fault, north of the Carquinez Strait. It passes through or near the cities of Alamo, Danville, San Ramon, Dublin, Pleasanton, Sunol, Milpitas, San Jose, Gilroy, and Hollister. Location To the east of the Hayward-Rodgers Creek fault, the Calaveras fault extends , splaying from the San Andreas fault near Hollister and terminating at Danville at its northern end. It runs east of the San Andreas, diverging from it in the vicinity of Hollister, Californi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Boundary
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault along a plate boundary where the motion is predominantly horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This results from oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addition or loss of lithosphere at the Earth's surface. Background Geophysicist an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aleutian Trench
The Aleutian Trench (or Aleutian Trough) is an oceanic trench along a convergent plate boundary which runs along the southern coastline of Alaska and the Aleutian islands. The trench extends for from a triple junction in the west with the Ulakhan Fault and the northern end of the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench, to a junction with the northern end of the Queen Charlotte Fault system in the east. It is classified as a "marginal trench" in the east as it runs along the margin of the continent. The subduction along the trench gives rise to the Aleutian Arc, a volcanic island arc, where it runs through the open sea west of the Alaska Peninsula. As a convergent plate boundary, the trench forms part of the boundary between two tectonic plates. Here, the Pacific plate is being subducted under the North American plate at a dip angle of nearly 45°. The rate of closure is per year. The Pacific plate subducting under the North American plate, leads to increased faulting. This subductio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Pacific Rise
The East Pacific Rise (EPR) is a mid-ocean rise (usually termed an oceanic rise and not a mid-ocean ridge due to its higher rate of spreading that results in less elevation increase and more regular terrain), at a divergent tectonic plate boundary, located along the floor of the Pacific Ocean. It separates the Pacific plate to the west from (north to south) the North American plate, the Rivera plate, the Cocos plate, the Nazca plate, and the Antarctic plate. It runs south from the Gulf of California in the Salton Sea basin in Southern California to a point near , where it joins the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) trending west-south-west towards Antarctica, near New Zealand (though in some uses the PAR is regarded as the southern section of the EPR). Much of the rise lies about off the South American coast and reaches a height about above the surrounding seafloor. Overview The oceanic crust is moving away from the East Pacific Rise to either side. Near Easter Island th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magma
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma (sometimes colloquially but incorrectly referred to as ''lava'') is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural satellites. Besides molten rock, magma may also contain suspended crystals and volcanic gas, gas bubbles. Magma is produced by melting of the mantle (geology), mantle or the Crust (geology), crust in various tectonics, tectonic settings, which on Earth include subduction zones, continental rift (geology), rift zones, mid-ocean ridges and Hotspot (geology), hotspots. Mantle and crustal melts migrate upwards through the crust where they are thought to be stored in magma chambers or trans-crustal crystal mush, crystal-rich mush zones. During magma's storage in the crust, its composition may be modified by Fractional crystallization (geology), fractional crystallization, contaminati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
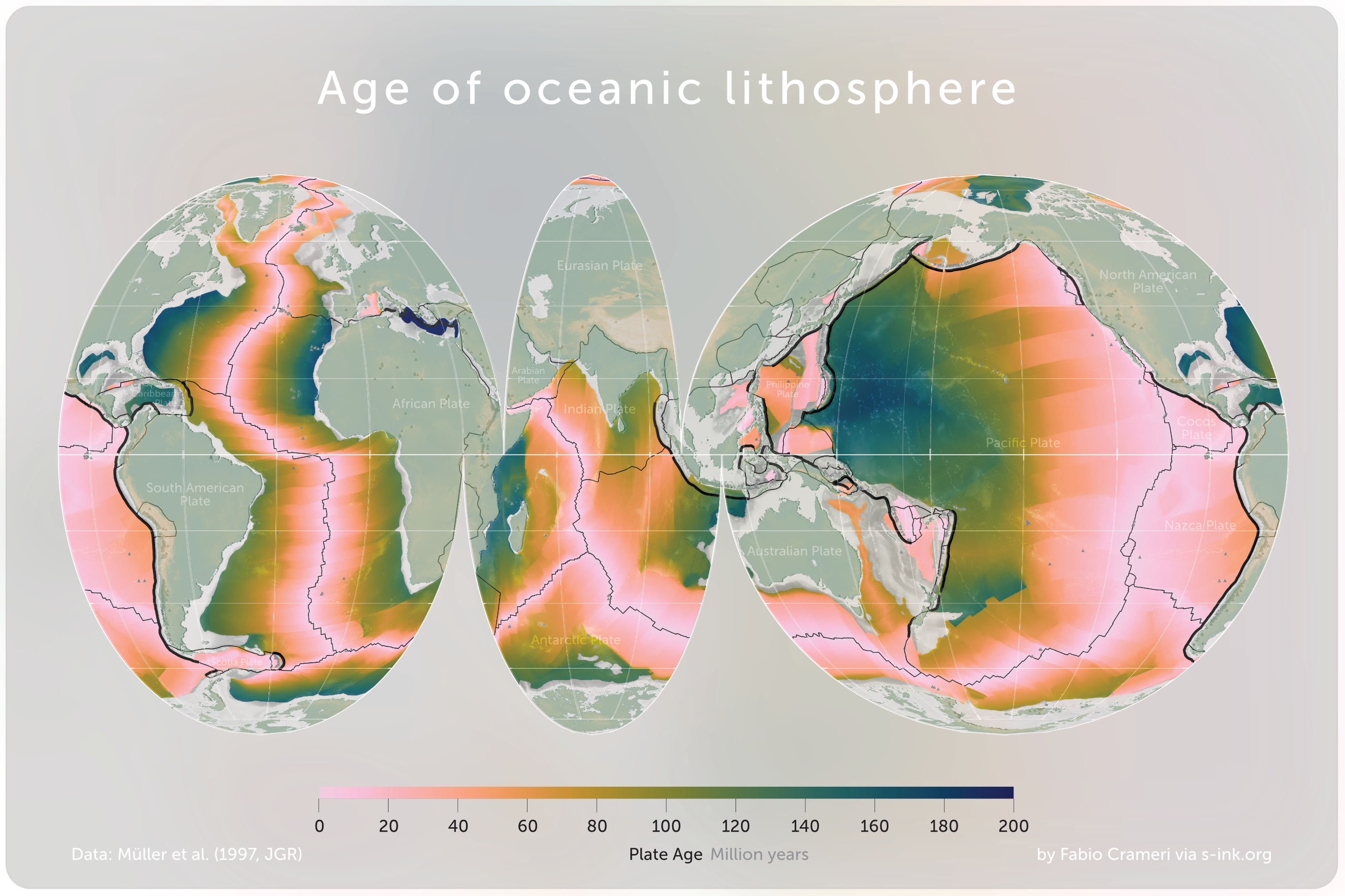
Seafloor Spreading
Seafloor spreading, or seafloor spread, is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. History of study Earlier theories by Alfred Wegener and Alexander du Toit of continental drift postulated that continents in motion "plowed" through the fixed and immovable seafloor. The idea that the seafloor itself moves and also carries the continents with it as it spreads from a central rift axis was proposed by Harold Hammond Hess from Princeton University and Robert Dietz of the U.S. Naval Electronics Laboratory in San Diego in the 1960s. The phenomenon is known today as plate tectonics. In locations where two plates move apart, at mid-ocean ridges, new seafloor is continually formed during seafloor spreading. Significance Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When oceanic plates diverge, tensional stress causes fractures to occur i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transform Fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, is a fault (geology), fault along a plate boundary where the motion (physics), motion is predominantly Horizontal plane, horizontal. It ends abruptly where it connects to another plate boundary, either another transform, a spreading ridge, or a subduction, subduction zone. A transform fault is a special case of a ''strike-slip fault'' that also forms a plate boundary. Most such faults are found in oceanic crust, where they accommodate the lateral offset between segments of Divergent boundary, divergent boundaries, forming a zigzag pattern. This results from oblique seafloor spreading where the direction of motion is not perpendicular to the trend of the overall divergent boundary. A smaller number of such faults are found on land, although these are generally better-known, such as the San Andreas Fault and North Anatolian Fault. Nomenclature Transform boundaries are also known as conservative plate boundaries because they involve no addit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Bureau Of Reclamation
The Bureau of Reclamation, formerly the United States Reclamation Service, is a federal agency under the U.S. Department of the Interior, which oversees water resource management, specifically as it applies to the oversight and operation of the diversion, delivery, and storage projects that it has built throughout the western United States for irrigation, water supply, and attendant hydroelectric power generation. It is currently the U.S.'s largest wholesaler of water, bringing water to more than 31 million people, and providing one in five Western farmers with irrigation water for 10 million acres of farmland, which produce 60% of the nation's vegetables and 25% of its fruits and nuts. The Bureau is also the second largest producer of hydroelectric power in the western U.S. On June 17, 1902, in accordance with the Reclamation Act, Secretary of the Interior Ethan Allen Hitchcock established the U.S. Reclamation Service within the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS). The n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |