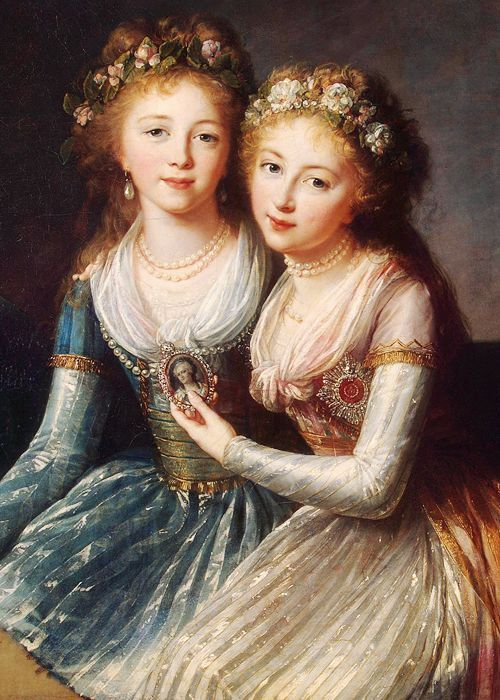|
Grand Duchess Alexandra Pavlovna Of Russia
Grand Duchess Alexandra Pavlovna of Russia (russian: Александра Павловна: 9 August 1783 S 29 Julyat Tsarskoye Selo – 16 March 1801 in Buda) was a daughter of Emperor Paul I of Russia and sister of emperors Alexander I and Nicholas I. She married Archduke Joseph of Austria, Palatine (Governor) of Hungary. Her marriage was the only Romanov- Habsburg marital alliance to date. Birth Grand Duchess Alexandra Pavlovna was born in Tsarskoye Selo as the third child and eldest daughter of Tsar Paul I of Russia and his second wife Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg (renamed Maria Feodorovna after her wedding). The sex of the child disappointed her paternal grandmother, Empress Catherine II. She wrote: The Empress' secretary Alexander Khrapovitsky wrote that the Empress considered the newborn Grand Duchess Alexandra very ugly, especially compared with her older brothers.Evgeny Karnovich: ''Alexandra Pavlovna'' in: ''Remarkable and enigmatic personalities of the 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archduke
Archduke (feminine: Archduchess; German: ''Erzherzog'', feminine form: ''Erzherzogin'') was the title borne from 1358 by the Habsburg rulers of the Archduchy of Austria, and later by all senior members of that dynasty. It denotes a rank within the former Holy Roman Empire (962–1806), which was below that of Emperor and King, roughly equal to Grand Duke, but above that of a Prince and Duke. The territory ruled by an Archduke or Archduchess was called an Archduchy. All remaining Archduchies ceased to exist in 1918. The current head of the House of Habsburg is Karl von Habsburg. Terminology The English word is first recorded in 1530, derived from Middle French ', a 15th-century derivation from Medieval Latin ', from Latin ''-'' ( Greek ) meaning "authority" or "primary" (see '' arch-'') and ' "duke" (literally "leader"). "Archduke" (german: Erzherzog; nl, Aartshertog) is a title distinct from "Grand Duke" (french: Grand-Duc; lb, Groussherzog; german: Großherzog; nl, Groothe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evgeny Karnovich
Evgeny Petrovich Karnovich (russian: Евге́ний Петро́вич Карно́вич; 15 November 1823 – 6 November 1885) was Russian writer, historian, journalist and editor. Born in rural Yaroslavl region into an affluent Ukrainian landlord's family, Karnovich started his literary career in the 1840s as a translator of Aristophanes' comedies and a poet, while working as a teacher, then a minor state official. Several years later he moved to Vilno, to become the head of the local Archeologist committee. In 1859, after retirement, Karnovich became a professional journalist, writing on the subjects of history, politics, social issues and jurisprudence, as well as publishing his own poems and stories. In 1858–1861 he was the head of the Contemporary Review section ''Sovremennik'', in 1865–1871, one of the leading figures in the ''Golos'' newspaper staff. He published the weekly magazine ''Mirovoi Posrednik'' (People's Attorney, 1861–1862), edited '' Birzhevyie Vedom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustaf Mauritz Armfelt
Count Gustaf Mauritz Armfelt (russian: Граф Густав-Маврикий Максимович Армфельт, tr, ; 31 March 1757 – 19 August 1814) was a Finnish- Swedish- Russian courtier and diplomat. In Finland, he is considered one of the greatest Finnish statesmen. His advice to Russia's Tsar Alexander I was of utmost importance for securing the autonomy of the Grand Duchy of Finland. Career Born in Tarvasjoki, Finland, he was the great grandson of Charles XII of Sweden's general, Carl Gustaf Armfeldt. In 1774, Armfelt became an ensign in the guards, but his frivolous behavior involving a duel provoked the displeasure of Gustav III of Sweden. As a result, he thought it prudent to go abroad 1778. Subsequently, however, in 1780, Armfelt met the king again at Spa in the Austrian Netherlands and completely won over the previously disgruntled monarch with his natural amiability, intelligence and social gifts. Henceforth, his fortune was made. At first, he was gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
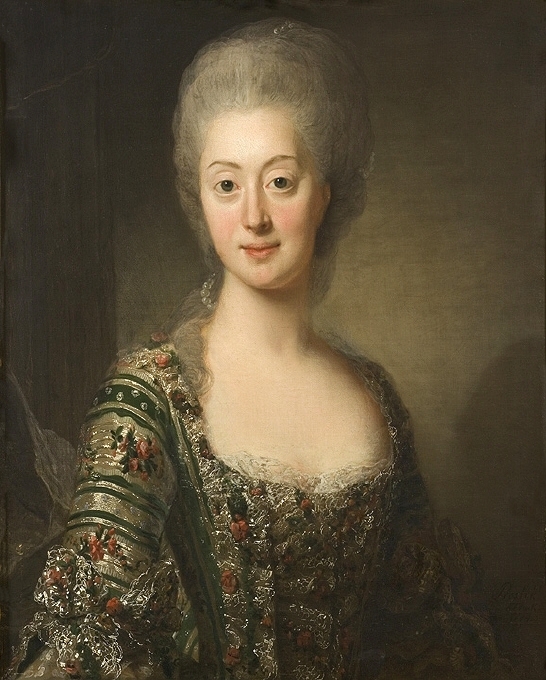
Elizabeth Alexeievna (Louise Of Baden)
Princess Louise of Baden (13/24 January 1779 – 4/16 May 1826) was, later known as Elizabeth Alexeievna ( rus, Елизавета Алексеевна), the Empress of Russia during her marriage with Emperor Alexander I. Princess of Baden Elizabeth Alexeievna was born in Karlsruhe, on as Princess Louise Maria Auguste of Baden of the House of Zähringen. She was the third of seven children of Charles Louis, Hereditary Prince of Baden, and his wife, Landgravine Amalie of Hesse-Darmstadt. At birth, the child was so small and weak that doctors feared that she would not live. Louise grew up in a close, warm family environment. She would remain particularly attached to her mother, with whom she maintained an intimate correspondence until her death (The Margravine of Baden outlived her daughter). She received a thoughtful education at the Baden court. She spoke and wrote both in French and German; studied history, geography, philosophy, and French and German literature.Rey, ''Alexan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
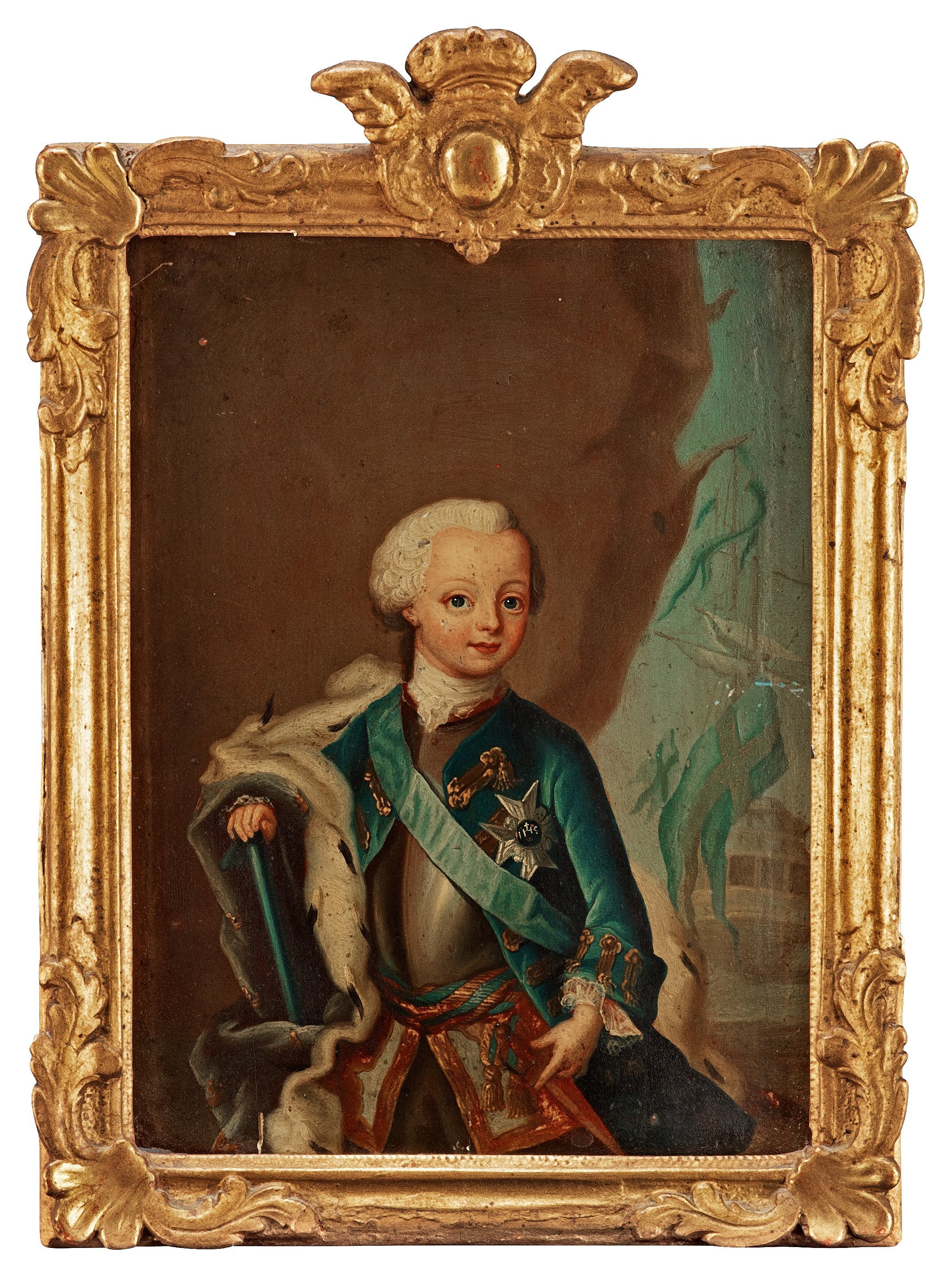
Charles XIII Of Sweden
Charles XIII, or Carl XIII ( sv, Karl XIII, 7 October 1748 – 5 February 1818), was King of Sweden from 1809 and King of Norway from 1814 to his death. He was the second son (and younger brother to King Gustav III) of King Adolf Frederick of Sweden and Louisa Ulrika of Prussia, sister of Frederick the Great. Though known as King Charles XIII in Sweden, he was actually the seventh Swedish king by that name, as Charles IX (reigned 1604–1611) had adopted his numeral after studying a fictitious history of Sweden. In Norway he is known as Charles II. Early life Prince Charles was placed under the tutelage of Hedvig Elisabet Strömfelt and then Ulrica Schönström. He was appointed grand admiral when he was but few days old. He was described as a good dancer at the amateur theatre of the royal court. Reportedly he was not very close to his mother. The Queen preferred her youngest children, Sophie Albertine and Frederick Adolf.Alma Söderhjelm (1945). ''Gustav III:s sysko ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Värälä
The Treaty of Värälä (sometimes known as the Treaty of Wereloe) was signed in Värälä, Elimäki, Elimäki Municipality, Finland under Swedish rule, Finland, between Russian Empire, Russia (represented by Otto Heinrich Igelström) and Gustavian era, Sweden (represented by Gustaf Mauritz Armfelt).Похлебкин В.В. Внешняя политика Руси, России и СССР за 1000 лет в именах, датах, фактах: Справочник. - М.: Междунар. отношения, 1995 It was signed on 14 August 1790 and concluded the Russo-Swedish War (1788-1790), Russo-Swedish War. The treaty confirmed ''status quo ante bellum'' with respect to the borders; however, Russia's right to interfere with Swedish interior affairs from the Treaty of Nystad was expressly revoked. The provisions of the previous Treaty of Abo were basically confirmed. A year later, on 19 October 1791, a convention was signed in Stockholm, whereby the countries pledged to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav IV Adolf Of Sweden
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland. The occupation of Finland in 1808–09 by Russian forces was the immediate cause of Gustav's violent overthrow by officers of his own army. Following his abdication on 29 March 1809, an Instrument of Government was hastily written, which severely circumscribed the powers of the monarchy. The "Instrument" was adopted in 1809 on 6 June, the National Day of Sweden now as well as in his time. It remained in force until replaced in 1974. The crown, now with strictly limited powers, passed to Gustav's uncle Charles XIII, who had no legitimate children; this want of heirs set into motion the quest for a successor, who was found the following year in the person of Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, the first monarch of the present royal family. ch 37 pp 203-19 Early life Gustav Adol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gustav III Of Sweden
Gustav III (29 March 1792), also called ''Gustavus III'', was King of Sweden from 1771 until his assassination in 1792. He was the eldest son of Adolf Frederick of Sweden and Queen Louisa Ulrika of Prussia. Gustav was a vocal opponent of what he saw as the abuse of political privileges seized by the nobility since the death of King Charles XII. Seizing power from the government in a coup d'état, called the Swedish Revolution, in 1772 that ended the Age of Liberty, he initiated a campaign to restore a measure of Royal autocracy, which was completed by the Union and Security Act of 1789, which swept away most of the powers exercised by the Swedish Riksdag (parliament) during the Age of Liberty, but at the same time it opened up the government for all citizens, thereby breaking the privileges of the nobility. A bulwark of enlightened absolutism, Gustav spent considerable public funds on cultural ventures, which were controversial among his critics, as well as military at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
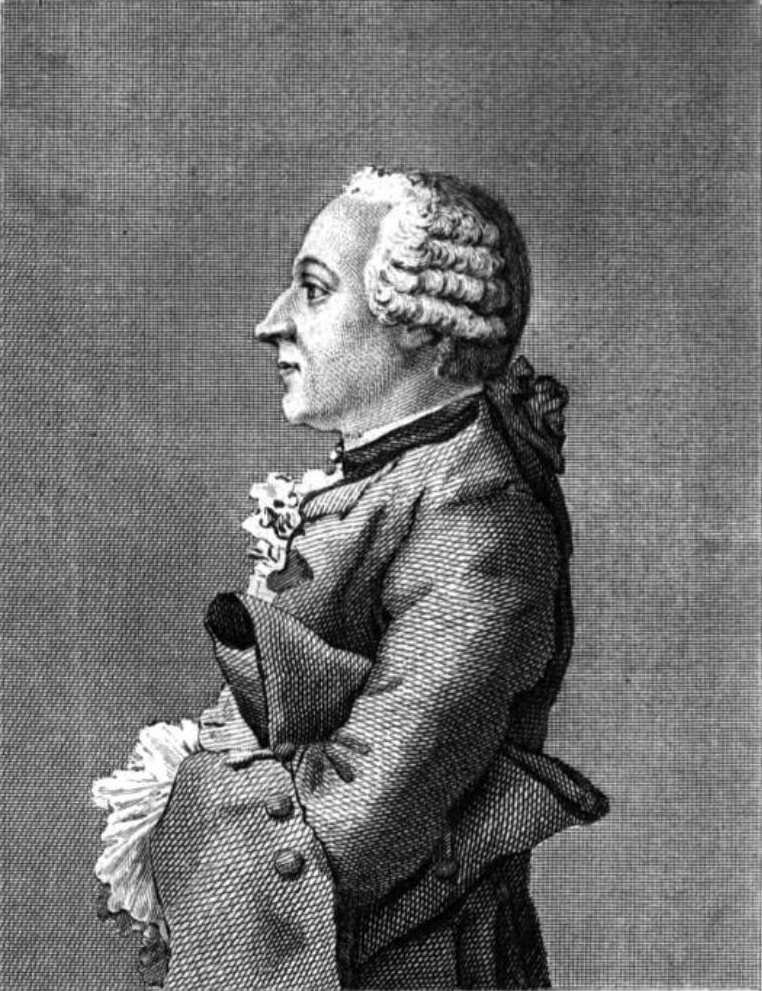
Friedrich Melchior, Baron Von Grimm
Friedrich Melchior, Baron von Grimm (26 September 172319 December 1807) was a German-born French-language journalist, art critic, diplomat and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie ou Dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers''. In 1765 Grimm wrote ''Poème lyrique'', an influential article for the Encyclopédie on lyric and opera librettos. Like Christoph Willibald Gluck and Ranieri de' Calzabigi, Grimm became interested in opera reform. According to Martin Fontius, a German literary theorist, "sooner or later a book entitled ''The Aesthetic Ideas of Grimm'' will have to be written." Early years Grimm was born at Regensburg, the son of Johann Melchior Grimm (1682–1749), a pastor, and Sibylle Margarete Grimm, (''née'' Koch) (1684–1774). He studied at the University of Leipzig, where he came under the influence of Johann Christian Gottsched and of Johann August Ernesti, to whom he was largely indebted for his critical appreciation of classical literatu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandra Pavlovna Of Russia In Russian Dress By Anonim (1790s, Gatchina)
Alexandra () is the feminine form of the given name Alexander (, ). Etymologically, the name is a compound of the Greek verb (; meaning 'to defend') and (; GEN , ; meaning 'man'). Thus it may be roughly translated as "defender of man" or "protector of man". The name Alexandra was one of the epithets given to the Greek goddess Hera and as such is usually taken to mean "one who comes to save warriors". The earliest attested form of the name is the Mycenaean Greek ( or //), written in the Linear B syllabic script.Tablet MY V 659 (61). Alexandra and its masculine equivalent, Alexander, are both common names in Greece as well as countries where Germanic, Romance, and Slavic languages are spoken. Variants * Alejandra, Alejandrina (diminutive) ( Spanish) * Aleksandra (Александра) ( Albanian, Bulgarian, Estonian, Latvian, Lithuanian, Macedonian, Polish, Russian, Serbo-Croatian) * Alessandra ( Italian) * Alessia (Italian) * Alex (various languages) * Alexa (En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlotte Von Lieven
Charlotte Margarete Fürstin von Lieven (Née Baroness von Gaugreben; 1748–1828), was a Russian princess of German origin and an Imperial governess. Early life She was born as daughter of Carl Caspar, Baron von Gaugreben (1716-1767) and Baroness Agnes Posse of Säby (b.1727). Charlotte married Baron Otto Heinrich von Lieven (1726-1781), member of one of the oldest aristocratic families of German Baltic origin. Court life She was in 1783 appointed with the task of educating his daughters and younger sons - Nicholas and Mikhail Pavlovich Grand Duke Mikhail Pavlovich of Russia (russian: Михаи́л Па́влович; ''Mikhail Pavlovich'') (8 February 1798 S 28 January– 9 September 1849 S 28 August was a Russian grand duke, the tenth child and fourth son of Paul I o .... She had a strong and influential position within the contemporary Russian court. References Alexander von Lieven: Der General Baron Otto Heinrich von Lieven und seine Gemahlin, die Staats ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elena Pavlovna
Elena Pavlovna (; 24 December 1784 S 13 December– 24 September 1803) was born a grand duchess of Russia as the daughter of Paul I, Emperor of all the Russias and later became the Hereditary Grand Duchess of Mecklenburg-Schwerin as the wife of Frederick Louis of Meclenburg-Schwerin (1778–1819). Early life Grand Duchess Elena Pavlovna Romanova of Russia was born in Saint Petersburg in the Russian Empire as the fourth child and second daughter of Tsesarevich Paul Petrovich of Russia (1754–1801) and his second wife, Tsesarevna Maria Feodorovna, born Duchess Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg (1759–1828). Out of her nine siblings, Elena was closest to her older sister Alexandra Pavlovna (1783–1801). She was educated privately at home, for the first years, under the supervision of her paternal grandmother, Catherine the Great (1729–1796). Her education was focused mainly on fine arts, literature and music. Marriage and life in Schwerin Marriage In 1798, negotiat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |