|
Governmental Theory Of Atonement
The governmental theory of the atonement (also known as the rectoral theory, or the moral government theory) is a doctrine in Christian theology concerning the meaning and effect of the death of Jesus Christ. It teaches that Christ suffered for humanity so that God could forgive humans without punishing them while still maintaining divine justice. In the modern era, it is more often taught in non-Calvinist Protestant circles, though Arminius, John Wesley, and other Arminians never spoke clearly of it. It is drawn primarily from the works of Hugo Grotius and later theologians such as John Miley and H. Orton Wiley. Definition and terminology Definition Governmental theory holds that Christ's suffering was a real and meaningful substitute for the punishment humans deserve, but it did not consist of Christ's receiving the exact punishment due to sinful people. Instead, God publicly demonstrated his displeasure with sin through the suffering of his own sinless and obedient Son as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Christian Theology
Christian theology is the theology – the systematic study of the divine and religion – of Christianity, Christian belief and practice. It concentrates primarily upon the texts of the Old Testament and of the New Testament, as well as on Christian tradition. Christian theologians use biblical exegesis, rationality, rational analysis and argument. Theologians may undertake the study of Christian theology for a variety of reasons, such as in order to: * help them better understand Christian tenets * make comparative religion, comparisons between Christianity and other traditions * Christian apologetics, defend Christianity against objections and criticism * facilitate reforms in the Christian church * assist in the evangelism, propagation of Christianity * draw on the resources of the Christian tradition to address some present situation or perceived need * education in Christian philosophy, especially in Neoplatonism, Neoplatonic philosophyLouth, Andrew. The Origins of the Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
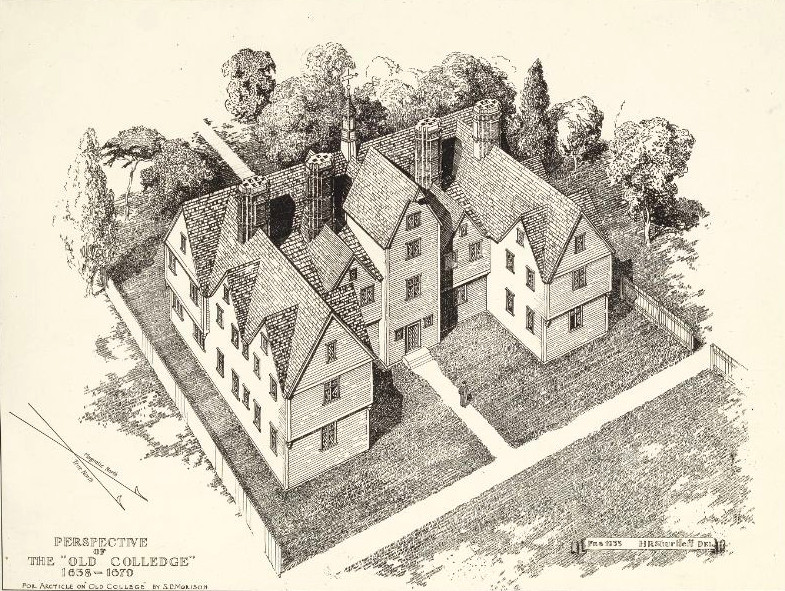
Harvard College
Harvard College is the undergraduate education, undergraduate college of Harvard University, a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Part of the Harvard Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Faculty of Arts and Sciences, Harvard College is Harvard University's traditional undergraduate program, offering BA (Bachelor of Arts) and BS (Bachelor of Science) degrees. It is highly selective, with fewer than four percent of applicants being offered admission as of 2022. Harvard College students participate in over 450 extracurricular organizations and nearly all live on campus. First-year students reside in or near Harvard Yard while upperclass students reside in other on-campus housing. History Harvard College was founded in 1636 by vote of the Massachusetts General Court, Great and General Court of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. Two years later, the college became home to North America's first known printing press, carri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
William Booth
William Booth (10 April 1829 – 20 August 1912) was an English Methodist preacher who, along with his wife, Catherine, founded the Salvation Army and became its first General (1878–1912). This Christian movement, founded in 1865, has a quasi-military structure and government and has spread from London to many parts of the world. It is one of the largest distributors of humanitarian aid. Early life William Booth was born in Sneinton, Nottingham, the second son of five children born to Samuel Booth and his second wife, Mary Moss. His birthplace is now a museum. Booth's father was a nailmaker and builder from Belper in Derbyshire but, during William's childhood, the family descended into poverty. In 1842, Samuel Booth, who could no longer afford his son's school fees, apprenticed the 13-year-old William to a pawnbroker. Samuel Booth died on 23 September 1842. Two years into his apprenticeship Booth had a religious conversion. He then read extensively and trained himself in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Penal Substitution
Penal substitution, also called penal substitutionary atonement and especially in older writings forensic theory,Vincent Taylor (theologian), Vincent Taylor, ''The Cross of Christ'' (London: Macmillan & Co, 1956), pp. 71–72: '...the ''four main types'', which have persisted throughout the centuries. The oldest theory is the ''Ransom Theory''...It held sway for a thousand years. ... The ''Forensic Theory'' is that of the Reformers and their successors.' is a theory of the Atonement in Christianity, atonement within Protestantism, Protestant Christian theology, which declares that Christ, voluntarily submitting to God the Father's plan, was punished (penalized) in the place of (substitution) sinners, thus Atonement (satisfaction view), satisfying the demands of justice and propitiation, so God can justly forgive sins making us at one with God (atonement). It began with the German Reformation leader Martin Luther and continued to develop within the Calvinism, Calvinist traditionJ. I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a Protestant Christianity, Christian Christian tradition, tradition whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's brother Charles Wesley were also significant early leaders in the movement. They were named ''Methodists'' for "the methodical way in which they carried out their Christian faith". Methodism originated as a Christian revival, revival movement within Anglicanism with roots in the Church of England in the 18th century and became a separate denomination after Wesley's death. The movement spread throughout the British Empire, the United States and beyond because of vigorous Christian mission, missionary work, and today has about 80 million adherents worldwide. Most List of Methodist denominations, Methodist denominations are members of the World Methodist Council. Wesleyan theology, which is upheld by the Methodist denominations, focuses on Sanc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Moral Influence Theory Of Atonement
A moral (from Latin ''morālis'') is a message that is conveyed or a lesson to be learned from a story or event. The moral may be left to the hearer, reader, or viewer to determine for themselves, or may be explicitly encapsulated in a maxim. A moral is a lesson in a story or real life. Finding morals As an example of an explicit maxim, at the end of Aesop's fable of the Tortoise and the Hare, in which the plodding and determined tortoise won a race against the much-faster yet extremely arrogant hare, the stated moral is "slow and steady wins the race". However, other morals can often be taken from the story itself; for instance, that arrogance or overconfidence in one's abilities may lead to failure or the loss of an event, race, or contest. The use of stock characters is a means of conveying the moral of the story by eliminating the complexity of personality and depicting the issues arising in the interplay between the characters, enabling the writer to generate a clear me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Charles Grandison Finney
Charles Grandison Finney (August 29, 1792 – August 16, 1875) was a controversial American Presbyterian minister and leader in the Second Great Awakening in the United States. He has been called the "Father of Old Christian revival, Revivalism". Finney rejected much of traditional Reformed theology. Finney was best known as a passionate revivalist preacher from 1825 to 1835 in the Burned-over District in Upstate New York and Manhattan, an opponent of Old School Presbyterian theology, an advocate of Christian perfectionism, and a religious writer. His religious views led him, together with several other evangelical leaders, to promote social reforms, such as abolitionism and equal education for women and African Americans. From 1835 he taught at Oberlin College of Ohio, which accepted students without regard to race or sex. He served as its second president from 1851 to 1865, and its faculty and students were activists for abolitionism, the Underground Railroad, and universal e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Revival Meeting
A revival meeting is a series of Christian religious services held to inspire active members of a church body to gain new converts and to call sinners to repent. Those who lead revival services are known as revivalists (or evangelists). Nineteenth-century Baptist preacher Charles Spurgeon said, "Many blessings may come to the unconverted in consequence of a revival among Christians, but the revival itself has to do only with those who already possess spiritual life." These meetings are usually conducted by churches or missionary organizations throughout the world. Notable historic revival meetings were conducted in the United States by evangelist Billy Sunday and in Wales by evangelist Evan Roberts. Revival services occur in local churches, brush arbor revivals, tent revivals, and camp meetings. Meetings A revival meeting usually consists of several consecutive nights of services conducted at the same time and location, most often the building belonging to the sponsoring co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jonathan Edwards (the Younger)
Jonathan Edwards (May 26, 1745 – August 1, 1801) was an American theologian and linguist. Life and career Born in Northampton, Massachusetts Bay, he was the ninth child and second son of Jonathan Edwards and Sarah (Pierpont) Edwards. In 1751, the family moved to Stockbridge, Massachusetts, where his exposure to language variation began. Both of Edwards' parents died during the year of 1758. He graduated from Princeton in 1765, after which he studied theology under Joseph Bellamy of Bethlehem, Connecticut. He was a tutor at Princeton from 1767 to 1769, and a pastor in New Haven, Connecticut from 1769 to 1795, where he was dismissed from this position due to doctrinal conflicts in the church. Despite this dismissal, he was called back to another church in Colebrook, Connecticut that same year. After serving as pastor in Colebrook, Connecticut from 1795 to 1799, he moved to Schenectady, New York, to serve as the president of Union College. Edwards died on August 1, 1801, and w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Jonathan Edwards (theologian)
Jonathan Edwards (October 5, 1703 – March 22, 1758) was an American Christian revival, revivalist preacher, philosopher, and Congregationalism in the United States, Congregationalist theologian. Edwards is widely regarded as one of America's most important and original philosophical theologians. Edwards' theological work is broad in scope but rooted in the Puritans, Puritan heritage as exemplified in the Westminster Confession of Faith, Westminster and Savoy Declaration, Savoy Confessions of Faith. Recent studies have emphasized how thoroughly Edwards grounded his life's work on conceptions of beauty, harmony, and ethical aptness, and how central the Age of Enlightenment was to his mindset. Edwards played a critical role in shaping the First Great Awakening and oversaw some of the first Christian revival, revivals in 1733–35 at First Church of Christ (Northampton, Massachusetts), his church in Northampton, Massachusetts. His work gave rise to a doctrine known as New England ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Calvinism
Reformed Christianity, also called Calvinism, is a major branch of Protestantism that began during the 16th-century Protestant Reformation. In the modern day, it is largely represented by the Continental Reformed Christian, Presbyterian, Congregational, and Waldensians traditions, as well as parts of the Methodist, Anglican (known as "Episcopal" in some regions) and Baptist traditions. Reformed theology emphasizes the authority of the Bible and the sovereignty of God, as well as covenant theology, a framework for understanding the Bible based on God's covenants with people. Reformed churches emphasize simplicity in worship. Several forms of ecclesiastical polity are exercised by Reformed churches, including presbyterian, congregational, and some episcopal. Articulated by John Calvin, the Reformed faith holds to a spiritual (pneumatic) presence of Christ in the Lord's Supper. Emerging in the 16th century, the Reformed tradition developed over several genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |