|
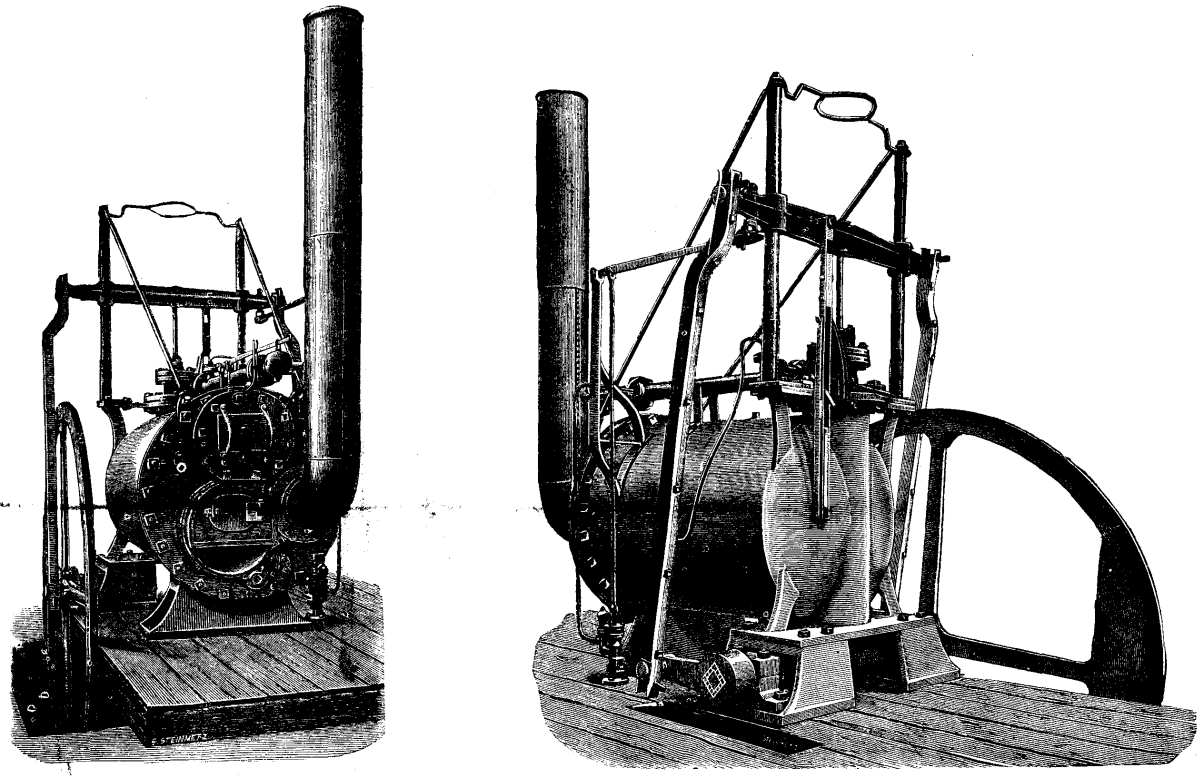
Geared Steam Locomotive
A geared steam locomotive is a type of steam locomotive which uses gearing, usually reduction gearing, in the drivetrain, as opposed to the common directly driven design. This gearing is part of the machinery within the locomotive and should not be confused with the pinion that propels a rack locomotive along the rack between the rails. The geared steam locomotives that have been built have been for conventional track, relying on the adhesion between wheels and rail. Explanation and rationale The steam locomotive, as commonly employed, has its pistons directly attached to cranks on the driving wheels; thus, there is no gearing, one revolution of the driving wheels is equivalent to one revolution of the crank and thus two power strokes per piston (steam locomotives are almost universally double-acting, unlike the more familiar internal combustion engine). The maximum rotational speed is fairly fixed for a given engine technology. Given the lack of any variable-ratio transmis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shay Locomotive
The Shay locomotive is a geared steam locomotive that originated and was primarily used in North America. The locomotives were built to the patents of Ephraim Shay, who has been credited with the popularization of the concept of a ''geared steam locomotive''. Although the design of Ephraim Shay's early locomotives differed from later ones, there is a clear line of development that joins all Shays. Shay locomotives were especially suited to logging, mining and industrial operations and could operate successfully on steep or poor quality track. Development Ephraim Shay (1839–1916), was a schoolteacher, a clerk in an American Civil War hospital, a civil servant, a logger, a merchant, a railway owner, and an inventor who lived in Michigan. In the 1860s, he became a logger and wanted a better way to move logs to the mill than on winter snow sleds. He built his own tramway in 1875, on gauge track on wooden ties, allowing him to log all year round. Two years later he develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ephraim Shay
Ephraim Shay (July 17, 1839 – April 19, 1916) was an American merchant, entrepreneur and self-taught railroad engineer who worked in the state of Michigan. He designed the first Shay locomotive and patented the type. He licensed it for manufacture through what became known as Lima Locomotive Works in Ohio; from 1882 to 1892 some 300 locomotives of this type were sold. Early life and military service Ephraim Shay was born on July 17, 1839, in Sherman Township, Huron County, Ohio. His parents were James and Phoebe (Probasco) Shay, whose families went back to colonial New York. His parents were of majority-English descent, with some Dutch and Polish ancestry. His mother's paternal line descended from immigrant George (Jurriaen) Probatski, who was from Breslau, Silesia (now Wroclaw, Poland). In 1654 Probatski went to the Netherlands and immigrated with some Dutch via Amsterdam and Brazil to New Netherland (New York). Over time, through Dutch and English marriages and variations, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Wheels
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunting locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets which are linked together within the set. Diameter Driving wheels are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltimore And Ohio Railroad
The Baltimore and Ohio Railroad was the first common carrier railroad and the oldest railroad in the United States, with its first section opening in 1830. Merchants from Baltimore, which had benefited to some extent from the construction of the National Road early in the century, wanted to do business with settlers crossing the Appalachian Mountains. The railroad faced competition from several existing and proposed enterprises, including the Albany-Schenectady Turnpike, built in 1797, the Erie Canal, which opened in 1825, and the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal. At first, the B&O was located entirely in the state of Maryland; its original line extending from the port of Baltimore west to Sandy Hook, Maryland, opened in 1834. There it connected with Harper's Ferry, first by boat, then by the Wager Bridge, across the Potomac River into Virginia, and also with the navigable Shenandoah River. Because of competition with the C&O Canal for trade with coal fields in western Maryland, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grasshopper Locomotive
''Atlantic'' was the name of a very early American steam locomotive built by inventor and foundry owner Phineas Davis for the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) in 1832. It is in fact the first commercially successful and practical American built locomotive and class prototype, and Davis' second constructed for the B&O, his first having won a design competition contest announced by the B&O in 1830. Design and construction Built at a cost of $4,500 (equal to $ today), the ''Atlantic'' weighed and had two vertical cylinders. It was commissioned after Davis' entry had won the competition for a steam locomotive design, but the contract was awarded to the inventor of the Tom Thumb; when the five locomotives commissioned failed the contracted delivery, B&O bought out the patents. A few of these were incorporated in the Atlantic by Davis, whether by specification or because Davis wanted them is unclear. The locomotives he delivered before his death in 1835 were the first commercially ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gear Ratio
A gear train is a mechanical system formed by mounting gears on a frame so the teeth of the gears engage. Gear teeth are designed to ensure the pitch circles of engaging gears roll on each other without slipping, providing a smooth transmission of rotation from one gear to the next. Features of gears and gear trains include: * The gear ratio of the pitch circles of mating gears defines the speed ratio and the mechanical advantage of the gear set. * A planetary gear train provides high gear reduction in a compact package. * It is possible to design gear teeth for gears that are non-circular, yet still transmit torque smoothly. * The speed ratios of chain and belt drives are computed in the same way as gear ratios. See bicycle gearing. The transmission of rotation between contacting toothed wheels can be traced back to the Antikythera mechanism of Greece and the south-pointing chariot of China. Illustrations by the Renaissance scientist Georgius Agricola show gear trains with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Driving Axle
On a steam locomotive, a driving wheel is a powered wheel which is driven by the locomotive's pistons (or turbine, in the case of a steam turbine locomotive). On a conventional, non-articulated locomotive, the driving wheels are all coupled together with side rods (also known as coupling rods); normally one pair is directly driven by the main rod (or connecting rod) which is connected to the end of the piston rod; power is transmitted to the others through the side rods. On diesel and electric locomotives, the driving wheels may be directly driven by the traction motors. Coupling rods are not usually used, and it is quite common for each axle to have its own motor. Jackshaft drive and coupling rods were used in the past (e.g. in the Swiss Crocodile locomotive) but their use is now confined to shunting locomotives. On an articulated locomotive or a duplex locomotive, driving wheels are grouped into sets which are linked together within the set. Diameter Driving wheels are g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods. The crankpins are also called ''rod bearing journals'', and they rotate within the "big end" of the connecting rods. Most modern crankshafts are located in the engine block. They are made from steel or cast iron, using either a forging, casting or machining process. Design The crankshaft located within the engine block, held in place via main bearings which allow the crankshaft to rotate within the block. The up-down motion of each piston is transferred to the crankshaft via connecting rods. A flywheel is often attached to one end of the crankshaft, in order to smoothen the power delivery and reduce vibration. A crankshaft is subjected to enormous stresses, in some cases more than per cylinder. Crankshafts for single-cylin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Side Rod
A coupling rod or side rod connects the driving wheels of a locomotive. Steam locomotives in particular usually have them, but some diesel and electric locomotives, especially older ones and shunters, also have them. The coupling rods transfer the power of drive to all wheels. Development Locomotion No. 1 was the first locomotive to employ coupling rods rather than chains. In the 1930s reliable roller bearing coupling rods were developed. Allowance for vertical motion In general, all railroad vehicles have spring suspension; without springs, irregularities in the track could lift wheels off the rail and cause impact damage to both rails and vehicles. Driving wheels are typically mounted so that they have around 1 inch (2.5 cm) of vertical motion. When there are only 2 coupled axles, this range of motion places only slight stress on the crank pins. With more axles, however, provision must be made to allow each axle to move vertically independently of the others without be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He was an early pioneer of steam-powered road and rail transport, and his most significant contributions were the development of the first high-pressure steam engine and the first working railway steam locomotive. The world's first locomotive-hauled railway journey took place on 21 February 1804, when Trevithick's unnamed steam locomotive hauled a train along the tramway of the Penydarren Ironworks, in Merthyr Tydfil, Wales. Turning his interests abroad Trevithick also worked as a mining consultant in Peru and later explored parts of Costa Rica. Throughout his professional career he went through many ups and downs and at one point faced financial ruin, also suffering from the strong rivalry of many mining and steam engineers of the day. Durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island country by area, covering . New Zealand is about east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps, owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and then developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. In 1840, representatives of the United Kingdom and Māori chiefs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_train.jpg)