|
Granule (cell Biology)
In cell biology, a granule is a small particle barely visible by light microscopy. The term is most often used to describe a secretory vesicle containing important components of cell physiology. Examples of granules include granulocytes, platelet granules, insulin granules, germane granules, starch granules, and stress granules. It is considered as a cell organelle. Types There are mainly 2 types of granules based on presence or absence of membrane: # Membrane bound granules. # Non Membrane bound granules. Eosinophilic Granules, Basophilic Granules, Secretory Granules are examples of Membrane bound granules. P-granules, Stress granules are examples for Non Membrane bound granules. In leukocytes A group of leukocytes, called granulocytes, are white blood cells containing enzyme granules that play a significant role in the immune system. Granulocytes include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils which attack bacteria or parasites, and respond to allergens. Each type of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all life, forms of life. Every cell consists of cytoplasm enclosed within a Cell membrane, membrane; many cells contain organelles, each with a specific function. The term comes from the Latin word meaning 'small room'. Most cells are only visible under a light microscope, microscope. Cells Abiogenesis, emerged on Earth about 4 billion years ago. All cells are capable of Self-replication, replication, protein synthesis, and cell motility, motility. Cells are broadly categorized into two types: eukaryotic cells, which possess a Cell nucleus, nucleus, and prokaryotic, prokaryotic cells, which lack a nucleus but have a nucleoid region. Prokaryotes are single-celled organisms such as bacteria, whereas eukaryotes can be either single-celled, such as amoebae, or multicellular organism, multicellular, such as some algae, plants, animals, and fungi. Eukaryotic cells contain organelles including Mitochondrion, mitochondria, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Killer Cell
Natural killer cells, also known as NK cells, are a type of cytotoxic lymphocyte critical to the innate immune system. They are a kind of large granular lymphocytes (LGL), and belong to the rapidly expanding family of known innate lymphoid cells (ILC) and represent 5–20% of all circulating lymphocytes in humans. The role of NK cells is analogous to that of cytotoxic T cells in the vertebrate adaptive immune response. NK cells provide rapid responses to virus-infected cells, stressed cells, tumor cells, and other intracellular pathogens based on signals from several activating and inhibitory receptors. Most immune cells detect the antigen presented on MHC class I, major histocompatibility complex I (MHC-I) on infected cell surfaces, but NK cells can recognize and kill stressed cells in the absence of antibodies and MHC, allowing for a much faster immune reaction. They were named "natural killers" because of the notion that they do not require activation to kill cells that are m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
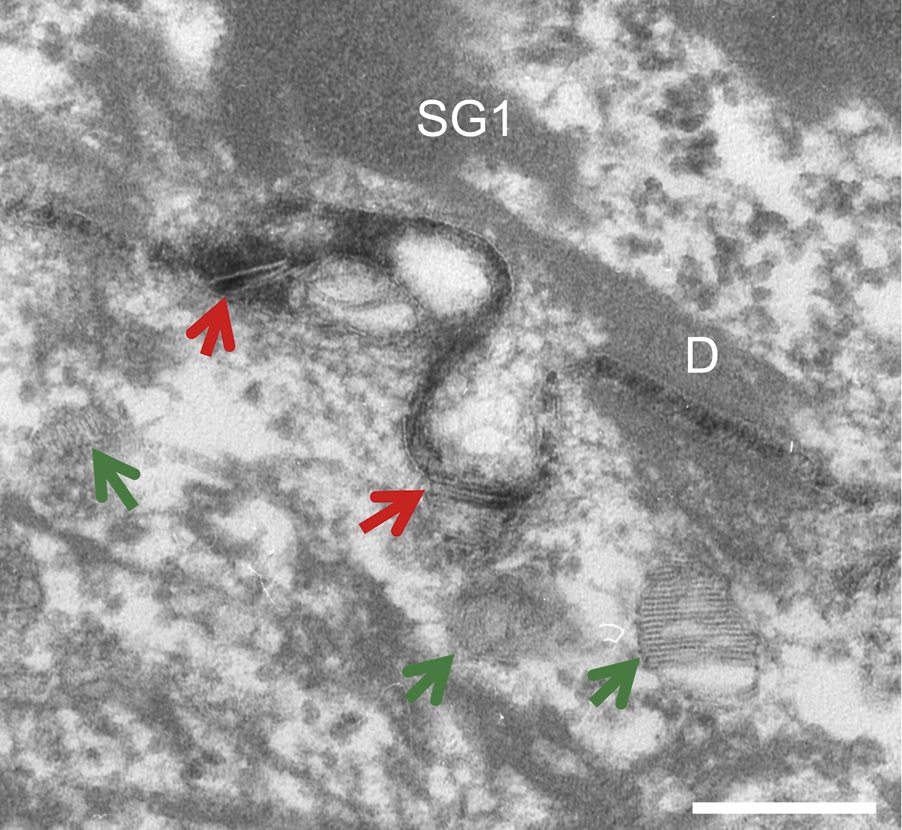
Exocytosis
Exocytosis is a term for the active transport process that transports large molecules from cell to the extracellular area. Hormones, proteins and neurotransmitters are examples of large molecules that can be transported out of the cell. Exocytosis is a crucial transport mechanism that enables polar molecules to flow through the cell membranes’ hydrophobic lipid bilayer. The transport process is essential to hormone secretion, immune response and neurotransmission. Both prokaryotes and eukaryotes undergo exocytosis. Prokaryotes secrete molecules and cellular waste through translocons that are localized to the cell membrane. In addition, they secrete molecules to other cells through specialized organs. Eukaryotes rely on multiple cellular processes to perform the exocytosis process. Eukaryotes have several organelles and a nucleus in the cytoplasm that are connected through multiple transport routes, that is formally known as the secretory pathway. This is a complex pathway with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
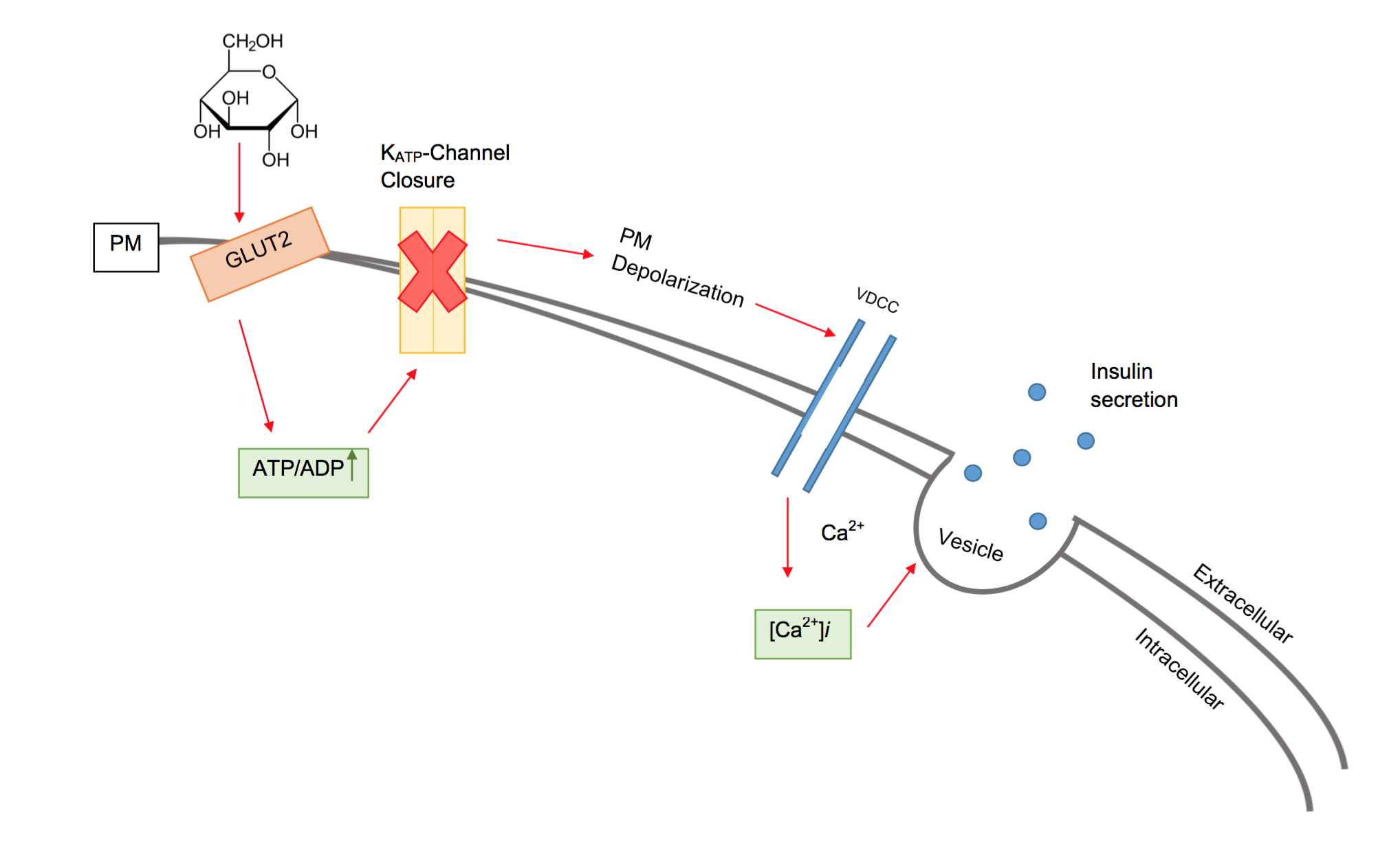
Insulin
Insulin (, from Latin ''insula'', 'island') is a peptide hormone produced by beta cells of the pancreatic islets encoded in humans by the insulin (''INS)'' gene. It is the main Anabolism, anabolic hormone of the body. It regulates the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and protein by promoting the absorption of glucose from the blood into cells of the liver, fat cell, fat, and skeletal muscles. In these tissues the absorbed glucose is converted into either glycogen, via glycogenesis, or Fatty acid metabolism#Glycolytic end products are used in the conversion of carbohydrates into fatty acids, fats (triglycerides), via lipogenesis; in the liver, glucose is converted into both. Glucose production and secretion by the liver are strongly inhibited by high concentrations of insulin in the blood. Circulating insulin also affects the synthesis of proteins in a wide variety of tissues. It is thus an anabolic hormone, promoting the conversion of small molecules in the blood into large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cell
Beta cells (β-cells) are specialized endocrine cells located within the pancreatic islets of Langerhans responsible for the production and release of insulin and amylin. Constituting ~50–70% of cells in human islets, beta cells play a vital role in maintaining blood glucose levels. Problems with beta cells can lead to disorders such as diabetes. Function The function of beta cells is primarily centered around the synthesis and secretion of hormones, particularly insulin and amylin. Both hormones work to keep blood glucose levels within a narrow, healthy range by different mechanisms. Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells, allowing them to use it for energy or store it for future use. Amylin helps regulate the rate at which glucose enters the bloodstream after a meal, slowing down the absorption of nutrients by inhibit gastric emptying. Insulin synthesis Beta cells are the only site of insulin synthesis in mammals. As glucose stimulates insulin secretion, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beta Cell Processed
Beta (, ; uppercase , lowercase , or cursive ; or ) is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals, it has a value of 2. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced bilabial fricative while in borrowed words is instead commonly transcribed as μπ. Letters that arose from beta include the Roman letter and the Cyrillic letters and . Name Like the names of most other Greek letters, the name of beta was adopted from the acrophonic name of the corresponding letter in Phoenician, which was the common Semitic word ('house', compare and ). In Greek, the name was , pronounced in Ancient Greek. It is spelled in modern monotonic orthography and pronounced . History The letter beta was derived from the Phoenician letter beth . The letter Β had the largest number of highly divergent local forms. Besides the standard form (either rounded or pointed, ), there were forms as varied as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lamellar Bodies
In cell biology, lamellar bodies (otherwise known as lamellar granules, membrane-coating granules (MCGs), keratinosomes or Odland bodies) are secretory organelles found in Alveolar cell, type II alveolar cells in the lungs, and in keratinocytes in the skin. They are oblong structures, appearing about 300-400 nm in width and 100-150 nm in length in transmission electron microscopy images. Lamellar bodies in the pulmonary alveolus, alveoli of the lungs fuse with the cell membrane and release pulmonary surfactant into the extracellular space. Role in lungs In alveolar cells the phosphatidylcholines (choline-based phospholipids) that are stored in the lamellar bodies serve as pulmonary surfactant after being exocytosis, released from the cell. In 1964, using transmission electron microscopy, which at that time was a relatively new tool for ultrastructural elucidation, John Balis identified the presence of lamellar bodies in type II alveolar cells, and further noted that u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CC-BY Icon
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work". A CC license is used when an author wants to give other people the right to share, use, and build upon a work that the author has created. CC provides an author flexibility (for example, they might choose to allow only non-commercial uses of a given work) and protects the people who use or redistribute an author's work from concerns of copyright infringement as long as they abide by the conditions that are specified in the license by which the author distributes the work. There are several types of Creative Commons licenses. Each license differs by several combinations that condition the terms of distribution. They were initially released on December 16, 2002, by Creative Commons, a U.S. non-profit corporation founded in 2001. There have also been five versions of the suite of licenses, numbered 1.0 through 4.0. Released in November ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelet Alpha-granule
Alpha granules, (α-granules) also known as platelet alpha-granules are a cellular component of platelets. Platelets contain different types of granules that perform different functions, and include alpha granules, dense granules, and lysosomes. Of these, alpha granules are the most common, making up 50% to 80% of the secretory granules. Alpha granules contain several growth factors. Contents Contents include insulin-like growth factor 1, platelet-derived growth factors, TGF beta, platelet factor 4 (which is a heparin-binding chemokine) and other clotting proteins (such as thrombospondin, fibronectin, factor V, and von Willebrand factor). The alpha granules express the adhesion molecule P-selectin and CD63. These are transferred to the membrane after synthesis. The other type of granules within platelets are called dense granules. Clinical significance A deficiency of alpha granules is known as gray platelet syndrome Gray platelet syndrome (GPS), or platelet alpha-granule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dense Granule
Dense granules (also known as dense bodies or delta granules) are specialized secretory organelles. Dense granules are found only in platelets and are smaller than alpha granules.Michelson, A. D. (2013). ''Platelets'' (Vol. 3rd ed). Amsterdam: Academic Press. The origin of these dense granules is still unknown, however, it is thought that may come from the mechanism involving the endocytotic pathway.Ambrosio, A. L., Boyle, J. A., & Di Pietro, S. M. (2012). Mechanism of platelet dense granule biogenesis: study of cargo transport and function of Rab32 and Rab38 in a model system. ''Blood'', ''120''(19), 4072–4081. Dense granules are a sub group of lysosome-related organelles (LRO). There are about three to eight of these in a normal human platelet.McNicol, A., & Israels, S. J. (1999). ''Platelet dense granules: Structure, function and implications for haemostasis'' In unicellular organisms They are found in animals and in unicellular organisms including Apicomplexa protozoans. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platelets
Platelets or thrombocytes () are a part of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping to form a blood clot. Platelets have no cell nucleus; they are fragments of cytoplasm from megakaryocytes which reside in bone marrow or lung tissue, and then enter the circulation. Platelets are found only in mammals, whereas in other vertebrates (e.g. birds, amphibians), thrombocytes circulate as intact mononuclear cells. One major function of platelets is to contribute to hemostasis: the process of stopping bleeding at the site where the lining of vessels (endothelium) has been interrupted. Platelets gather at the site and, unless the interruption is physically too large, they plug the hole. First, platelets attach to substances outside the interrupted endothelium: ''adhesion''. Second, they change shape, turn on receptors and secrete chemical messengers: ''activation''. Third, they connect to each other throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Degranulation
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial, cytotoxic, or other molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells. It is used by several different cells involved in the immune system, including granulocytes (neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, and mast cells). It is also used by certain lymphocytes such as natural killer (NK) cells and cytotoxic T cells, whose main purpose is to destroy invading microorganisms. Mast cells Degranulation in mast cells is part of an inflammatory response, and substances such as histamine are released. Granules from mast cells mediate processes such as "vasodilation, vascular homeostasis, innate and adaptive immune responses, angiogenesis, and venom detoxification." Antigens interact with IgE molecules already bound to high affinity Fc receptors on the surface of mast cells to induce degranulation, via the activation of tyrosine kinases within the cell. The mast cell releases a mixture of compoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |