|
Gartner's Duct
Gartner's duct, also known as Gartner's canal or the ductus longitudinalis epoophori, is a potential embryological remnant in human female development of the mesonephric duct in the development of the urinary and reproductive organs. It was discovered and described in 1822 by Hermann Treschow Gartner. Gartner's duct is located in the uterus' broad ligament. Its position is parallel with the lateral uterine tube and lateral walls of vagina and cervix. The paired mesonephric ducts in the male, in contrast, go on to form the paired epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory duct and seminal vesicle. In females, they may persist between the layer of the broad ligament of the uterus and in the wall of the vagina. Clinical significance These may give rise to Gartner's duct cysts. See also *List of homologues of the human reproductive system This list of related male and female reproductive organs shows how the male and female reproductive organs and the development of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolffian Duct
The mesonephric duct (also known as the Wolffian duct, archinephric duct, Leydig's duct or nephric duct) is a paired organ that forms during the embryonic development of humans and other mammals and gives rise to male reproductive organs. Structure The mesonephric duct connects the primitive kidney, the '' mesonephros'', to the cloaca. It also serves as the primordium for male urogenital structures including the epididymis, vas deferens, and seminal vesicles. Development In both male and female the mesonephric duct develops into the trigone of urinary bladder, a part of the bladder wall, but the sexes differentiate in other ways during development of the urinary and reproductive organs. Male In a male, it develops into a system of connected organs between the efferent ducts of the testis and the prostate, namely the epididymis, the vas deferens, and the seminal vesicle. The prostate forms from the urogenital sinus and the efferent ducts form from the meso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Male
Male (symbol: ♂) is the sex of an organism that produces the gamete (sex cell) known as sperm, which fuses with the larger female gamete, or ovum, in the process of fertilization. A male organism cannot reproduce sexually without access to at least one ovum from a female, but some organisms can reproduce both sexually and asexually. Most male mammals, including male humans, have a Y chromosome, which codes for the production of larger amounts of testosterone to develop male reproductive organs. Not all species share a common sex-determination system. In most animals, including humans, sex is determined genetically; however, species such as ''Cymothoa exigua'' change sex depending on the number of females present in the vicinity. In humans, the word ''male'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Overview The existence of separate sexes has evolved independently at different times and in different lineages, an example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gartner's Duct Cyst
A Gartner's duct cyst (sometimes incorrectly referred to as ''vaginal inclusion cyst'') is a benign vaginal cyst that originates from the Gartner's duct, which is a vestigial remnant of the mesonephric duct (wolffian duct) in females. They are typically small asymptomatic cysts that occur along the lateral walls of the vagina, following the course of the duct. They can present in adolescence with painful menstruation (dysmenorrhea) or difficulty inserting a tampon. They can also enlarge to substantial proportions and be mistaken for urethral diverticulum or cystocele. In some rare instances, they can be congenital. There is a small association between Gartner's duct cysts and metanephric urinary anomalies, such as ectopic ureter and ipsilateral renal hypoplasia. Symptoms of a Gartner's duct cyst include: infections, bladder dysfunction, abdominal pain, vaginal discharge, and urinary incontinence Urinary incontinence (UI), also known as involuntary urination, is any uncontrolled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Ligament Of The Uterus
The broad ligament of the uterus is the wide fold of peritoneum that connects the sides of the uterus to the walls and floor of the pelvis. Structure Subdivisions Contents The contents of the broad ligament include the following: * Reproductive ** uterine tubes (or Fallopian tube) ** ovary (some sources consider the ovary to be on the broad ligament, but not in it.) * vessels ** ovarian artery (in the suspensory ligament) ** uterine artery (in reality, travels in the cardinal ligament) * ligaments ** ovarian ligament ** round ligament of uterus ** suspensory ligament of the ovary (Some sources consider it a part of the broad ligament, while other sources just consider it a "termination" of the ligament.) Relations The peritoneum surrounds the uterus like a flat sheet that folds over its fundus, covering it anteriorly and posteriorly; on the sides of the uterus, this sheet of peritoneum comes in direct contact with itself, forming the double layer of peritoneum known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Female
Female ( symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction. A female has larger gametes than a male. Females and males are results of the anisogamous reproduction system, wherein gametes are of different sizes, unlike isogamy where they are the same size. The exact mechanism of female gamete evolution remains unknown. In species that have males and females, sex-determination may be based on either sex chromosomes, or environmental conditions. Most female mammals, including female humans, have two X chromosomes. Female characteristics vary between different species with some species having pronounced secondary female sex characteristics, such as the presence of pronounced mammary glands in mammals. In humans, the word ''female'' can also be used to refer to gender in the social sense of gender role or gender identity. Etymology and usage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
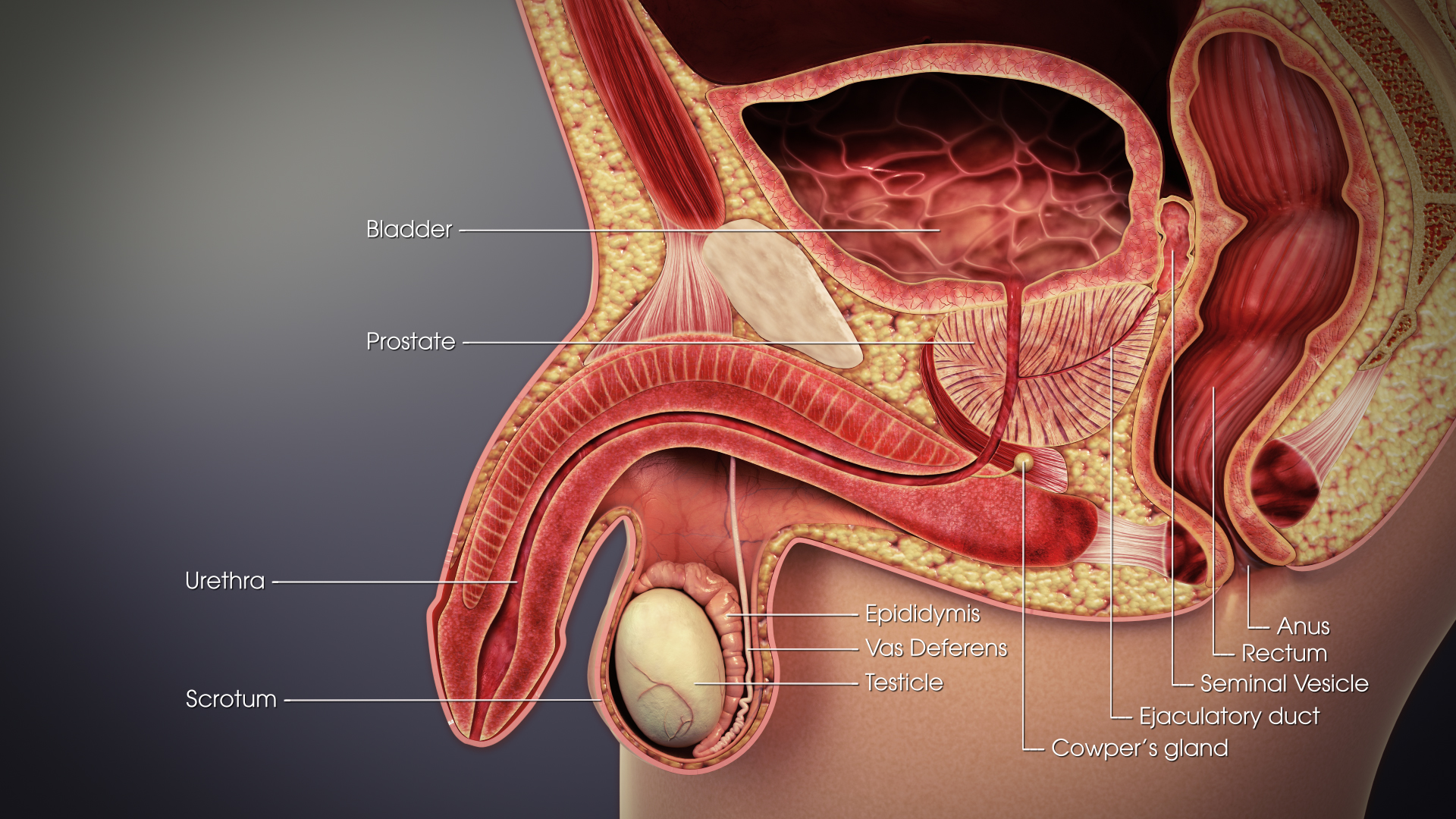
Seminal Vesicle
The seminal vesicles (also called vesicular glands, or seminal glands) are a pair of two convoluted tubular glands that lie behind the urinary bladder of some male mammals. They secrete fluid that partly composes the semen. The vesicles are 5–10 cm in size, 3–5 cm in diameter, and are located between the bladder and the rectum. They have multiple outpouchings which contain secretory glands, which join together with the vas deferens at the ejaculatory duct. They receive blood from the vesiculodeferential artery, and drain into the vesiculodeferential veins. The glands are lined with column-shaped and cuboidal cells. The vesicles are present in many groups of mammals, but not marsupials, monotremes or carnivores. Inflammation of the seminal vesicles is called seminal vesiculitis, most often is due to bacterial infection as a result of a sexually transmitted disease or following a surgical procedure. Seminal vesiculitis can cause pain in the lower abdomen, scrot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ejaculatory Duct
The ejaculatory ducts (''ductus ejaculatorii'') are paired structures in male anatomy. Each ejaculatory duct is formed by the union of the vas deferens with the duct of the seminal vesicle. They pass through the prostate, and open into the urethra above the seminal colliculus. During ejaculation, semen passes through the prostate gland, enters the urethra and exits the body via the urinary meatus. Function Ejaculation Ejaculation occurs in two stages, the emission stage and the expulsion stage.Rathus, S. A., Nevid, J. S., Fichner-Rathus, L., Herold, E. S. (2010). ''Human Sexuality in a World of Diversity''. Pearsons Education Canada, Pearson Canada Inc. Toronto, ON. The emission stage involves the workings of several structures of the ejaculatory duct; contractions of the prostate gland, the seminal vesicles, the bulbourethral gland and the vas deferens push fluids into the prostatic urethra. The semen is stored here until ejaculation occurs. Muscles at the base of the penis c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vas Deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube which exits the abdominal cavity through the inguinal canal. Etymology ''Vas deferens'' is Latin, meaning "carrying-away vessel"; the plural version is ''vasa deferentia''. ''Ductus deferens'' is also Latin, meaning "carrying-away duct"; the plural version is ''ducti deferentes''. Structure There are two vasa deferentia, connecting the left and right epididymis with the seminal vesicles to form the ejaculatory duct in order to move sperm. The (human) vas deferens measures 30–35 cm in length, and 2–3 mm in diameter. The vas deferens is continuous proximally with the tail of the epididymis. The vas deferens exhibits a tortuous, convoluted initial/proximal section (which measures 2–3 cm in length). Distally, it form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epididymis
The epididymis (; plural: epididymides or ) is a tube that connects a testicle to a vas deferens in the male reproductive system. It is a single, narrow, tightly-coiled tube in adult humans, in length. It serves as an interconnection between the multiple efferent ducts at the rear of a testicle (proximally), and the vas deferens (distally). Anatomy The epididymis is situated posterior and somewhat lateral to the testis. The epididymis is invested completely by the tunica vaginalis (which is continuous with the tunica vaginalis covering the testis). The epididymis can be divided into three main regions: * The head ( la, caput). The head of the epididymis receives spermatozoa via the efferent ducts of the mediastinum testis, mediastinium of the testis at the superior pole of the testis. The head is characterized histologically by a thick epithelium with long stereocilia (described below) and a little smooth muscle. It is involved in absorbing fluid to make the sperm more concentra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cervix
The cervix or cervix uteri (Latin, 'neck of the uterus') is the lower part of the uterus (womb) in the human female reproductive system. The cervix is usually 2 to 3 cm long (~1 inch) and roughly cylindrical in shape, which changes during pregnancy. The narrow, central cervical canal runs along its entire length, connecting the uterine cavity and the lumen of the vagina. The opening into the uterus is called the internal os, and the opening into the vagina is called the external os. The lower part of the cervix, known as the vaginal portion of the cervix (or ectocervix), bulges into the top of the vagina. The cervix has been documented anatomically since at least the time of Hippocrates, over 2,000 years ago. The cervical canal is a passage through which sperm must travel to fertilize an egg cell after sexual intercourse. Several methods of contraception, including cervical caps and cervical diaphragms, aim to block or prevent the passage of sperm through the cervic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryological
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, ''-logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses. Additionally, embryology encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth, known as teratology. Early embryology was proposed by Marcello Malpighi, and known as preformationism, the theory that organisms develop from pre-existing miniature versions of themselves. Aristotle proposed the theory that is now accepted, epigenesis. Epigenesis is the idea that organisms develop from seed or egg in a sequence of steps. Modern embryology, developed from the work of Karl Ernst von Baer, though accurate observations had been made in Italy by anatomists such as Aldrovandi and Leonardo da Vinci in the Renaissance. Comparative embryology Preformationism and epigenesis As recently as the 18th century, the prevailing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals, the vagina is the elastic, muscular part of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vestibule to the cervix. The outer vaginal opening is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucosal tissue called the hymen. At the deep end, the cervix (neck of the uterus) bulges into the vagina. The vagina allows for sexual intercourse and birth. It also channels menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. Although research on the vagina is especially lacking for different animals, its location, structure and size are documented as varying among species. Female mammals usually have two external openings in the vulva; these are the urethral opening for the urinary tract and the vaginal opening for the genital tract. This is different from male mammals, who usually have a single urethral opening for both urination and reproduction. The vaginal opening is much larger than the nearby urethral openi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |