|
Greater Central Philippine Languages
The Greater Central Philippine languages are a proposed subgroup of the Austronesian language family, defined by the change of Proto-Malayo-Polynesian ''*R'' to ''*g''. They are spoken in the central and southern parts of the Philippines and in northern Sulawesi, Indonesia. This subgroup was first proposed by Robert Blust (1991) based on lexical and phonological evidence, and is accepted by most specialists in the field. Most of the major languages of the Philippines belong to the Greater Central Philippine subgroup: Tagalog, the Visayan languages Cebuano, Hiligaynon, Waray; Central Bikol, the Danao languages Maranao and Magindanaon. On the island of Sulawesi, Indonesia, Gorontalo is the third-largest language by number of speakers. History According to Blust, the current distribution of the Greater Central Philippine languages is the result of an expansion that occurred around 500 B.C. and which led to levelling of much of the linguistic diversity in the central a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines, officially the Republic of the Philippines, is an Archipelagic state, archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. Located in the western Pacific Ocean, it consists of List of islands of the Philippines, 7,641 islands, with a total area of roughly 300,000 square kilometers, which are broadly categorized in Island groups of the Philippines, three main geographical divisions from north to south: Luzon, Visayas, and Mindanao. With a population of over 110 million, it is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, twelfth-most-populous country. The Philippines is bounded by the South China Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, and the Celebes Sea to the south. It shares maritime borders with Taiwan to the north, Japan to the northeast, Palau to the east and southeast, Indonesia to the south, Malaysia to the southwest, Vietnam to the west, and China to the northwest. It has Ethnic groups in the Philippines, diverse ethnicities and Culture o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cebuano Language
Cebuano ( )Cebuano on Merriam-Webster.com is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken in the southern Philippines by Cebuano people and other Ethnic groups in the Philippines, ethnic groups as a secondary language. It is natively, though informally, called by the generic name Bisayâ (), or Binisayâ () (both terms are translated into English as ''Visayan'', though this should not be confused with other Bisayan languages) and sometimes referred to in English sources as Cebuan ( ). It is spoken by the Visayans, Visayan ethnolinguistic groups native to the islands of Cebu, Bohol, Siquijor, the eastern half of Negros Island, Negros, the western half of Leyte, the northern coastal areas of Northern Mindanao and the eastern part of Zamboanga del Norte due to Captaincy General of the Philippines, Spanish settlements during the 18th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
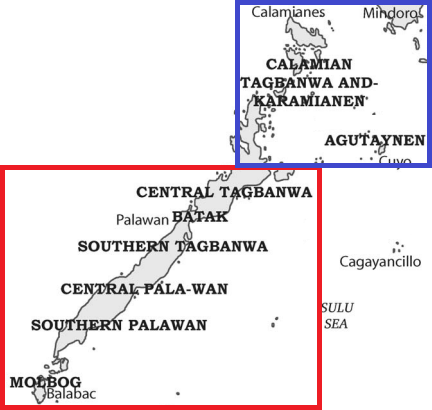
Kalamian Languages
The Kalamian languages are a small cluster of languages spoken in the Philippines: Calamian Tagbanwa and Agutaynen language, Agutaynen. Other languages called Tagbanwa, the Aborlan Tagbanwa language and Central Tagbanwa language are members of the Palawanic languages. These are among the few languages of the Philippines which continue to be written in Tagbanwa script, indigenous scripts, though mostly for poetry. Classification The Kalamian languages are a primary branch of the Philippine languages, Philippine language family, notable for reflecting Proto-Malayo-Polynesian language, Proto-Malayo-Polynesian ''*q'' as ''k'' and ''*R'' as ''l'', while reducing original ''*k'' to zero. References *Himes, Ronald S. 2007.The Kalamian microgroup of Philippine languages. ''Studies in Philippine languages and cultures'' 15:54-72. Further reading *Zorc, R. David. 1972. Agutaynon notes'. *Zorc, R. David. 1972. Kalamian notes'. See also *Tagbanwa script Calamian languages, Ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindoro
Mindoro is the seventh largest and eighth-most populous island in the Philippines. With a total land area of 10,571 km2 ( 4,082 sq.mi ), it has a population of 1,408,454, as of the 2020 census. It is located off the southwestern coast of Luzon and northeast of Palawan. Mindoro is divided into two provinces: Occidental Mindoro and Oriental Mindoro. Calapan is the only city on the island, while San Jose is the largest settlement on the island with a total population of 143,430 inhabitants as of 2015. The southern coast of Mindoro forms the northeastern extremum of the Sulu Sea. Mount Halcon is the highest point on the island, standing at above sea level located in Oriental Mindoro. Mount Baco is the island's second highest mountain with an elevation of , located in the province of Occidental Mindoro. Etymology The name Mindoro was likely a corruption of the native name ''Minolo.'' Domingo Navarette ('Tratados...', 1676) wrote "The island which the natives call Minolo is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Mindoro Languages
The Northern Mindoro (North Mangyan) languages are one of two small clusters of languages spoken by the Mangyan people of Mindoro Island in the Philippines. The languages are Alangan, Iraya, and Tadyawan. There is some evidence that points at a closer relationship of the Northern Mindoro languages with the Central Luzon languages. Both branches share the phonological innovation Proto-Austronesian *R > and some common lexical items such as 'to see', 'cold'. See also * Southern Mindoro languages *Ratagnon language Ratagnon (also translated as Latagnon or Datagnon, and Aradigi) is a regional language spoken by the Ratagnon people, an indigenous group from Occidental Mindoro. It is a part of the Bisayan language family and is closely related to other Phili ... References Further reading *Barbian, Karl-Josef. 1977. ''The Mangyan languages of Mindoro''. Cebu City: University of San Carlos. *Barbian, Karl-Josef. 1977. ''English-Mangyan vocabulary''. Cebu City: Universit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panay
Panay is the sixth-largest and fourth-most populous island in the Philippines, with a total land area of and a total population of 4,542,926, as of 2020 census. Panay comprises 4.4 percent of the entire population of the country. The City of Iloilo is its largest settlement, with a total population of 457,626 inhabitants as of the 2020 census. Panay is a triangular island, located in the western part of the Visayas. It is about across. It is divided into four Provinces of the Philippines, provinces: Aklan, Antique (province), Antique, Capiz, and Iloilo, all in the Western Visayas Regions of the Philippines, Region. Just off the mid-southeastern coast lies the island-province of Guimaras. It is located southeast of the island of Mindoro and northwest of Negros Island, Negros across the Guimaras Strait. To the north and northeast is the Sibuyan Sea, Jintotolo Channel and the island-provinces of Romblon and Masbate; to the west and southwest is the Sulu Sea and the Palawan archipe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ati Language (Philippines)
Ati (''Inati''), or Binisaya nga Inati, is an Austronesian language of the island of Panay in the Philippines. The variety spoken in northern Panay is also called Sogodnin. The Ati people also speak Kinaray-a and Hiligaynon. Classification and consider Inati to be an isolate within the Philippine languages. It differs markedly from the Visayan languages and has many features not found in the Central Philippine languages. Inati shows some unique sound changes. *Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *R > Inati , such as PMP * > Inati *Proto-Malayo-Polynesian *ə > Inati (as in the Central Luzon languages), not PMP *ə > or , as in the Visayan languages Distribution and dialects lists the following Ati communities in the Philippines, with populations given in parentheses: *Iloilo (1,902): Anilao (341), Barotac Viejo (867), Cabatuan (31), Calinog (163), Dueñas (43), Dumangas (50), Janiuay (22), New Lucena (59), Passi (103), San Miguel (17), San Rafael (110), Santa Barbara (12), Tigb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzon
Luzon ( , ) is the largest and most populous List of islands in the Philippines, island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the List of islands of the Philippines, Philippine archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million , it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the List of islands by population, 4th most populous island in the world. It is the List of islands by area, 15th largest island in the world by land area. ''Luzon'' may also refer to one of the three primary Island groups of the Philippines, island groups in the country. In this usage, it includes the Luzon Mainland, the Batanes and Babuyan Islands, Babuyan groups of islands to the north, Polillo Islands to the east, and the outlying islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque and Mindoro, among others, to the south. The islands o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manide Language
Manide is a Philippine language spoken throughout the province of Camarines Norte in Bicol region and near the eastern edge of Quezon in Southern Tagalog of southern Luzon in the Philippines. Manide is spoken by nearly 4,000 Negrito people, most of whom reside in the towns of Labo, Jose Panganiban, and Paracale. History Between 1903 and 1924, John M. Garvan (1963) visited Negrito Filipino communities in the region of Luzon and recorded the name Manide. Many of the Manide population children still grow up speaking Manide. Classification Manide is the most divergent out of the three other Negrito languages in Southern Luzon, namely Inagta Alabat, Inagta Rinconada, and Inagta Partido (although Inagta Rinconada and Inagta Partido belong to the Bikol subgroup and not the Manide-Alabat subgroup). In a survey of 1000 lexical items, 285 appeared to be unique, including new coinages which are forms that experienced semantic and or phonological shifts over time. In comparison, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gorontalo Language
The Gorontalo language (also called Hulontalo) is a language spoken in Gorontalo, Gorontalo Province, Sulawesi, Indonesia by the Gorontalo people. With around one million speakers (2000 census), it is a major language of northern Sulawesi. Considerable lexical influence comes from Malay language, Malay, Arabic language, Arabic, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Dutch language, Dutch, and the North Halmahera languages. The Gorontalo region used to be controlled by the Sultanate of Ternate. Manado Malay and Indonesian language, Indonesian are also spoken in the area. Despite its relatively large number of speakers, Gorontalo is under much pressure from Malay varieties, especially in urban settings. Sizable Gorontalo communities can be found in Manado, the capital of North Sulawesi, as well as Jakarta. Classification The Gorontalo language belongs to the Gorontalic language group, which is part of the Gorontalo–Mongondow languages, Gorontalo-Mongondow languages family, a branc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magindanao Language
Maguindanaon (, Jawi: ), or Magindanawn is an Austronesian language spoken by Maguindanaon people who form majority of the population of eponymous provinces of Maguindanao del Norte and Maguindanao del Sur in the Philippines. It is also spoken by sizable minorities in different parts of Mindanao such as the cities of Zamboanga, Davao, General Santos, and Cagayan de Oro, and the provinces of North Cotabato, Sultan Kudarat, South Cotabato, Sarangani, Zamboanga del Sur, Zamboanga Sibugay, Davao del Sur, Davao Occidental, Bukidnon as well as Metro Manila, Bulacan, Cavite, Rizal and Laguna. As of 2020, the language is ranked to be the ninth leading language spoken at home in the Philippines with only 365,032 households still speaking the language. History The Maguindanaon language is the native language of the Maguindanaon people of the province of Maguindanao located in the west of Mindanao island in the south of the Philippines. It was the language of the Sultanate of Maguindan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maranao Language
Maranao (; Jawi Script, Jawi: ), sometimes spelled as Maranaw, Meranaw or Mëranaw, is an Austronesian languages, Austronesian language spoken by the Maranao people in the provinces of Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte and their respective cities of Marawi and Iligan City, Iligan located in the Philippines, as well found also in Sabah, Malaysia. It is spoken among the Moro people, Moros within the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao. It is more closer to Iranun language, Iranun than to Maguindanao language, Maguindanao within the Danao languages, Danao subgroup. Distribution : Maranao is spoken in the following provinces of: • Entire Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte • Northwestern municipalities of Maguindanao del Norte: Barira, Buldon, Parang, Maguindanao del Norte, Parang, Matanog, Sultan Mastura, and Sultan Kudarat, Maguindanao del Norte, Sultan Kudarat • Northwestern municipalities of Cotabato: Alamada, Banisilan, Carmen, Cotabato, Carmen, Lib ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |