|
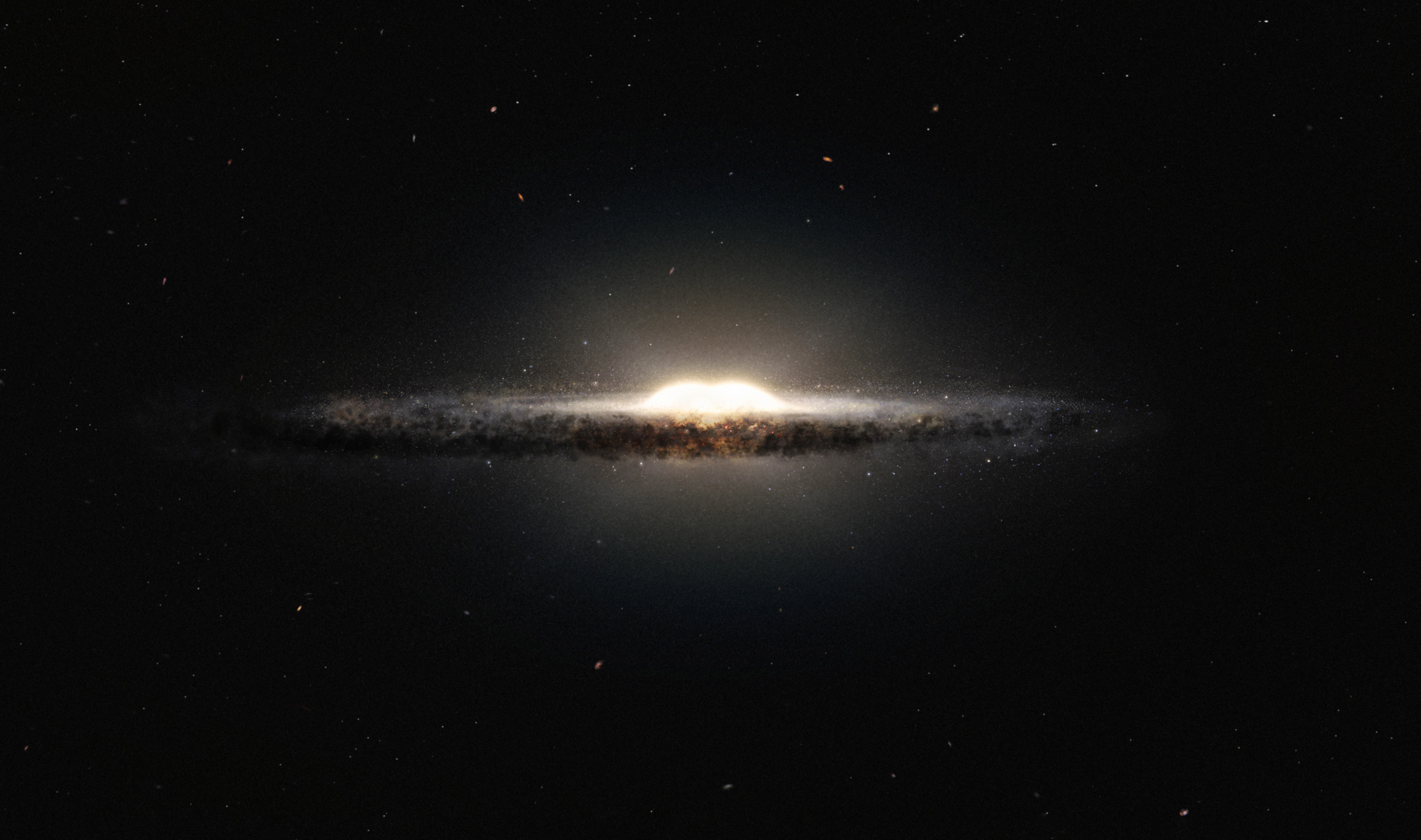
Galactic Lens
Galactic lens in the structure of galaxies a component with an almost uniform distribution of the surface brightness, which can be noticeable in the region between the bulge and the disk. Most likely, these structures arise from the "blurring" of the bars. Synopsis The lens in the structure of galaxies is an elliptical-shaped component with a nearly uniform distribution of surface brightness and sharp boundaries, whose contribution can be seen in the region between the bulge and the disk, and sometimes in other regions as well. The lenses are triaxial ellipsoids: in the direction perpendicular to the galactic plane, they are flattened, but not as much as the disks, and in the projection on the disk plane, the ratio of their major and minor axes is on average 0.9. It is known that lenses are closely connected with bars and are often found in galaxies with bars - in 54% of SB0-SBa galaxies and in 76% of SBab-SBc galaxies. In those cases when a galaxy contains both a bar and a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NGC 4909 DSS
NGC commonly refers to: * New General Catalogue of Nebulae and Clusters of Stars, a catalogue of deep sky objects in astronomy NGC may also refer to: Companies * NGC Corporation, name of US electric company Dynegy, Inc. from 1995 to 1998 * National Gas Company of Trinidad and Tobago, state-owned natural gas company in Trinidad and Tobago * National Grid plc, a former name of National Grid Electricity Transmission plc, the operator of the British electricity transmission system * Northrop Grumman Corporation, aerospace and defense conglomerate formed from the merger of Northrop Corporation and Grumman Corporation in 1994 * Numismatic Guaranty Corporation, coin certification company in the United States Other uses * National Gallery of Canada, art gallery founded in 1880 in Ottawa, Canada * National Geographic, documentary and reality television channel established in the United States in 2001 formerly called National Geographic Channel * Native Girls Code, US non-profit organisat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Brightness
In astronomy, surface brightness (SB) quantifies the apparent brightness or flux density per unit angular area of a spatially extended object such as a galaxy or nebula, or of the night sky background. An object's surface brightness depends on its surface luminosity density, i.e., its luminosity emitted per unit surface area. In visible and infrared astronomy, surface brightness is often quoted on a magnitude scale, in magnitudes per square arcsecond (MPSAS) in a particular filter band or photometric system. Measurement of the surface brightnesses of celestial objects is called surface photometry. General description The total magnitude is a measure of the brightness of an extended object such as a nebula, cluster, galaxy or comet. It can be obtained by summing up the luminosity over the area of the object. Alternatively, a photometer can be used by applying apertures or slits of different sizes of diameter. The background light is then subtracted from the measurement to obtain t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Bulge
In astronomy, a galactic bulge (or simply bulge) is a tightly packed group of stars within a larger star formation. The term almost exclusively refers to the central group of stars found in most spiral galaxies (see galactic spheroid). Bulges were historically thought to be elliptical galaxies that happened to have a disk of stars around them, but high-resolution images using the Hubble Space Telescope have revealed that many bulges lie at the heart of a spiral galaxy. It is now thought that there are at least two types of bulges: bulges that are like ellipticals and bulges that are like spiral galaxies. Classical bulges Bulges that have properties similar to those of elliptical galaxies are often called "classical bulges" due to their similarity to the historic view of bulges. These bulges are composed primarily of stars that are older, Population II stars, and hence have a reddish hue (see stellar evolution). These stars are also in orbits that are essentially random c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galactic Disc
A galactic disc (or galactic disk) is a component of disc galaxies, such as spiral galaxies and lenticular galaxies. Galactic discs consist of a stellar component (composed of most of the galaxy's stars) and a gaseous component (mostly composed of cool gas and dust). The stellar population of galactic discs tend to exhibit very little random motion with most of its stars undergoing nearly circular orbits about the galactic center. Discs can be fairly thin because the disc material's motion lies predominantly on the plane of the disc (very little vertical motion). The Milky Way's disc, for example is approximately 1 kly thick but thickness can vary for discs in other galaxies. Stellar component Exponential surface brightness profiles Galactic discs have surface brightness profiles that very closely follow exponential functions in both the radial and vertical directions. Radial profile The surface brightness radial profile of the galactic disc of a typical disc galaxy (view ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galaxy Morphological Classification
Galaxy morphological classification is a system used by astronomers to divide galaxies into groups based on their visual appearance. There are several schemes in use by which galaxies can be classified according to their morphologies, the most famous being the Hubble sequence, devised by Edwin Hubble and later expanded by Gérard de Vaucouleurs and Allan Sandage. However, galaxy classification and morphology are now largely done using computational methods and physical morphology. Hubble sequence The Hubble sequence is a morphological classification scheme for galaxies invented by Edwin Hubble in 1926. It is often known colloquially as the “Hubble tuning-fork” because of the shape in which it is traditionally represented. Hubble's scheme divides galaxies into three broad classes based on their visual appearance (originally on photographic plates): * Elliptical galaxies have smooth, featureless light distributions and appear as ellipses in images. They are denoted by the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gérard De Vaucouleurs
Gérard Henri de Vaucouleurs (25 April 1918 – 7 October 1995) was a French astronomer. Life and career Born in Paris, he had an early interest in amateur astronomy and received his undergraduate degree in 1939 at the Sorbonne in that city. After military service in World War II, he resumed his pursuit of astronomy. He was married to fellow astronomer Antoinette de Vaucouleurs on October 31, 1944, and the couple would frequently collaborate on astronomical research. Fluent in English, he spent 1949–51 in England, 1951–57 in Australia, the latter at Mount Stromlo Observatory, 1957–58 at Lowell Observatory in Arizona and 1958–60 at Harvard. In 1960 he was appointed to the University of Texas at Austin, where he spent the rest of his career. He died of a heart attack in his home in Austin at the age of 77. His earliest work had concerned the planet Mars and while at Harvard he used telescope observations from 1909 to 1958 to study the areographic coord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |