|
Gospel Of The Ebionites
The Gospel of the Ebionites is the conventional name given by scholars to an apocryphal gospel extant only as seven brief quotations in a heresiology known as the '' Panarion'', by Epiphanius of Salamis; he misidentified it as the "Hebrew" gospel, believing it to be a truncated and modified version of the Gospel of Matthew. The quotations were embedded in a polemic to point out inconsistencies in the beliefs and practices of a Jewish Christian sect known as the Ebionites relative to Nicene orthodoxy. The surviving fragments derive from a gospel harmony of the Synoptic Gospels, composed in Greek with various expansions and abridgments reflecting the theology of the writer. Distinctive features include the absence of the virgin birth and of the genealogy of Jesus; an Adoptionist Christology, in which Jesus is chosen to be God's Son at the time of his Baptism; the abolition of the Jewish sacrifices by Jesus; and an advocacy of vegetarianism. The omission of the genealo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christology
In Christianity, Christology is a branch of Christian theology, theology that concerns Jesus. Different denominations have different opinions on questions such as whether Jesus was human, divine, or both, and as a messiah what his role would be in the freeing of the Jewish people from foreign rulers or in the prophesied Kingdom of God (Christianity), Kingdom of God, and in the Salvation in Christianity, salvation from what would otherwise be the consequences of sin. The earliest Christian writings gave several titles to Jesus, such as Son of Man, Son of God, Messiah, and , which were all derived from Hebrew scripture. These terms centered around two opposing themes, namely "Jesus as a Pre-existence of Christ, preexistent figure who Incarnation (Christianity), becomes human and then Session of Christ, returns to God", versus adoptionism – that Jesus was a human who was "adopted" by God at his baptism, crucifixion, or resurrection. Prior to 2007, the scholarly consensus was tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of The Twelve
The ''Gospel of the Twelve'' (), possibly also referred to as the ''Gospel of the Apostles'', is a lost gospel mentioned by Origen in '' Homilies on Luke'' as part of a list of heretical works. Schneemelcher's standard edition of the ''New Testament Apocrypha'' states that Jerome incorrectly identified the ''Gospel of the Twelve'', which he referred to as the ''Gospel according to the Apostles'', with the Gospel of the Hebrews (''Dial. adv. Pelag. III 2''), whereas Origen clearly distinguished between them (''Homilies on Luke'' 1.1). Ambrose and Bede may have also made allusions to it. A relationship has been postulated between this otherwise unknown gospel and the Gospel of the Ebionites The Gospel of the Ebionites is the conventional name given by scholars to an apocryphal gospel extant only as seven brief quotations in a heresiology known as the '' Panarion'', by Epiphanius of Salamis; he misidentified it as the "Hebrew" ...., p.166 - "Against Jerome, ... Origen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
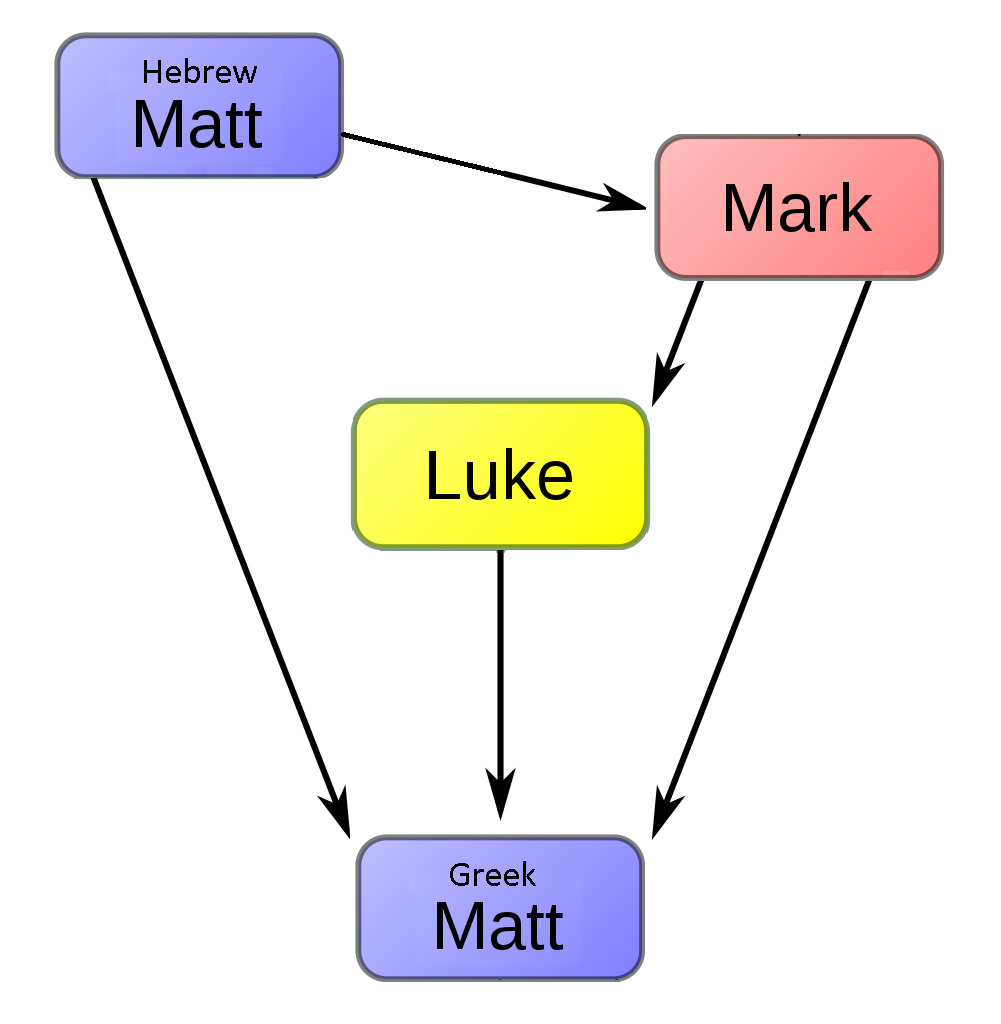
Hebrew Gospel Hypothesis
The Hebrew Gospel hypothesis (''proto-Gospel hypothesis'' or ''Aramaic Matthew hypothesis'') is that a lost gospel, written in Hebrew or Aramaic, predated the four canonical gospels. In the 18th and early 19th century several scholars suggested that a Hebrew proto-gospel (a so-called Ur-Gospel) was the main source or one of several sources for the canonical gospels. This theorizing would later give birth to the two source-hypothesis that views Q as a proto-gospel but believes this proto-gospel to have been written in Koine Greek. After the widespread scholarly acceptance of the two-source hypothesis, scholarly interest in the Hebrew gospel hypothesis dwindled. Modern variants of the Hebrew gospel hypothesis survive, but have not found favor with scholars as a whole. The foundation of the Hebrew gospel hypothesis is usually an early Christian tradition from the 2nd-century bishop Papias of Hierapolis. According to Papias, Matthew the Apostle was the first to compose a gospel, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Fathers
The Church Fathers, Early Church Fathers, Christian Fathers, or Fathers of the Church were ancient and influential Christian theologians and writers who established the intellectual and doctrinal foundations of Christianity. The historical period in which they worked became known as the Patristics, Patristic Era and spans approximately from the late 1st to mid-8th centuries, flourishing in particular during the 4th and 5th centuries, when Christianity was in the process of establishing itself as the State church of the Roman Empire, state church of the Roman Empire. For many denominations of Christianity, the writings of the Ante-Nicene Fathers, Nicene Fathers and Christianity in the 5th century#Post-Nicene Fathers, Post-Nicene Fathers are included in Sacred tradition, Sacred Tradition. As such, in traditional dogmatic theology, authors considered Church Fathers are treated as authoritative for the establishment of doctrine. The academic field of patristics, the study of the Chu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of The Nazarenes
The Gospel of the Nazarenes (also ''Nazareans'', ''Nazaraeans'', ''Nazoreans'', or ''Nazoraeans'') is the traditional but hypothetical name given by some scholars to distinguish some of the references to, or citations of, non- canonical Jewish-Christian Gospels extant in patristic writings from other citations believed to derive from different Gospels. Collation into ''Gospel of the Nazarenes'' Due to contradictions in the account of the baptism of Jesus, and other reasons, most scholars in the 20th century consider that the ''Gospel of the Nazarenes'' is distinct from the '' Gospel of the Hebrews'' and '' Gospel of the Ebionites'', even though Jerome linked the Nazarenes to the Ebionites in their shared use of the ''Gospel of the Hebrews''. Text editions of ''Gospel of the Nazarenes'' The current standard critical edition of the text is found in Wilhelm Schneemelcher's ''New Testament Apocrypha'', where 36 verses, GN 1 to GN 36, are collated. GN 1 to GN 23 are mainly from J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gospel Of The Hebrews
The Gospel of the Hebrews (), or Gospel according to the Hebrews, is a lost Jewish–Christian gospel. The text of the gospel is lost, with only fragments of it surviving as brief quotations by the early Church Fathers and in apocryphal writings. The fragments contain traditions of Jesus' pre-existence, incarnation, baptism, and probably of his temptation, along with some of his sayings. Distinctive features include a Christology characterized by the belief that the Holy Spirit is Jesus' Divine Mother and a first resurrection appearance to James, the brother of Jesus, showing high regard for James as the leader of the Jewish Christian church in Jerusalem. It was probably composed in Greek in the first decades of the 2nd century and is believed to have been used by Greek-speaking Jewish Christians in Egypt during that century. The Gospel of the Hebrews is the only Jewish–Christian gospel that the Church Fathers referred to by name, believing there was only one Hebrew Gos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish-Christian Gospels
Jewish Christians were the followers of a Jewish religious sect that emerged in Roman Judea during the late Second Temple period, under the Herodian tetrarchy (1st century AD). These Jews believed that Jesus was the prophesied Messiah and they continued their adherence to Jewish law. Jewish Christianity is the historical foundation of Early Christianity, which later developed into Nicene Christianity (which comprises the Roman Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Protestant traditions) and other Christian denominations. Christianity started with Jewish eschatological expectations, and it developed into the worship of Jesus as the result of his earthly ministry in Galilee and Jerusalem, his crucifixion, and the post-resurrection experiences of his followers. Jewish Christians drifted apart from Second Temple Judaism, and their form of Judaism eventually became a minority strand within mainstream Judaism, as it had almost disappeared by the 5th century AD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Christianity
Early Christianity, otherwise called the Early Church or Paleo-Christianity, describes the History of Christianity, historical era of the Christianity, Christian religion up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325. Spread of Christianity, Christianity spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to History of the Jews in the Roman Empire, already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewish diaspora throughout the Eastern Mediterranean. The first followers of Christianity were Jews who had Proselyte, converted to the faith, i.e. Jewish Christians, as well as Phoenicia, Phoenicians, i.e. Christianity in Lebanon, Lebanese Christians. Early Christianity contains the Apostolic Age and is followed by, and substantially overlaps with, the Patristic era. The Apostolic sees claim to have been founded by one or more of the Apostles in the New Testament, apostles of Jesus, who are said to have Dispersion of the A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perea
Perea or Peraea (Greek: Περαία, " the country beyond") was the term used mainly during the early Roman period for part of ancient Transjordan. It lay broadly east of Judea and Samaria, which were situated on the western side of the Jordan River, and southwest of the Decapolis. Perea was part of the kingdom of Herod the Great and his descendants, and later of subsequent Roman provinces that included Iudaea. Geography Perea was a slender piece of land east of the Jordan River. It stretched from Wadi Yabis in the north to Wadi Mujib (Nahal Arnon) in the south. The region extended from the Jordan River westwards to the foothills eastward towards Amman (then known as Philadelphia). Josephus notes that Perea's northern boundary was near Pella, while to the east, it bordered the territories of Gerasa and Philadelphia (both part of the Decapolis) and Heshbon. To the south, it was adjacent to the Land of Moab, with Machaerus marking its southernmost fortress. Encompassing r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Albertus Klijn
Albertus Frederik Johannes Klijn (17 April 1923 – 30 May 2012) was a Dutch scholar of the New Testament and early Judaism and Christianity at the Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. He was best known for his introductory work on the New Testament, and then later for his publications on early Christian apocryphal literature. Klijn studied theology at Rijksuniversiteit Utrecht, and submitted his doctoral dissertation in 1949 on the "Western" Text of the Gospels and Acts. In 1951 he became a Reformed pastor in Heinkenszand, Zeeland. Four years later he began teaching, returning to the University of Utrecht as a lecturer. In 1967 Klijn was appointed professor of early Christian literature and interpretation of the New Testament at the Rijksuniversiteit Groningen. It was at Groningen that he began to specialize in second-temple Jewish pseudepigrapha and in early Christian literature. Klijn was the editor of the series "De prediking van het Nieuwe Testament: Een theologische comme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vegetarianism
Vegetarianism is the practice of abstaining from the Eating, consumption of meat (red meat, poultry, seafood, insects as food, insects, and the flesh of any other animal). It may also include abstaining from eating all by-products of animal slaughter. A person who practices vegetarianism is known as a vegetarian. Vegetarianism may be adopted for various reasons. Many people ethics of eating meat, object to eating meat out of respect for Sentience, sentient animal life. Such ethical motivations have been codified vegetarianism and religion, under various religious beliefs as well as animal rights advocacy. Other motivations for vegetarianism are health-related, political, Environmental vegetarianism, environmental, cultural, aesthetic, Economic vegetarianism, economic, gastronomy, taste-related, or relate to other personality psychology, personal preferences. A small number of towns and cities around the world are exclusively vegetarian or have outlawed meat, including Rishikesh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |