|
Grammatical Conjugation
In linguistics, conjugation ( ) is the creation of derived forms of a verb from its principal parts by inflection (alteration of form according to rules of grammar). For instance, the verb ''break'' can be conjugated to form the words ''break'', ''breaks'', and ''broke''. While English has a relatively simple conjugation, other languages such as French and Arabic or Spanish are more complex, with each verb having dozens of conjugated forms. Some languages such as Georgian and Basque (some verbs only) have highly complex conjugation systems with hundreds of possible conjugations for every verb. Verbs may inflect for grammatical categories such as person, number, gender, case, tense, aspect, mood, voice, possession, definiteness, politeness, causativity, clusivity, interrogatives, transitivity, valency, polarity, telicity, volition, mirativity, evidentiality, animacy, associativity, pluractionality, and reciprocity. Verbs may also be affected by agreement, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conjugation Of Verb-es
Conjugation or conjugate may refer to: Linguistics * Grammatical conjugation, the modification of a verb from its basic form * Emotive conjugation or Russell's conjugation, the use of loaded language Mathematics * Complex conjugation, the change of sign of the imaginary part of a complex number * Conjugate (square roots), the change of sign of a square root in an expression * Conjugate element (field theory), a generalization of the preceding conjugations to roots of a polynomial of any degree * Conjugate transpose, the complex conjugate of the transpose of a matrix * Harmonic conjugate in complex analysis * Conjugate (graph theory), an alternative term for a line graph, i.e. a graph representing the edge adjacencies of another graph *In group theory, various notions are called conjugation: ** Inner automorphism, a type of conjugation homomorphism ** Conjugacy class in group theory, related to matrix similarity in linear algebra ** Conjugation (group theory), the image of an el ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Case
A grammatical case is a category of nouns and noun modifiers (determiners, adjectives, participles, and Numeral (linguistics), numerals) that corresponds to one or more potential grammatical functions for a Nominal group (functional grammar), nominal group in a wording. In various languages, nominal groups consisting of a noun and its modifiers belong to one of a few such categories. For instance, in English language, English, one says ''I see them'' and ''they see me'': the nominative case, nominative pronouns ''I/they'' represent the perceiver, and the accusative case, accusative pronouns ''me/them'' represent the phenomenon perceived. Here, nominative and accusative are cases, that is, categories of pronouns corresponding to the functions they have in representation. English has largely lost its inflected case system but personal pronouns still have three cases, which are simplified forms of the nominative, accusative (including functions formerly handled by the Dative case, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affirmation And Negation
In linguistics and grammar, affirmation ( abbreviated ) and negation () are ways in which grammar encodes positive and negative polarity into verb phrases, clauses, or utterances. An affirmative (positive) form is used to express the validity or truth of a basic assertion, while a negative form expresses its falsity. For example, the affirmative sentence "Joe is here" asserts that it is true that Joe is currently located near the speaker. Conversely, the negative sentence "Joe is not here" asserts that it is not true that Joe is currently located near the speaker. The grammatical category associated with affirmatives and negatives is called polarity. This means that a clause, sentence, verb phrase, etc. may be said to have either affirmative or negative polarity (its polarity may be either affirmative or negative). Affirmative is typically the unmarked polarity, whereas a negative statement is marked in some way. Negative polarity can be indicated by negating words or particle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valency (linguistics)
In linguistics, valency or valence is the number and type of arguments and complements controlled by a predicate, content verbs being typical predicates. Valency is related, though not identical, to subcategorization and transitivity, which count only object arguments – valency counts all arguments, including the subject. The linguistic meaning of valency derives from the definition of valency in chemistry. Like valency found in chemistry, there is the binding of specific elements. In the grammatical theory of valency, the verbs organize sentences by binding the specific elements. Examples of elements that would be bound would be the complement and the actant. Although the term originates from valence in chemistry, linguistic valency has a close analogy in mathematics under the term arity. The valency metaphor appeared first in linguistics in Charles Sanders Peirce's essay "The Logic of Relatives" in 1897, and it then surfaced in the works of a number of linguists decade ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transitivity (grammar)
Transitivity is a linguistics property that relates to whether a verb, participle, or gerund denotes a Object (grammar), transitive object. It is closely related to valency (linguistics), valency, which considers other argument (linguistics), arguments in addition to transitive objects. English grammar makes a binary distinction between intransitive verbs (e.g. ''arrive'', ''belong'', or ''die'', which do not denote a transitive object) and transitive verbs (e.g., ''announce'', ''bring'', or ''complete'', which must denote a transitive object). Many languages, including English, have ditransitive verbs that denote two objects, and some verbs may be ambitransitive verb, ambitransitive in a manner that is either transitive (e.g., "I ''read'' the book" or "We ''won'' the game") or intransitive (e.g., "I ''read'' until bedtime" or "We ''won''") depending on the given context. History The notion of transitivity, as well as other notions that today are the basics of linguistics, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogative
An interrogative clause is a clause whose form is typically associated with question-like meanings. For instance, the English sentence (linguistics), sentence "Is Hannah sick?" has interrogative syntax which distinguishes it from its Declarative sentence, declarative counterpart "Hannah is sick". Also, the additional question mark closing the statement assures that the reader is informed of the interrogative mood. Interrogative clauses may sometimes be embedded within a phrase, for example: "Paul knows who is sick", where the interrogative clause "who is sick" serves as complement (linguistics), complement of the embedding verb "know". Languages vary in how they form interrogatives. When a language has a dedicated interrogative inflectional form, it is often referred to as interrogative grammatical mood. Interrogative mood or other interrogative forms may be denoted by the list of glossing abbreviations, glossing abbreviation . Question types Interrogative sentences are generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
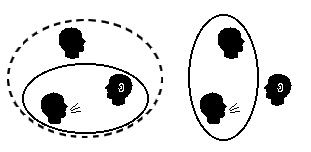
Clusivity
In linguistics, clusivity is a grammatical distinction between ''inclusive'' and ''exclusive'' first-person pronouns and verbal morphology, also called ''inclusive " we"'' and ''exclusive "we"''. Inclusive "we" specifically includes the addressee, while exclusive "we" specifically excludes the addressee; in other words, two (or more) words that both translate to "we", one meaning "you and I, and possibly someone else", the other meaning "me and some other person or persons, but not you". While imagining that this sort of distinction could be made in other persons (particularly the second) is straightforward, in fact the existence of second-person clusivity (you vs. you and they) in natural languages is controversial and not well attested. While clusivity is not a feature of the English language, it is found in many languages around the world. The first published description of the inclusive-exclusive distinction by a European linguist was in a description of languages of Peru in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causative
In linguistics, a causative (abbreviated ) is a valency-increasing operationPayne, Thomas E. (1997). Describing morphosyntax: A guide for field linguists'' Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. p. 173–186. that indicates that a subject either causes someone or something else to do or be something or causes a change in state of a non- volitional event. Normally, it brings in a new argument (the causer), A, into a transitive clause, with the original subject S becoming the object O. All languages have ways to express causation but differ in the means. Most, if not all, languages have specific or ''lexical'' causative forms (such as English ''rise'' → ''raise'', ''lie'' → ''lay'', ''sit'' → ''set''). Some languages also have morphological devices (such as inflection) that change verbs into their causative forms or change adjectives into verbs of ''becoming''. Other languages employ periphrasis, with control verbs, idiomatic expressions or auxiliary verbs. There tends to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Politeness
Politeness is the practical application of good manners or etiquette so as not to offend others and to put them at ease. It is a culturally defined phenomenon, and therefore what is considered polite in one culture can sometimes be quite rude or simply eccentric in another cultural context. While the goal of politeness is to refrain from behaving in an offensive way so as not to offend others, and to make all people feel relaxed and comfortable with one another, these culturally defined standards at times may be broken within the context of personal boundaries – this is known as ''positive politeness''. Types Anthropologists Penelope Brown and Stephen Levinson identified four kinds of politeness, deriving from Erving Goffman's concept of face: # Negative politeness is the act of making a request less infringing, such as "If you don't mind..." or "If it isn't too much trouble..."; respects a person's right to act freely. This is a variety of ''deference''. There is a grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definiteness
In linguistics, definiteness is a semantic feature of noun phrases that distinguishes between referents or senses that are identifiable in a given context (definite noun phrases) and those that are not (indefinite noun phrases). The prototypical definite noun phrase picks out a unique, familiar, specific referent such as ''the sun'' or ''Australia'', as opposed to indefinite examples like ''an idea'' or ''some fish''. There is considerable variation in the expression of definiteness across languages, and some languages such as Japanese do not generally mark it, so the same expression can be definite in some contexts and indefinite in others. In other languages, such as English, it is usually marked by the selection of determiner (e.g., ''the'' vs. ''a''). Still other languages, such as Danish, mark definiteness morphologically by changing the noun itself (e.g. Danish ''en'' ''mand'' (a man), ''manden'' (the man)). Definiteness as a grammatical category There are times whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Possession (linguistics)
In linguistics, possession is an asymmetric relationship between two constituents, the referent of one of which (the possessor) in some sense possesses (owns, has as a part, rules over, etc.) the referent of the other (the possessed). Possession may be marked in many ways, such as simple juxtaposition of nouns, possessive case, possessed case, construct state (as in Arabic and Nêlêmwa), or adpositions ( possessive suffixes, possessive adjectives). For example, English uses a possessive clitic, '' 's''; a preposition, ''of''; and adjectives, ''my'', ''your'', ''his'', ''her'', etc. Predicates denoting possession may be formed either by using a verb (such as the English ''have'') or by other means, such as existential clauses (as is usual in languages such as Russian). Some languages have more than two possessive classes. In Papua New Guinea, for example, the Anêm language has at least 20 and the Amele language has 32. Alienable and inalienable There are many t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Voice
In linguistics, grammaticality is determined by the conformity to language usage as derived by the grammar of a particular speech variety. The notion of grammaticality rose alongside the theory of generative grammar, the goal of which is to formulate rules that define well-formed, grammatical sentences. These rules of grammaticality also provide explanations of ill-formed, ungrammatical sentences. In theoretical linguistics, a speaker's judgement on the well-formedness of a linguistic 'string'—called a grammaticality judgement—is based on whether the sentence is interpreted in accordance with the rules and constraints of the relevant grammar. If the rules and constraints of the particular lect are followed, then the sentence is judged to be grammatical. In contrast, an ungrammatical sentence is one that violates the rules of the given language variety. Linguists use grammaticality judgements to investigate the syntactic structure of sentences. Generative linguists are larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |