|
Godfrey Of Heinsberg, Count Of Loon
Godfrey de Heinsberg (died 1395), Lord of Daelenbroeck, Count of Looz and Count of Chiny (1361–1362), son of John of Heinsberg, Lord of Daelenbroeck (brother of the preceding count Thierry de Heinsberg). Upon the death of his uncle Thierry in 1361, Godfrey claimed his estates and proclaimed himself Count of Looz and Chiny. However, Engelbert III of the Marck, Prince-Bishop of Liege, was far less merciful to Godfrey than to Thierry, and pursued the claims to the counties that Adolph of the Marck had negotiated with Louis IV the Younger in an agreement in 1190. This is interesting (but not surprising) in that Engelbert was the brother-in-law of Godfrey, having married Richardis of Jülich (died 1360), sister of Godfrey’s wife Philippa. Engelbert proclaimed the annexation of Looz and Chiny for the Chapter of St. Lambert in Liege on May 5, 1361, and his troops occupied the county from June 1361. On January 25, 1362, Godfrey sold the counties and their rights to Arnold of Rumi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
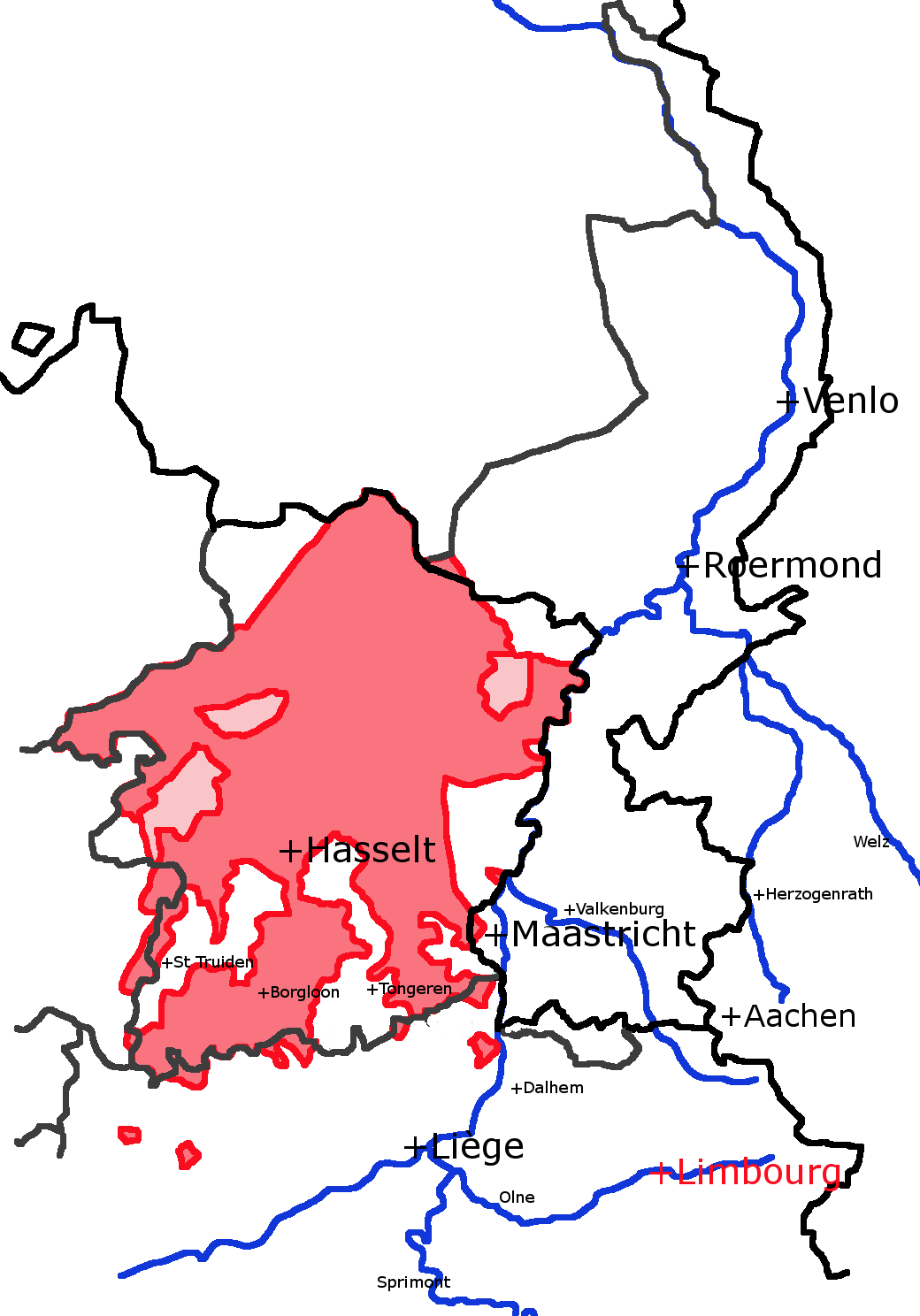
Count Of Looz
The County of Loon ( , , ) was a county in the Holy Roman Empire, which corresponded approximately with the Belgian province of Limburg (Belgium), Limburg. It was named after the original seat of its count, Loon, which is today called Borgloon. During the middle ages the counts moved their court to a more central position in Kuringen, which is today a part of Hasselt, the modern capital of the region. From its beginnings, Loon was associated with the Prince-bishop of Liège and by 1190 the count had come under the bishop's overlordship. In the fourteenth century the male line ended for a second time, at which point the prince-bishops themselves took over the county directly. Loon approximately represented the Dutch-speaking (archaic ) part of the princedom. All of the Dutch-speaking towns in the Prince-Bishopric, with the status of being so-called "Good Cities" (french: bonnes villes), were in Loon, and are in Belgian Limburg today. These were Beringen, Belgium, Beringen, Bilzen, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Counts Of Chiny
The counts of Chiny were part of the nobility of Lotharingia that ruled from the 9th to the 14th century in what is now part of Belgium. It has been proposed that the County of Chiny was created in the early 10th century out of the ancient county of Ivois. The county now forms part of the province of Luxembourg in present-day Belgium. The county of Chiny included the present-day cantons of Virton, Etalle, Florenville, Neufchâteau, Montmédy and Carignan, as well as the castles of Warcq on the Meuse, which was built in 971 by Otto, ancestor of the later Counts of Chiny. It has also been proposed that there is a close relationship between the counts of Chiny and the early counts of Looz, the counts of Verdun and the bishops of Verdun.Jeantin, J. François Louis. (185859)Histoire du comté de Chiny et des pays haut-wallons Paris: J. Tardieu. The family of the counts of Chiny merged with the family of the counts of Looz. The final count of Chiny, Arnold IV de Rumingy, sold the coun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thierry De Heinsberg, Count Of Looz
Diederik of Heinsberg (French: ''Thierry'', German: ''Dietrich'', English: ''Theodoric'') (died between 17 and 21 January 1361), Count of Loon (French: ''Looz'') and Count of Chiny (1336-1361), was the son of Godfrey II, Lord of Heinsberg (son of Diederik, Lord of Heinsberg, and Joanna of Leuven), and Matilda (daughter of Arnold V, Count of Loon and Chiny, and Marguerite Vianden). In 1336, Diederik's uncle Louis IV, Count of Loon and Chiny, died without having had children, and a succession crises emerged. An agreement of 1190 stipulated that if the House of Loon were extinguished, the county would then be integrated with the Principality of Liège. The reaction of the Chapter of Saint-Lambert was immediate. The Prince-Bishop of Liège Adolph of La Marck moved to incorporate the County of Loon into the principality, while Diederik maneuvered to assume the title of count. However, since Diederik had married Adolph's sister and the bishop was fond of their son, family relations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engelbert III Of The Marck, Archbishop Of Cologne
Engelbert III von der Mark (English: Engelbert III of the Mark) (1304 – 25 August 1368) was the Archbishop-Elector of Cologne from 1364 until 1368 and the Prince-Bishop of Liège (as Engelbert) from 1345 until 1364. Engelbert was the second son of Count Engelbert II of the Mark. Through the influence of his uncle Adolph II of the Marck, Bishop of Liège, he became the Provost of Liège in 1332. Later he was also mentioned as being a Provost in Cologne. After the death of his uncle, he was appointed Prince-Bishop of Liège by Pope Clement VI. In 1362 he applied to become the Archbishop-Elector of Cologne, but his nephew Adolph III gained it in 1363. Nevertheless, after Adolph abdicated in the following year he was appointed Archbishop-Elector in 1364 by Pope Urban V and resigned the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. Engelbert was beset by health problems soon after taking office. In 1366 he accepted coadjutors to assist in the running of the archdiocese, and the Archbishop-Elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Bishops And Prince-bishops Of Liège
This is a list of the bishops and prince-bishops of Liège. It includes the bishops of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Liège and its predecessor see of Tongeren and Maastricht. From 972 to 1795, the bishops of Liège also ruled a lordship (not co-extensive with their diocese) known as the Prince-Bishopric of Liège. Bishops of Tongeren-Maastricht-Liège, 315–971 See in Tongeren (4th-century) * St. Maternus of Tongeren (?) (c. 315) *Saint Servatius (342–384) See in Maastricht (380s? to 718) * Falco (c. 498–c. 512) *Domitian (?–560) * Saint Monulphus (549–588) * Saint Gondulphus (589–614) * Saint Ebregise ? (614–627) * Saint John I Agnus (627–647) *Saint Amand (647–650) *Saint Remaclus (652–662) * Saint Theodard (662–669) * Saint Lambert, patron saint of the diocese (669–705 or later) *Saint Hubert, patron saint of the city (705 or before – 727) See in Maastricht and/or Liège (718 to 810) *Floribert of Liège (727–736 or 738) * (736 or 738–769) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis IV Of Chiny
Louis IV the Young (1173 – 7 October 1226), count of Chiny from 1189 to 1226, son of Louis III, count of Chiny, and Sophie. Louis was the last of the first dynasty of counts of Chiny. Having no son, he prepared his eldest daughter Jeanne as his successor. Louis marked his reign by issuing the first postage stamp in the county. He succeeded as count in 1189 when his father died on the Third Crusade, but was under the supervision of his mother and uncle Thierry, Lord of Mellier, because of his young age. He likely participated in the Albigensian Crusade, where he died in Cahors. He married Matilda of Avesnes, widow of Nicolas IV, Lord of Rumigny, and daughter of James, Lord of Avesnes and Conde, and Adele, Lady of Guise. They had three children: * Jeanne, Countess of Chiny, married to Arnold IV, Count of Looz * Agnes, Lady of Givet and Abemont * Isabelle, married to Otto, Lord of Trazegnies. Isabelle was referred to as Madame de Florenville during the Tournament of Chauven ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arnold VI De Rumigny, Count Of Looz
Arnold VI de Rumigny (died May 1373), Count of Looz and Count of Chiny (as Arnold IV) (1362–1364), son of William of Oreye, Lord of Rumigny (by donation of Louis IV, Count of Looz in 1331), and Jeanne de Looz, daughter of Arnold V, Count of Loon and Chiny, and, Marguerite Vianden, Lady of Perwez and Grimbergen. In 1336, at the death of his uncle, Louis IV, Count of Loon and Chiny, Arnold laid claim to the estates, but without success. Instead, the estates passed to another nephew, Thierry de Heinsberg. Finally, on January 25, 1362, he bought the rights to the counties from his cousin Godfrey, Count of Looz and Chiny. Looz, however, was still occupied by the troops of Engelbert III of the Marck, Prince-Bishop of Liege. On December 25, Arnold approached the Emperor Charles IV for his help in financing the reconquest of Looz, but he failed in that endeavor. Without options, he sold the counties to Wenceslaus Wenceslaus, Wenceslas, Wenzeslaus and Wenzslaus (and other similar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William V, Duke Of Jülich
William V, Duke of Jülich ( – 25/26 February 1361) was a German nobleman. Some authors call him William I, because he was the first ''Duke of Jülich''; the earlier Williams had been ''Count of Jülich''. Other authors call the subject of this article "William VI"; they count the son and co-ruler of William IV as William V. William V was the eldest son of Gerhard V of Jülich and Elisabeth of Brabant-Aarschot, daughter of Godfrey of Brabant.Walther Möller, ''Stammtafeln westdeutscher Adelsgeschlechter im Mittelalter'' (Darmstadt, 1922, reprint Verlag Degener & Co., 1995), Vol. 1, page 14. William V was a key political figure of his time, being a brother-in-law to both Edward III of England and Emperor Ludwig IV. He spent enormous sums of money to have his brother Walram of Jülich appointed as Archbishop of Cologne over Adolph II of the Marck. In 1337 he was crucially involved in the German-English alliance which caused the start of the Hundred Years' War. William was an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joanna Of Hainaut
Joanna of Hainault (1315–1374) was a Duchess of Jülich by marriage to William V, Duke of Jülich. She was the third daughter of William I, Count of Hainaut, and Joan of Valois. She was a younger sister of Philippa of Hainault, Queen of England, and Margaret II, Countess of Hainault. Life Joanna married William V, Duke of Jülich, their children were as follows: *Gerhard VI of Jülich, Count of Berg and Ravensberg, grandfather of Adolph I, Duke of Cleves *William II, Duke of Jülich *Richardis of Jülich, married Count Engelbert III of the Mark *Philippa of Jülich, married Godfrey II of Heinsberg *Reinold *Joanna of Jülich, married William I, Count of Isenburg-Wied *Isabella of Jülich, married John Plantagenet, 3rd Earl of Kent Ancestry {{ahnentafel , collapsed=yes , align=center , boxstyle_1=background-color: #fcc; , boxstyle_2=background-color: #fb9; , boxstyle_3=background-color: #ffc; , boxstyle_4=background-color: #bfc; , boxstyle_5=background-color: #9fe; , 1= 1. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John II Of Loon
John II of Loon (died 1438), Lord of Jülich, Heinsberg and Löwenberg (''Herr zu Julich und Heinsberg''), son of Godfrey de Heinsberg, Count of Looz, and Philippa of Jülich, daughter of William V, Duke of Jülich, and Joanna of Hainaut. Although John was the first son of Godfrey, he did not inherit the countship of Looz, the title instead going to Arnold of Rumingy. John married first Margaret (Margareta van Gennep, died 1419) and second Anna of Solms (d. 1433) Countess of Solms-Braunfels. John and Margaret had four children: * Johann III (died before 1441), married Walpurg von Mörs. Their daughter Margaret married Philip II of Nassau-Weilburg. * Wilhelm I (died 24 April 1439), married Elizabeth von Blankenheim, daughter of Gerhard IX, Count of Blankenheim, great-great-grandson of Gerard I, Count of Durbuy. * John of Heinsberg (died 1459), Bishop of Liège (1419-1455) * Philippa (died 1464), married Wilhelm von Wied-Isenburg. John and Anna of Solms-Braunfels had two child ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utrecht
Utrecht ( , , ) is the List of cities in the Netherlands by province, fourth-largest city and a List of municipalities of the Netherlands, municipality of the Netherlands, capital and most populous city of the Provinces of the Netherlands, province of Utrecht (province), Utrecht. It is located in the eastern corner of the Randstad conurbation, in the very centre of mainland Netherlands, about 35 km south east of the capital Amsterdam and 45 km north east of Rotterdam. It has a population of 361,966 as of 1 December 2021. Utrecht's ancient city centre features many buildings and structures, several dating as far back as the High Middle Ages. It has been the religious centre of the Netherlands since the 8th century. It was the most important city in the Netherlands until the Dutch Golden Age, when it was surpassed by Amsterdam as the country's cultural centre and most populous city. Utrecht is home to Utrecht University, the largest university in the Netherlands, as well as seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maastricht
Maastricht ( , , ; li, Mestreech ; french: Maestricht ; es, Mastrique ) is a city and a municipality in the southeastern Netherlands. It is the capital and largest city of the province of Limburg. Maastricht is located on both sides of the Meuse ( nl, Maas), at the point where the Jeker joins it. Mount Saint Peter (''Sint-Pietersberg'') is largely situated within the city's municipal borders. Maastricht is about 175 km south east of the capital Amsterdam and 65 km from Eindhoven; it is adjacent to the border with Belgium and is part of the Meuse-Rhine Euroregion, an international metropolis with a population of about 3.9 million, which includes the nearby German and Belgian cities of Aachen, Liège and Hasselt. Maastricht developed from a Roman settlement (''Trajectum ad Mosam'') to a medieval religious centre. In the 16th century it became a garrison town and in the 19th century an early industrial centre. Today, the city is a thriving cultural and regional hub. It beca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
