|
HLA-A11
HLA-A11 (A11) is a human leukocyte antigen serotype within HLA-A "A" serotype group. The serotype is determined by the antibody recognition of α11 subset of HLA-A α-chains. For A11, the alpha "A" chain are encoded by the HLA-A allele group and the β-chain are encoded by B2M locus. This group currently is dominated by A*1101. A11 and A are almost synonymous in meaning. A11 is more common in East Asia than elsewhere, it is part of several long haplotypes that appear to have been frequent in the ancient peoples of Asia. Serotype Serotyping of A11 demonstrates better recognition of the *1101 gene products and poorer recognition of other A*11 gene products. There are ~40 recognized alleles of A*11. There is only one null classified as A11. In infectious disease Associations have been observed between A11 and familial otosclerosis, pulmonary tuberculosis, leprosy, and cytomegalovirus infection with epilepsy. These and other studies suggest an involvement between A11 and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History And Naming Of Human Leukocyte Antigens
Human leukocyte antigens (HLA) began as a list of antigens identified as a result of transplant rejection. The antigens were initially identified by categorizing and performing massive statistical analyses on interactions between blood types.Davis, Daniel M. The Compatibility Gene. How Our Bodies Fight Disease, Attract Others, and Define Our Selves. Oxford: Oxford UP, 2014. Print. This process is based upon the principle of serotypes. HLA are not typical antigens, like those found on surface of infectious agents. HLAs are Alloimmunity, ''allo''antigens, they vary from individual to individual as a result of genetic differences. An organ called the thymus is responsible for ensuring that any T-cells that attack self proteins are not allowed to live. In essence, every individual's immune system is tuned to the specific set of HLA and self proteins produced by that individual; where this goes awry is when tissues are transferred to another person. Since individuals almost always have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytomegalovirus
''Cytomegalovirus'' (CMV) (from ''cyto-'' 'cell' via Greek - 'container' + 'big, megalo-' + -''virus'' via Latin 'poison') is a genus of viruses in the order '' Herpesvirales'', in the family '' Herpesviridae'', in the subfamily '' Betaherpesvirinae''. Humans and other primates serve as natural hosts. The 11 species in this genus include '' human betaherpesvirus 5'' (HCMV, human cytomegalovirus, HHV-5), which is the species that infects humans. Diseases associated with HHV-5 include mononucleosis and pneumonia, and congenital CMV in infants can lead to deafness and ambulatory problems. In the medical literature, most mentions of CMV without further specification refer implicitly to human CMV. Human CMV is the most studied of all cytomegaloviruses. MX2/MXB protein was identified as a restriction factor for herpesviruses, which acts at a very early stage of the replication cycle and MX2/MXB restriction of herpesvirus requires GTPase activity. Taxonomy Within the '' Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is a cancer arising from the cervix or in any layer of the wall of the cervix. It is due to the abnormal growth of cells that can invade or spread to other parts of the body. Early on, typically no symptoms are seen. Later symptoms may include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse. While bleeding after sex may not be serious, it may also indicate the presence of cervical cancer. Virtually all cervical cancer cases (99%) are linked to genital human papillomavirus infection (HPV); most who have had HPV infections, however, do not develop cervical cancer. HPV 16 and 18 strains are responsible for approximately 70% of cervical cancer cases globally and nearly 50% of high grade cervical pre-cancers. Minor risk factors include smoking, a weak immune system, birth control pills, starting sex at a young age, and having many sexual partners. Genetic factors also contribute to cervical cancer risk. Cervical cancer typically develo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
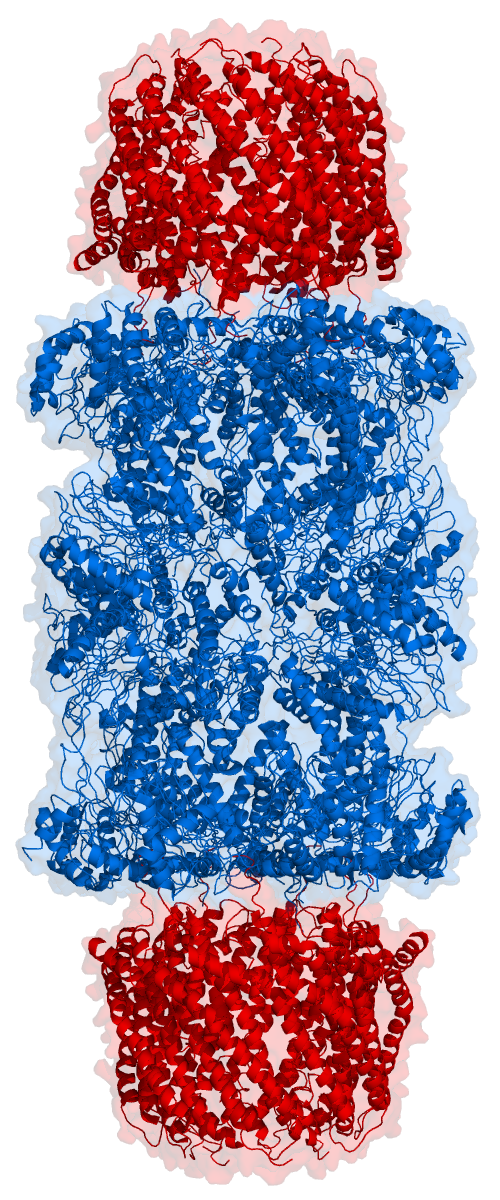
Proteosome
Proteasomes are essential protein complexes responsible for the degradation of proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases. Proteasomes are found inside all eukaryotes and archaea, and in some bacteria. In eukaryotes, proteasomes are located both in the cell nucleus, nucleus and in the cytoplasm. The proteasomal degradation pathway is essential for many cellular processes, including the cell cycle, the regulation of gene expression, and responses to oxidative stress. The importance of proteolytic degradation inside cells and the role of ubiquitin in proteolytic pathways was acknowledged in the award of the 2004 Nobel Prize in Chemistry to Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin Rose. The core 20S proteasome (blue in the adjacent figure) is a cylindrical, compartmental protein complex of four stacked rings forming a central pore. Each ring is composed of seven individual proteins. The inner t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TAP1
Transporter associated with antigen processing 1 (TAP1) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TAP1'' gene. A member of the ATP-binding cassette transporter family, it is also known as ABCB2. Function The membrane-associated protein encoded by this gene is a member of the superfamily of ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporters. ABC proteins transport various molecules across extra- and intra-cellular membranes. ABC genes are divided into seven distinct subfamilies (ABC1, MDR/TAP, MRP, ALD, OABP, GCN20, White). This protein is a member of the MDR/TAP subfamily. Members of the MDR/TAP subfamily are involved in multidrug resistance. The protein encoded by this gene is involved in the pumping of degraded cytosolic peptides across the endoplasmic reticulum into the membrane-bound compartment where class I molecules assemble. Mutations in this gene may be associated with ankylosing spondylitis, insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus, and celiac disease. See also * ATP-binding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytotoxic T-lymphocytes
A cytotoxic T cell (also known as TC, cytotoxic T lymphocyte, CTL, T-killer cell, cytolytic T cell, CD8+ T-cell or killer T cell) is a T lymphocyte (a type of white blood cell) that kills cancer cells, cells that are infected by intracellular pathogens such as viruses or bacteria, or cells that are damaged in other ways. Most cytotoxic T cells express T-cell receptors (TCRs) that can recognize a specific antigen. An antigen is a molecule capable of stimulating an immune response and is often produced by cancer cells, viruses, bacteria or intracellular signals. Antigens inside a cell are bound to class I MHC molecules, and brought to the surface of the cell by the class I MHC molecule, where they can be recognized by the T cell. If the TCR is specific for that antigen, it binds to the complex of the class I MHC molecule and the antigen, and the T cell destroys the cell. In order for the TCR to bind to the class I MHC molecule, the former must be accompanied by a glycoprotein call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Burkitt's Lymphoma
Burkitt's lymphoma is a cancer of the lymphatic system, particularly B lymphocytes found in the germinal center. It is named after Denis Parsons Burkitt, the Irish surgeon who first described the disease in 1958 while working in equatorial Africa. It is a highly aggressive form of cancer which often, but not always, manifests after a person develops acquired immunodeficiency from infection with Epstein–Barr virus, Epstein-Barr Virus or HIV, Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The overall cure rate for Burkitt's lymphoma in developed countries is about 90%. Burkitt's lymphoma is uncommon in adults, in whom it has a worse prognosis. Classification Burkitt lymphoma can be divided into three main clinical variants: the endemic, the Sporadic cancer, sporadic, and the immunodeficiency-associated variants. By morphology (biology), morphology (i.e., microscopic appearance), immunophenotype, and genetics, the variants of Burkitt lymphoma are alike. * The endemic variant (also called " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hodgkin's Lymphoma
Hodgkin lymphoma (HL) is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cell called lymphocytes, where multinucleated Reed–Sternberg cells (RS cells) are present in the lymph nodes. The condition was named after the English physician Thomas Hodgkin, who first described it in 1832. Symptoms may include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. Often, non-painful enlarged lymph nodes occur in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. Persons affected may feel tired or be itchy. The two major types of Hodgkin lymphoma are classic Hodgkin lymphoma and nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma. About half of cases of Hodgkin lymphoma are due to Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and these are generally the classic form. Other risk factors include a family history of the condition and having HIV/AIDS. Diagnosis is conducted by confirming the presence of cancer and identifying Reed–Sternberg cells in lymph node biopsies. The virus-positive cases are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epstein–Barr Virus
The Epstein–Barr virus (EBV), also known as human herpesvirus 4 (HHV-4), is one of the nine known Herpesviridae#Human herpesvirus types, human herpesvirus types in the Herpesviridae, herpes family, and is one of the most common viruses in humans. EBV is a DNA virus#Double-stranded DNA viruses, double-stranded DNA virus. EBV is the first identified oncogenic virus, a virus that can cause cancer. EBV establishes permanent infection in human B cells. It uncommonly causes infectious mononucleosis and is also tightly linked to many Malignancy, malignant diseases (cancers and autoimmune diseases). Various vaccine formulations have been tested in animals and humans; however, none of them were able to prevent EBV infection, thus, no vaccine has been approved to date. Infectious mononucleosis ("mono" or "glandular fever"), is characterized by extreme fatigue, fever, sore throat, and swollen lymph nodes. EBV is also associated with various non-malignant, premalignant, and malignant E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphoproliferative Disease
Lymphoproliferative disorders (LPDs) refer to a specific class of diagnoses, comprising a group of several conditions, in which lymphocytes are produced in excessive quantities. These disorders primarily present in patients who have a compromised immune system. Due to this factor, there are instances of these conditions being equated with " immunoproliferative disorders"; although, in terms of nomenclature, lymphoproliferative disorders are a subclass of immunoproliferative disorders—along with hypergammaglobulinemia and paraproteinemias. Lymphoproliferative disorders (examples) * Follicular lymphoma * Chronic lymphocytic leukemia * Acute lymphoblastic leukemia * Hairy cell leukemia * Hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) * B-cell lymphomas * T-cell lymphomas * Multiple myeloma * Waldenström's macroglobulinemia * Wiskott–Aldrich syndrome * Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) * Lymphocyte-variant hypereosinophilia * Pityriasis lichenoides (PL, PLC, PLVA) * Post-tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of Non-communicable disease, non-communicable Neurological disorder, neurological disorders characterized by a tendency for recurrent, unprovoked Seizure, seizures. A seizure is a sudden burst of abnormal electrical activity in the brain that can cause a variety of symptoms, ranging from brief lapses of awareness or muscle jerks to prolonged convulsions. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly, such as broken bones, or through causing accidents. The diagnosis of epilepsy typically requires at least two unprovoked seizures occurring more than 24 hours apart. In some cases, however, it may be diagnosed after a single unprovoked seizure if clinical evidence suggests a high risk of recurrence. Isolated seizures that occur without recurrence risk or are provoked by identifiable causes are not considered indicative of epilepsy. The underlying cause is often unknown, but epilepsy can result from brain injury, stroke, infections, Brain tumor, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |