|
Geography Of Equatorial Guinea
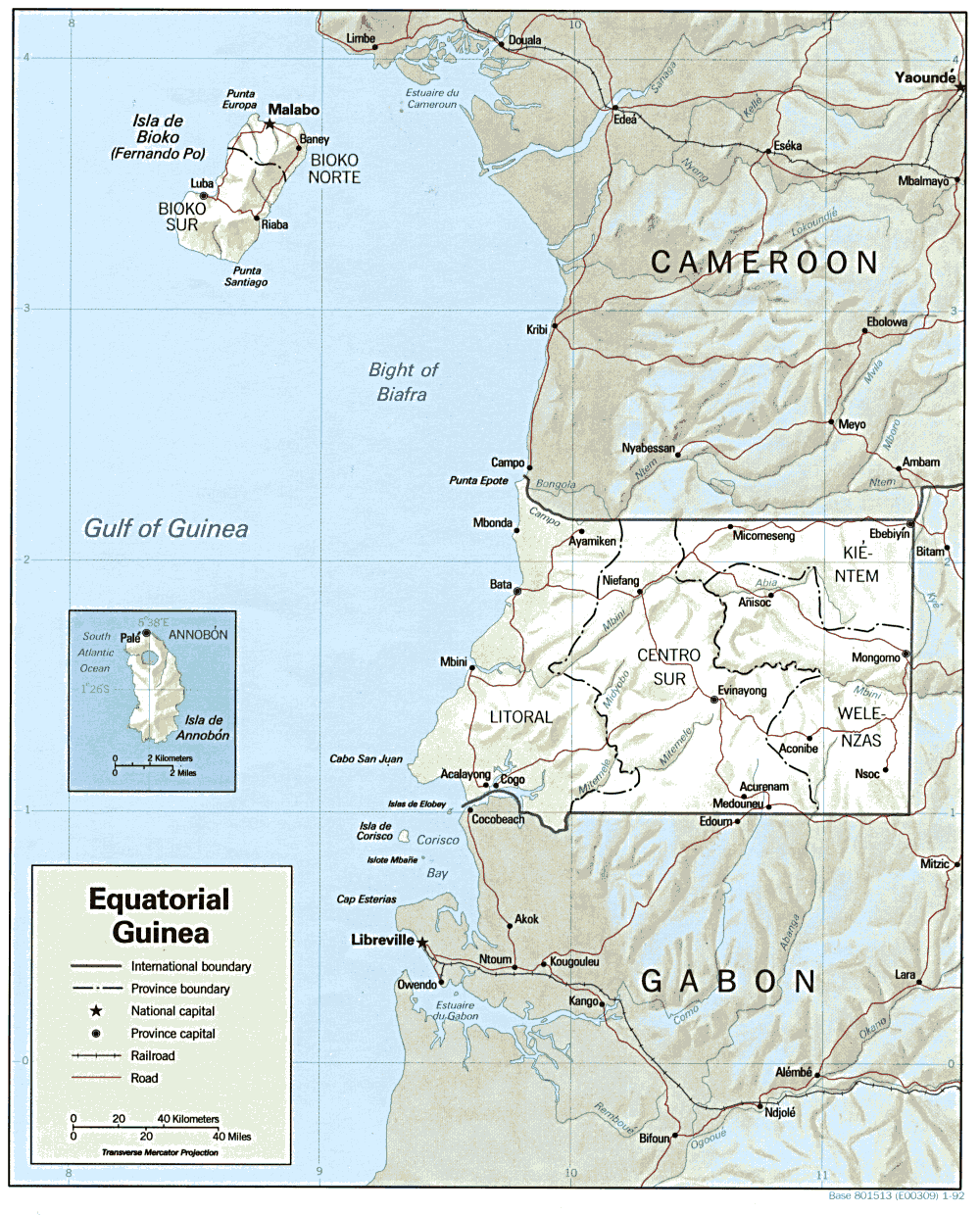
The Republic of Equatorial Guinea is located in west central Africa. Bioko Island lies about from Cameroon. Annobón Island lies about southwest of Bioko Island. The larger continental region of Río Muni lies between Cameroon and Gabon on the mainland; it includes the islands of Corisco, Elobey Grande, Elobey Chico, and adjacent islets. The total land area is . It has an Exclusive Economic Zone of . Bioko Island, called Fernando Po until the 1970s, is the largest island in the Gulf of Guinea - . It is shaped like a boot, with two large volcanic formations separated by a valley that bisects the island at its narrowest point. The coastline is steep and rugged in the south but lower and more accessible in the north, with excellent harbors at Malabo and Luba, and several scenic beaches between those towns. On the continent, Río Muni covers . The coastal plain gives way to a succession of valleys separated by low hills and spurs of the Crystal Mountains. The Rio Benito (Mbini) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Guinea Map
{{Disambiguation ...
Equatorial may refer to something related to: *Earth's equator **the tropics, the Earth's equatorial region **tropical climate *the Celestial equator ** equatorial orbit **equatorial coordinate system ** equatorial mount, of telescopes * equatorial bond, a type of chemical bond orientation See also * * Equator (other) An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and midway between the poles. On Earth, ''the Equator'', at 0° latitude, divides the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. Equator ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annobón
Annobón ( es, Provincia de Annobón; pt, Ano-Bom), and formerly as ''Anno Bom'' and ''Annabona'', is a province (smallest province in both area and population) of Equatorial Guinea consisting of the island of Annobón, formerly also Pigalu and Pagalu, and its associated islets in the Gulf of Guinea. According to the 2015 census, Annobón had 5,314 inhabitants, a small population increase from the 5,008 registered by the 2001 census. The official language is Spanish but most of the inhabitants speak a creole form of Portuguese. The island's main industries are fishing and forestry. Annobón is the only island of the country located in the Southern Hemisphere of the Atlantic Ocean. The provincial capital is San Antonio de Palé on the north side of the island; the other town is Mabana, formerly known as San Pedro. The roadstead is relatively safe, and some passing vessels take advantage of it in order to obtain water and fresh provisions, of which Annobón has offered an abu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bight Of Biafra
The Bight of Biafra (known as the Bight of Bonny in Nigeria) is a bight off the West African coast, in the easternmost part of the Gulf of Guinea. Geography The Bight of Biafra, or Mafra (named after the town Mafra in southern Portugal), between Capes Formosa and Lopez, is the most eastern part of the Gulf of Guinea; it contains the islands Bioko quatorial Guinea São Tomé and Príncipe. The name Biafra – as indicating the country – fell into disuse in the later part of the 19th century A 1710 map indicates that the region known as "Biafra" (Biafra) was located in present-day Cameroon. The Bight of Biafra extends east from the River Delta of the Niger in the north until it reaches Cape Lopez in Gabon. Besides the Niger River, other rivers reaching the bay are the Cross River, Calabar River, Ndian, Wouri, Sanaga, Nyong River, Ntem, Mbia, Mbini, Muni and Komo River. The main islands in the Bay are Bioko and Príncipe; other important islands are Ilhéu Bom Bom, Ilhéu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rio Benito
The Benito is a river in Equatorial Guinea. It is known locally as the Mbini River, and, at least as it flows in its westerly part through the Monte Alen National Park, as the Uoro River. The river rises in Gabon and crosses into Equatorial Guinea where it divides the country roughly along the middle, running east to west. At the mouth to the Atlantic Ocean lies the town of Mbini, as well as large mangrove stands that extend inland. Only this portion of the river is navigable. The river is used to float logs for forestry operations.''The geography of modern Africa'' By William Adams Hance, p. 291 (on Google Books The cichlid genus Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of living and fossil organisms as well as viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family. In binomial nom ... '' Benitochromis'' takes the first part of its name from the Benito River. References R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crystal Mountains (Africa)
Crystal Mountains (''Monts de Cristal'') is a group of low mountains (or hills, as all peaks are below 1,000m) inland of the Atlantic coast of Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, the Republic of the Congo, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, and Angola. It is the edge of the interior Woleu-Ntem Plateau against the coastal lowland which has a steep descent deeply cut by streams and waterfalls. Part of the area is preserved in Gabon as the Crystal Mountains National Park Crystal Mountains National Park (french: Parc National des Monts de Cristal) is a twin park and one of the 13 national parks of Gabon. It is situated in the Monts de Crystal on the western edge of the Woleu-Ntem Plateau, between Equatorial Gui .... Mont Mbilan is the highest point (about 925m) in the park. Seni Mont (611m) receives the highest rainfall in all of Gabon (350 cm/year). Fauna Two species of frogs, '' Leptopelis crystallinoron'' and '' Leptodactylodon stevarti'', are only known from the Crystal Mount ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luba, Equatorial Guinea
Luba (formerly San Carlos) (pop. 7,000) is the second-largest town on Bioko in Equatorial Guinea, a port for the logging industry on the island's west coast beneath volcanic peaks. Attractions in Luba include several beaches and a colonial hospital. The city may be reached either by sea or by a main road linking Luba to the country's capital, Malabo. The road is now accessible; it takes about an hour to drive from Malabo to Luba. In 1999, a free port opened near the town, creating deepwater access for larger and oil industry vessels, an alternative to the congested port of Malabo for re-supplying on fuel, water and other materials. As of 2010 a new highway was under construction from Luba via Belebú Balachá through the Luba Crater Scientific Reserve The Gran Caldera de Luba Scientific Reserve ( es, Reserva Científica de la Gran Caldera de Luba) is a protected area of on the volcanic island of Bioko (formerly called Fernando Pó), a part of Equatorial Guinea. The dense rai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malabo
Malabo ( , ; formerly Santa Isabel) is the capital of Equatorial Guinea and the province of Bioko Norte. It is located on the north coast of the island of Bioko, ( bvb, Etulá, and as ''Fernando Pó'' by the Europeans). In 2018, the city had a population of approximately 297,000 inhabitants. Spanish is the official language of the city and of the country as well, but Pichinglis is used as a language of wider communication across Bioko island, including Malabo. Malabo is the oldest city in Equatorial Guinea. Ciudad de la Paz is a planned community under construction in mainland Equatorial Guinea which was designed to replace Malabo as the capital. The institutions of governance of Equatorial Guinea began the process of locating to Ciudad de la Paz in February 2017. History European discovery and Portuguese occupation In 1472, in an attempt to find a new route to India, the Portuguese navigator Fernão do Pó, encountered the island of Bioko, which he called ''Formosa''.Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Guinea
The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in the gulf. Among the many rivers that drain into the Gulf of Guinea are the Niger River, Niger and the Volta River, Volta. The coastline on the gulf includes the Bight of Benin and the Bight of Bonny. Name The origin of the name Guinea is thought to be an area in the region, although the specifics are disputed. Bovill (1995) gives a thorough description: The name "Guinea (region), Guinea" was also applied to south coast of West Africa, north of the Gulf of Guinea, which became known as "Upper Guinea", and the west coast of Southern Africa, to the east, which became known as "Lower Guinea". The name "Guinea" is still attached to the names of three countries in Africa: Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, and Equatorial Guinea, as well as New Guinea in Mel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elobey Chico
Elobey Chico, or Little Elobey, is a small island off the coast of Equatorial Guinea, lying near the mouth of the Mitémélé River. The island is now uninhabited but was once the ''de facto'' colonial capital of the Spanish territory of Río Muni Río Muni (called ''Mbini'' in Fang) is the Continental Region (called ''Región Continental'' in Spanish) of Equatorial Guinea, and comprises the mainland geographical region, covering . The name is derived from the Muni River, along which .... Officially, the island was associated with Fernando Pó, but the connection seemed to be little more than fiction. The majority of the factories were owned by Hamburg Merchants.Elisee Reclus, ''Africa, Vol.3'', p.402 See also * Elobey, Annobón and Corisco References Islands of Equatorial Guinea Uninhabited islands {{EquatorialGuinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elobey Grande
Elobey Grande, or Great Elobey, is an island of Equatorial Guinea, lying at the mouth of the Mitémélé River. It is sparsely inhabited. Elobey Chico is a smaller island offshore, now uninhabited but once the colonial capital of the Río Muni. The island is located in the Gulf of Guinea The Gulf of Guinea is the northeasternmost part of the tropical Atlantic Ocean from Cape Lopez in Gabon, north and west to Cape Palmas in Liberia. The intersection of the Equator and Prime Meridian (zero degrees latitude and longitude) is in .... See also * Elobey, Annobón and Corisco References Islands of Equatorial Guinea {{EquatorialGuinea-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |