|
HMG-CoA Reductase
HMG-CoA reductase (3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-coenzyme A reductase, official symbol HMGCR) is the rate-limiting enzyme (NADH-dependent, ; NADPH-dependent, ) of the mevalonate pathway, the metabolic pathway that produces cholesterol and other isoprenoids. HMGCR catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonic acid, a necessary step in the biosynthesis of cholesterol. Normally in mammalian cells this enzyme is competitively suppressed so that its effect is controlled. This enzyme is the target of the widely available cholesterol-lowering drugs known collectively as the statins, which help treat dyslipidemia. HMG-CoA reductase is anchored in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum, and was long regarded as having seven transmembrane domains, with the active site located in a long carboxyl terminal domain in the cytosol. More recent evidence shows it to contain eight transmembrane domains. In humans, the gene for HMG-CoA reductase (NADPH) is located on the long arm of the fif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Density Lipoprotein
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoprotein that transport all fat molecules around the body in extracellular water. These groups, from least dense to most dense, are chylomicrons (aka ULDL by the overall density naming convention), very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL), intermediate-density lipoprotein (IDL), low-density lipoprotein (LDL) and high-density lipoprotein (HDL). LDL delivers fat molecules to cells. LDL has been associated with the progression of atherosclerosis. Overview Lipoproteins transfer lipids (fats) around the body in the extracellular fluid, making fats available to body cells for receptor-mediated endocytosis. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins, typically 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by a single apolipoprotein B for LDL and the larger particles). A single LDL particle is about 22–27.5 nanometers in diameter, typically transporting 3,000 to 6,000 fat molecules per particle and varyi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simvastatin
Simvastatin, sold under the brand name Zocor among others, is a statin, a type of lipid-lowering medication. It is used along with exercise, diet, and weight loss to decrease hyperlipidemia, elevated lipid levels. It is also used to decrease the risk of Cardiovascular disease, heart problems in those at high risk. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include constipation, headaches, and nausea. Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, muscle breakdown, liver problems, and increased blood sugar levels. A lower dose may be needed in people with chronic kidney disease, kidney problems. There is evidence of harm to the developing baby when taken during pregnancy and it should not be used by those who are breastfeeding. It is in the statin class of medications and works by decreasing the manufacture of cholesterol by the liver. Simvastatin is made from the fungus ''Aspergillus terreus''. It was patented by Merck and Co., Merck in 1980, and came into medical use in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitavastatin
Pitavastatin (usually as a calcium salt) is a member of the blood cholesterol lowering medication class of statins. Pitavastatin is an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme that catalyses the first step of cholesterol synthesis. It was patented in 1987 and approved for medical use in 2003. It is available in Japan, South Korea and in India. In the US, it received FDA approval in 2009. Kowa Pharmaceuticals, a subsidiary of Kowa (company), Kowa Company, is the owner of the American patent to pitavastatin. Medical uses Pitavastatin is indicated for hypercholesterolaemia (elevated cholesterol) and for the prevention of cardiovascular disease. A 2009 study of the 104-week LIVES trial found pitavastatin increased HDL cholesterol, especially in patients with HDL lower than 40 mg/dL, who had a 24.6% rise, in addition to reducing LDL cholesterol 31.3%. HDL improved in patients who switched from other statins and rose over time. In the 70-month CIRCLE observational study, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluvastatin
Fluvastatin is a member of the statin drug class, used to treat hypercholesterolemia and to prevent cardiovascular disease. It was patented in 1982 and approved for medical use in 1994. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Adverse effects Adverse effects are comparable to other statins. Common are nausea, indigestion, insomnia and headache. Myalgia (muscle pain), and rarely rhabdomyolysis, characteristic side effects for statins, can also occur. Interactions Contrary to lovastatin, simvastatin and atorvastatin, fluvastatin has no relevant interactions with drugs that inhibit the liver enzyme CYP3A4, and a generally lower potential for interactions than most other statins. Fluconazole, a potent inhibitor of CYP2C9, does increase fluvastatin levels. Pharmacology Mechanism of action Fluvastatin works by blocking the liver enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which facilitates an important step in cholesterol synthesis. Pharmacodynamics In a Coc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pravastatin
Pravastatin, sold under the brand name Pravachol among others, is a statin medication, used for preventing cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treating abnormal lipids. It is suggested to be used together with diet changes, exercise, and weight loss. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include joint pain, diarrhea, nausea, headaches, and muscle pains. Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, liver problems, and diabetes. Use during pregnancy may harm the fetus. Like all statins, pravastatin works by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme found in liver that plays a role in producing cholesterol. Pravastatin was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1989. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 37th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 16million prescriptions. Medical uses Pravastatin is primarily used for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atorvastatin
Atorvastatin, sold under the brand name Lipitor among others, is a statin medication used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and to treat abnormal lipid levels. For the prevention of cardiovascular disease, statins are a first-line treatment in reducing cholesterol. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects may include diarrhea, heartburn, nausea, muscle pain (typically mild and dose-dependent) and, less frequently, joint pain. Muscle symptoms often occur during the first year and are commonly influenced by pre-existing health issues and the nocebo effect. Most patients can continue therapy with dose adjustment or statin switching. Rare (<0.1%) but serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis (severe muscle disorder), liver problems and diabetes. Use during may harm the |
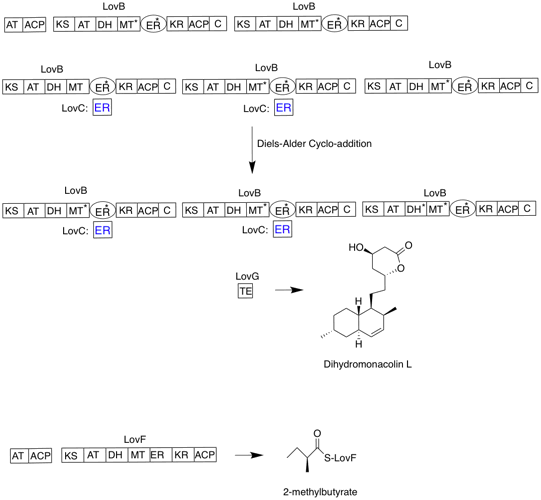
Lovastatin
Lovastatin, sold under the brand name Mevacor among others, is a statin medication, to treat high blood cholesterol and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Its use is recommended together with lifestyle changes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include diarrhea, constipation, headache, muscles pains, rash, and trouble sleeping. Serious side effects may include liver problems, muscle breakdown, and kidney failure. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby and use during breastfeeding is not recommended. It works by decreasing the liver's ability to produce cholesterol by blocking the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase. Lovastatin was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1987. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 111th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 5million prescriptions. Medical uses The primary uses of lovastatin is f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosuvastatin
Rosuvastatin, sold under the brand name Crestor among others, is a statin medication, used to prevent cardiovascular disease in those at high risk and treat dyslipidemia, abnormal lipids. It is recommended to be used with dietary changes, exercise, and weight loss. It is taken Oral administration, orally (by mouth). Common side effects include abdominal pain, nausea, headaches, and myalgia, muscle pains. Serious side effects may include rhabdomyolysis, liver problems, and diabetes. Use during pregnancy may harm the baby. Like all statins, rosuvastatin works by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, an enzyme found in the liver that plays a role in producing cholesterol. Rosuvastatin was patented in 1991 and approved for medical use in the United States in 2003. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the thirteenth most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 37million prescriptions. In Australia, it was one of the top 10 most prescribed m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heart Disease
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is any disease involving the heart or blood vessels. CVDs constitute a class of diseases that includes: coronary artery diseases (e.g. angina pectoris, angina, myocardial infarction, heart attack), heart failure, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, Thrombosis, thromboembolic disease, and venous thrombosis. The underlying mechanisms vary depending on the disease. It is estimated that dietary risk factors are associated with 53% of CVD deaths. Coronary artery disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease involve atherosclerosis. This may be caused by hypertension, high blood pressure, tobacco smoking, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of physical exercise, exercise, obesity, hypercholesterolaemia, high blood cholesterol, poor diet, excessive alcoholic beverage, alcohol consumption, and poor sleep, amo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMG-CoA Reductase Inhibitor
Statins (or HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors) are a class of medications that lower cholesterol. They are prescribed typically to people who are at high risk of cardiovascular disease. Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) carriers of cholesterol play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis and coronary heart disease via the mechanisms described by the lipid hypothesis. As lipid-lowering medications, statins are effective in lowering LDL cholesterol; they are widely used for primary prevention in people at high risk of cardiovascular disease, as well as in secondary prevention for those who have developed cardiovascular disease. Side effects of statins include muscle pain, increased risk of diabetes, and abnormal blood levels of certain liver enzymes. Additionally, they have rare but severe adverse effects, particularly muscle damage, and very rarely rhabdomyolysis. They act by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which plays a central role in the production of choleste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drugs
A drug is any chemical substance other than a nutrient or an essential dietary ingredient, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. Consumption of drugs can be via inhalation, injection, smoking, ingestion, absorption via a patch on the skin, suppository, or dissolution under the tongue. In pharmacology, a drug is a chemical substance, typically of known structure, which, when administered to a living organism, produces a biological effect. A pharmaceutical drug, also called a medication or medicine, is a chemical substance used to treat, cure, prevent, or diagnose a disease or to promote well-being. Traditionally drugs were obtained through extraction from medicinal plants, but more recently also by organic synthesis. Pharmaceutical drugs may be used for a limited duration, or on a regular basis for chronic disorders. Classification Pharmaceutical drugs are often classified into drug classes—groups of related drugs that hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |