|
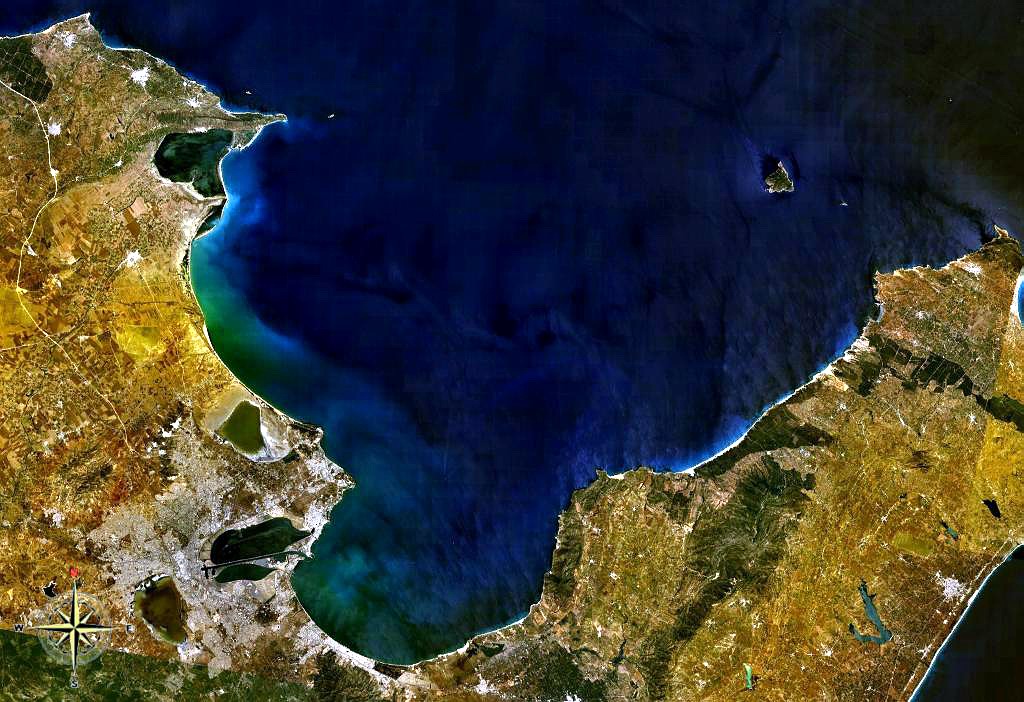
Gulf Of İzmit
Gulf of İzmit (), also referred to as İzmit Bay, is a bay at the easternmost edge of the Sea of Marmara, in Kocaeli Province, Turkey. The gulf takes its name from the city of İzmit. Other cities and towns around the bay are Gebze, Körfez, Gölcük, and Altınova. In the east–west direction, it extends for a length of about , while in the north–south direction its width varies from at the narrowest spots to about at its widest. The İzmit Bay Bridge is a suspension bridge that bridges the gulf. The North Anatolian Fault Zone, the most prominent active fault in Turkey and the source of numerous large earthquakes throughout history, passes through the Gulf of İzmit. Etymology İzmit’s ancient names were Gulf of Astacus, Sinus Astacenus (), Olbianus Sinus (), and Gulf of Nicomedia. It took the names Gulf of Astacus and Sinus Astacenus from the city Astacus. See also * Astacus in Bithynia * Nicomedia (modern İzmit) – the eastern and most senior capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Izmit, Turkey
A gulf is a large inlet from an ocean or their seas into a landmass, larger and typically (though not always) with a narrower opening than a bay (geography), bay. The term was used traditionally for large, highly indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden. See also * References External links * {{Geography-stub Gulfs, Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Anatolian Fault Zone
The North Anatolian Fault (NAF; ) is an active right-lateral strike-slip fault in northern Anatolia, and is the transform boundary between the Eurasian plate and the Anatolian sub-plate. The fault extends westward from a junction with the East Anatolian Fault at the Karliova triple junction in eastern Turkey, across northern Turkey and into the Aegean Sea for a length of 1200−1500 kilometers. It runs about 20 km south of Istanbul. The North Anatolian Fault is similar in many ways to the San Andreas Fault in California. Both are continental transforms with similar lengths and slip rates. The Sea of Marmara near Istanbul is an extensional basin similar to the Salton Trough in California, where a releasing bend in the strike slip system creates a pull-apart basin. Significant earthquakes Since the disastrous 1939 Erzincan earthquake, there have been seven earthquakes measuring over 7.0 in magnitude, each happening at a point progressively further west. Seismologist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
İzmit Körfez Circuit
İzmit Körfez Circuit () is a motor sports race track about west of İzmit, in Körfez district of Kocaeli Province, Turkey. Sponsored by the Turkish Automobile Sports Federation (TOSFED) and built by the Istanbul Motorsports Club (İMK), it was inaugurated in 1993 as the first asphalted race track in Turkey. The venue is home to motor sport races in various categories. Located at the northeastern coast of Marmara Sea, İzmit Körfez Circuit is situated around a small Fener Lake (Fenergölü), which belongs to the Municipality of Körfez District. The venue can be easily reached from Istanbul and İzmit by the motorway O-4 or highway D-100 at the exit Körfez. The race track, at length, has nine turns and runs clockwise. The circuit provides the greatest number of motor sport racing events in Turkey. In addition to Turkish championships, several racing organizations of private companies as well as various motor sport types in different categories are held here. On an avera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrarchy
The Tetrarchy was the system instituted by Roman emperor Diocletian in 293 AD to govern the ancient Roman Empire by dividing it between two emperors, the ''augusti'', and their junior colleagues and designated successors, the ''caesares''. Initially Diocletian chose Maximian as his ''caesar'' in 285, raising him to co-''augustus'' the following year; Maximian was to govern the western provinces and Diocletian would administer the eastern ones. The role of the ''augustus'' was likened to Jupiter (mythology), Jupiter, while his ''caesar'' was akin to Jupiter's son Hercules. Galerius and Constantius Chlorus, Constantius were appointed ''caesares'' in March 293. Diocletian and Maximian retired on 1 May 305, raising Galerius and Constantius to the rank of ''augustus''. Their places as ''caesares'' were in turn taken by Valerius Severus and Maximinus Daza. The orderly system of two senior and two junior rulers endured until Constantius died in July 306, and his son Constantine the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ruled the Mediterranean and much of Europe, Western Asia and North Africa. The Roman people, Romans conquered most of this during the Roman Republic, Republic, and it was ruled by emperors following Octavian's assumption of effective sole rule in 27 BC. The Western Roman Empire, western empire collapsed in 476 AD, but the Byzantine Empire, eastern empire lasted until the fall of Constantinople in 1453. By 100 BC, the city of Rome had expanded its rule from the Italian peninsula to most of the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean and beyond. However, it was severely destabilised by List of Roman civil wars and revolts, civil wars and political conflicts, which culminated in the Wars of Augustus, victory of Octavian over Mark Antony and Cleopatra at the Battle of Actium in 31 BC, and the subsequent conquest of the Ptolemaic Kingdom in Egypt. In 27 BC, the Roman Senate granted Octavian overarching military power () and the new title of ''Augustus (title), Augustus'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astacus (Bithynia)
Astacus (Greek ) is an ancient city in Bithynia; it was also called Olbia . Its site is located near the modern Başiskele. History There are contradictory accounts of its founding: * The ''Bibliotheca historica'' (1st century BCE) of Diodorus Siculus, Book XII, Chapter 34, states: "And while these events he Battle of Potidaeawere taking place, the Athenians founded in the Propontis a city which was given the name of Astacus". Siculus' annalistic narrative allows the founding to be dated to the year 435 BCE. * The '' Annals">annalistic narrative allows the founding to be dated to the year 435 BCE. * The ''Geographica">Annals">annalistic narrative allows the founding to be dated to the year 435 BCE. * The ''Megarians and the Athens">Athenians (), and afterwards of Doidalsos. On the other hand, Siculus mentions only the Athenians as founders, while Pomponius Mela (''De situ orbis libri III'') and Memnon of Heraclea (through Photios I of Constantinople) attributed the founding o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicomedia
Nicomedia (; , ''Nikomedeia''; modern İzmit) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek city located in what is now Turkey. In 286, Nicomedia became the eastern and most senior capital city of the Roman Empire (chosen by the emperor Diocletian who ruled in the east), a status which the city maintained during the Tetrarchy system (293–324). The Tetrarchy ended with the Battle of Chrysopolis (Üsküdar#Chrysopolis, Üsküdar) in 324, when Constantine the Great, Constantine defeated Licinius and became the sole emperor. In 330 Constantine chose for himself the nearby Byzantium (which was renamed Constantinople, modern Istanbul) as the new capital of the Roman Empire. The city was incorporated into the Ottoman Empire with the victory of Sultan Orhan Gazi against the Byzantine Empire. The Byzantines managed to retake it in the aftermath of the Battle of Ankara, but it fell definitively to the Ottomans in 1419. History It was founded in 712–711 BC as a Megarian colony and was original ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astacus In Bithynia
Astacus (Greek ) is an ancient city in Bithynia; it was also called Olbia . Its site is located near the modern Başiskele. History There are contradictory accounts of its founding: * The ''Bibliotheca historica'' (1st century BCE) of Diodorus Siculus, Book XII, Chapter 34, states: "And while these events he Battle of Potidaeawere taking place, the Athenians founded in the Propontis a city which was given the name of Astacus". Siculus' annalistic narrative allows the founding to be dated to the year 435 BCE. * The '' Annals">annalistic narrative allows the founding to be dated to the year 435 BCE. * The ''Geographica">Annals">annalistic narrative allows the founding to be dated to the year 435 BCE. * The ''Megarians and the Athens">Athenians (), and afterwards of Doidalsos. On the other hand, Siculus mentions only the Athenians as founders, while Pomponius Mela (''De situ orbis libri III'') and Memnon of Heraclea (through Photios I of Constantinople) attributed the founding o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake
An earthquakealso called a quake, tremor, or tembloris the shaking of the Earth's surface resulting from a sudden release of energy in the lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from those so weak they cannot be felt, to those violent enough to propel objects and people into the air, damage critical infrastructure, and wreak destruction across entire cities. The seismic activity of an area is the frequency, type, and size of earthquakes experienced over a particular time. The seismicity at a particular location in the Earth is the average rate of seismic energy release per unit volume. In its most general sense, the word ''earthquake'' is used to describe any seismic event that generates seismic waves. Earthquakes can occur naturally or be induced by human activities, such as mining, fracking, and nuclear weapons testing. The initial point of rupture is called the hypocenter or focus, while the ground level directly above it is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Active Fault
An active fault is a fault that is likely to become the source of another earthquake sometime in the future. Geologists commonly consider faults to be active if there has been movement observed or evidence of seismic activity during the last 10,000 years. * Active faulting is considered to be a geologic hazard – one related to earthquakes as a cause. Effects of movement on an active fault include strong ground motion, surface faulting, tectonic deformation, landslides and rockfalls, liquefaction, tsunamis, and seiches. Quaternary faults are those active faults that have been recognized at the surface and which have evidence of movement during the Quaternary Period. Related geological disciplines for ''active-fault'' studies include geomorphology, seismology, reflection seismology, plate tectonics, geodetics and remote sensing, risk analysis, and others. Location Active faults tend to occur in the vicinity of tectonic plate boundaries, and active fault research h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suspension Bridge
A suspension bridge is a type of bridge in which the deck (bridge), deck is hung below suspension wire rope, cables on vertical suspenders. The first modern examples of this type of bridge were built in the early 1800s. Simple suspension bridges, which lack vertical suspenders, have a long history in many mountainous parts of the world. Besides the bridge type most commonly called suspension bridges, covered in this article, there are other types of suspension bridges. The type covered here has cables suspended between towers, with vertical ''suspender cables'' that transfer the Structural load#Live load, imposed loads, transient load, live and Structural load#Dead load, dead loads of the deck below, upon which traffic crosses. This arrangement allows the deck to be level or to arc upward for additional clearance. Like other suspension bridge types, this type often is constructed without the use of falsework. The suspension cables must be anchored at each end of the bridge, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Marmara
The Sea of Marmara, also known as the Sea of Marmora or the Marmara Sea, is a small inland sea entirely within the borders of Turkey. It links the Black Sea and the Aegean Sea via the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits, separating Turkey's European and Asian sides. It has an area of , and its dimensions are . Its greatest depth is . Name The Sea of Marmara is named after the largest island on its south side, called Marmara Island because it is rich in marble ( Greek , ''mármaron'' 'marble'). In classical antiquity, it was known as the Propontis, from the Greek words ''pro'' 'before' and ''pontos'' 'sea', reflecting the fact that the Ancient Greeks used to sail through it to reach the Black Sea, which they called ''Pontos''. Mythology In Greek mythology, a storm on the Propontis brought the Argonauts back to an island they had left, precipitating a battle in which either Jason or Heracles killed King Cyzicus, who had mistaken them for his Pelasgian enemies. Geography ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |