|
Great Northern Railway (Ireland)
The Great Northern Railway (Ireland) (GNR(I), GNRI or simply GNR) was an Irish gauge () railway company in Ireland. It was formed in 1876 by a merger of the Irish North Western Railway (INW), Northern Railway of Ireland, and Ulster Railway. The governments of Ireland and Northern Ireland jointly nationalised the company in 1953, and the company was liquidated in 1958: assets were split on national lines between the Ulster Transport Authority and CIÉ, Córas Iompair Éireann. Foundation The Ulster, D&D and D&BJct railways together formed the main line between Dublin and Belfast, with the D&BJct completing the final section in 1852 to join the Ulster at . The GNRI's other main lines were between Derry and and between Omagh and Portadown. The Portadown, Dungannon and Omagh Junction Railway together with the Londonderry and Enniskillen Railway enabled GNRI trains between Derry and Belfast to compete with the Belfast and Northern Counties Railway, and both this and the Dundalk rou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish North Western Railway
Irish North Western Railway (INW) was an Irish gauge () railway company in Ireland. Development The company was founded as the Dundalk and Enniskillen Railway (D&ER) and opened the first section of its line, from to , in 1849. In Dundalk the D&ER line crossed the Dublin and Belfast Junction Railway main line, which was completed between and its own separate station in the same year. The D&ER extended westwards, reaching in 1854, in 1855 and in 1858. In 1859 the D&ER reached where it connected with the Londonderry and Enniskillen Railway (L&ER). The L&ER had been completed in 1854 but had been unprofitable, so in 1860 it leased its line in perpetuity to the D&ER. This gave the D&ER a direct route between Dundalk and . In 1862 the INW opened a branch from southwards to . In the same year the company renamed itself the Irish North Western Railway. In 1863 the Ulster Railway reached Clones where it made a junction with the INW. In 1868 the Enniskillen and Bundoran R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leinster
Leinster ( ; or ) is one of the four provinces of Ireland, in the southeast of Ireland. The modern province comprises the ancient Kingdoms of Meath, Leinster and Osraige, which existed during Gaelic Ireland. Following the 12th-century Norman invasion of Ireland, the historic "fifths" of Leinster and Meath gradually merged, mainly due to the impact of the Pale, which straddled both, thereby forming the present-day province of Leinster. The ancient kingdoms were shired into a number of counties for administrative and judicial purposes. In later centuries, local government legislation has prompted further sub-division of the historic counties. Leinster has no official function for local-government purposes. However, it is an officially recognised subdivision of Ireland and is listed on ISO 3166-2 as one of the four provinces of Ireland. "IE-L" is attributed to Leinster as its ''country sub-division'' code. Leinster had a population of 2,858,501 according to the prelim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railbuses
A railbus is a lightweight passenger railcar with an automotive engine. It shares many aspects of its construction with a bus, typically having a bus (original or modified) body and four wheels (2 axles) on a fixed base instead of on bogies. Originally designed and developed during the 1930s, railbuses have evolved into larger dimensions with characteristics similar in appearance to a light railcar, with the terms ''railcar'' and ''railbus'' often used interchangeably. Railbuses designed for use specifically on little-used railway lines were commonly employed in countries such as Germany, Italy, France, the United Kingdom, and Sweden. Today, railbuses are being replaced by modern, light DMU railcar designs. Modern diesel-electric railcars, which can be run coupled as multiple units, like the Stadler RS1, the RegioSprinter of Siemens, or the successor Siemens Desiro, share the role and specifications with railbuses (albeit with improvements in noise, low floor design, fuel ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belfast Great Victoria Street Railway Station
Great Victoria Street was a railway station that served the Belfast City Centre, city centre of Belfast, Northern Ireland. It was one of two main stations in the city, along with , and was nearest to the city centre. The station was situated beside Great Victoria Street, Belfast, Great Victoria Street and shared a site with the Europa Buscentre, Belfast's former main bus station. The railway and bus stations were replaced by the adjacent Belfast Grand Central station with the official opening on 13 October 2024. Great Victoria Street railway station closed permanently on 10 May 2024, with a bus transfer service operating until rail services commenced from Belfast Grand Central, with a service to Dublin at 8:05 a.m. on 13 October 2024. Europa Buscentre closed permanently on 7 September 2024, with bus services immediately transferring to the new station, commencing with a service to Dublin at 5 a.m. on 8 September 2024. Great Victoria Street was the busiest railway station in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Connolly Railway Station
Connolly station () or Dublin Connolly is the busiest railway station in Dublin and Ireland, and is a focal point in the Irish route network. On the North side of the River Liffey, it provides InterCity, Enterprise and commuter services to the north, north-west, south-east and south-west. The north–south Dublin Area Rapid Transit (DART) and Luas red line light rail services also pass through the station. The station offices are the headquarters of Irish Rail, Iarnród Éireann. Opened in 1844 as ''Dublin Station'', the ornate facade has a distinctive Italianate tower at its centre. History On 24 May 1844 the Dublin and Drogheda Railway (DDR) began public operations from an interim terminus at the Royal Canal, and on the same day the foundation stone for what is now Connolly station was laid by Earl de Grey, Lord Lieutenant of Ireland. The station was opened for operations on 29 November 1844 as ''Dublin Station'', but was renamed ''Amiens Street Station'' ten ye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of Ireland
The Partition of Ireland () was the process by which the Government of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (UK) divided Ireland into two self-governing polities: Northern Ireland and Southern Ireland (the area today known as the Republic of Ireland, or simply Ireland). It was enacted on 3 May 1921 under the Government of Ireland Act 1920. The Act intended both territories to remain within the United Kingdom and contained provisions for their eventual reunification. The smaller Northern Ireland territory was duly created with a devolved government (Home Rule) and remained part of the UK. Although the larger Southern Ireland was also created, its administration was not recognised by most of its citizens, who instead recognised the self-declared 32-county Irish Republic. Ireland had a (largely Catholic) nationalist majority who wanted self-governance or independence. Prior to partition, the Irish Parliamentary Party used its control of the balance of power in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beyer, Peacock & Company
Beyer, Peacock and Company was an English general engineering company and railway locomotive manufacturer with a factory in Openshaw, Manchester. Charles Beyer, Richard Peacock and Henry Robertson founded the company in 1854. The company closed its railway operations in the early 1960s. It retained its stock market listing until 1976, when it was bought and absorbed by National Chemical Industries of Saudi Arabia. Founders German-born Charles Beyer had undertaken engineering training related to cotton milling in Dresden before moving to England in 1831 aged 21. He became draughtsman at Sharp, Stewart and Company, Sharp, Roberts and Company's Atlas works in central Manchester, which manufactured cotton mill machinery and had just started building locomotives for the Liverpool and Manchester Railway. There he was mentored by head engineer and prolific inventor of cotton mill machinery Richard Roberts (engineer), Richard Roberts. By the time he resigned 22 years later he was well ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
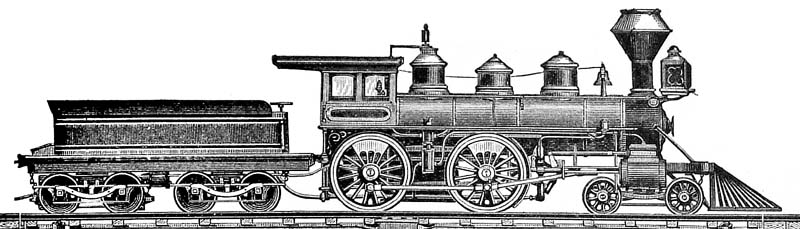
GNRI Class V
The Great Northern Railway V class steam locomotives were 4-4-0 three-cylinder compound locomotives built in 1932 by Beyer, Peacock & Company for the Great Northern Railway (Ireland). Design The V class was intended for the GNR's most important passenger service, the Dublin – Belfast expresses. The GNRI Class S, S and S2 Classes that had previously served the route were giving trouble as boiler pressure had been raised to increase power and performance. This increased maintenance (particularly with broken crank axles) and as a result the boiler pressure was brought back down. This obliged the GNR to develop a more powerful engine. George Glover designed the resultant 'V' class with on-site experience learnt from the design teams for the British LMS Compound 4-4-0 compound locomotives. The locomotives were ordered from Beyer, Peacock & Company and delivered in 1932. They cost £5,847, which was £3,000 less than the SG3 Class 0-6-0s built ten years before. Beyer, Peacock bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0, in the Whyte notation, denotes a steam locomotive with a wheel arrangement of four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and no trailing wheels. First built in the 1830s, locomotives with this wheel arrangement were known as "standard" or "Eight-Wheeler" type. In the first half of the 19th century, almost every major railroad in North America owned and operated locomotives of this type, and many rebuilt their and locomotives as 4-4-0s.Kinert, Reed. (1962). ''Early American steam locomotives; 1st seven decades: 1830-1900''. Seattle, WA: Superior Publishing Company. In April 1872, '' Railroad Gazette'' used "American" as the name of the type. The type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. The vast majority of 4- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dundalk Locomotive Works
Dundalk ( ; ) is the county town of County Louth, Ireland. The town is situated on the Castletown River, which flows into Dundalk Bay on the north-east coast of Ireland, and is halfway between Dublin and Belfast, close to and south of the border with Northern Ireland. It is surrounded by several townlands and villages that form the wider Dundalk Municipal District. It is the seventh largest urban area in Ireland, with a population of 43,112 as of the 2022 census. Dundalk has been inhabited since the Neolithic period. It was established as a Norman stronghold in the 12th century following the Norman invasion of Ireland, and became the northernmost outpost of The Pale in the Late Middle Ages. Located where the northernmost point of the province of Leinster meets the province of Ulster, the town came to be known as the "Gap of the North". The modern street layout dates from the early 18th century and owes its form to James Hamilton (later 1st Earl of Clanbrassil). The legends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the absence of trailing wheels. In the mid-19th century, this wheel arrangement became the second-most-popular configuration for new steam locomotives in the United States, where this type is commonly referred to as a ten-wheeler.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York, NY: Dover Publications. p. 57. As locomotives pulling trains of lightweight all-wood passenger cars from the 1890 to the 1920s, they were exceptionally stable at near speeds on the New York Central's New York-to-Chicago Water Level Route and on the Reading Railroad's line from Camden to Atlantic City, New Jersey. Overview Tender locomotives During the second half of the nineteenth and first half of the twen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Southern & Western Railway
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) was an Irish gauge () railway company in Ireland from 1844 until 1924. The grew by building lines and making a series of takeovers, until in the late 19th and early 20th centuries it was the largest of Ireland's "Big Four" railway networks. At its peak the had an network, of which were double track. The core of the was the Dublin Kingsbridge – main line; Ireland's "Premier Line", and still one of her most important main line railways. The company's headquarters were at Kingsbridge station. At its greatest extent the included, in addition to the Dublin – Cork main line, the Dublin – and – Waterford lines and numerous branch lines. Origins There had been earlier attempts to set up main line railways to the south of Ireland but the 1840s efforts of Peter Purcell, a wealthy landowner and mail coach operator, and his associates were ultimately to prove successful with the implementation of a bill passed on 6 August 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |