|
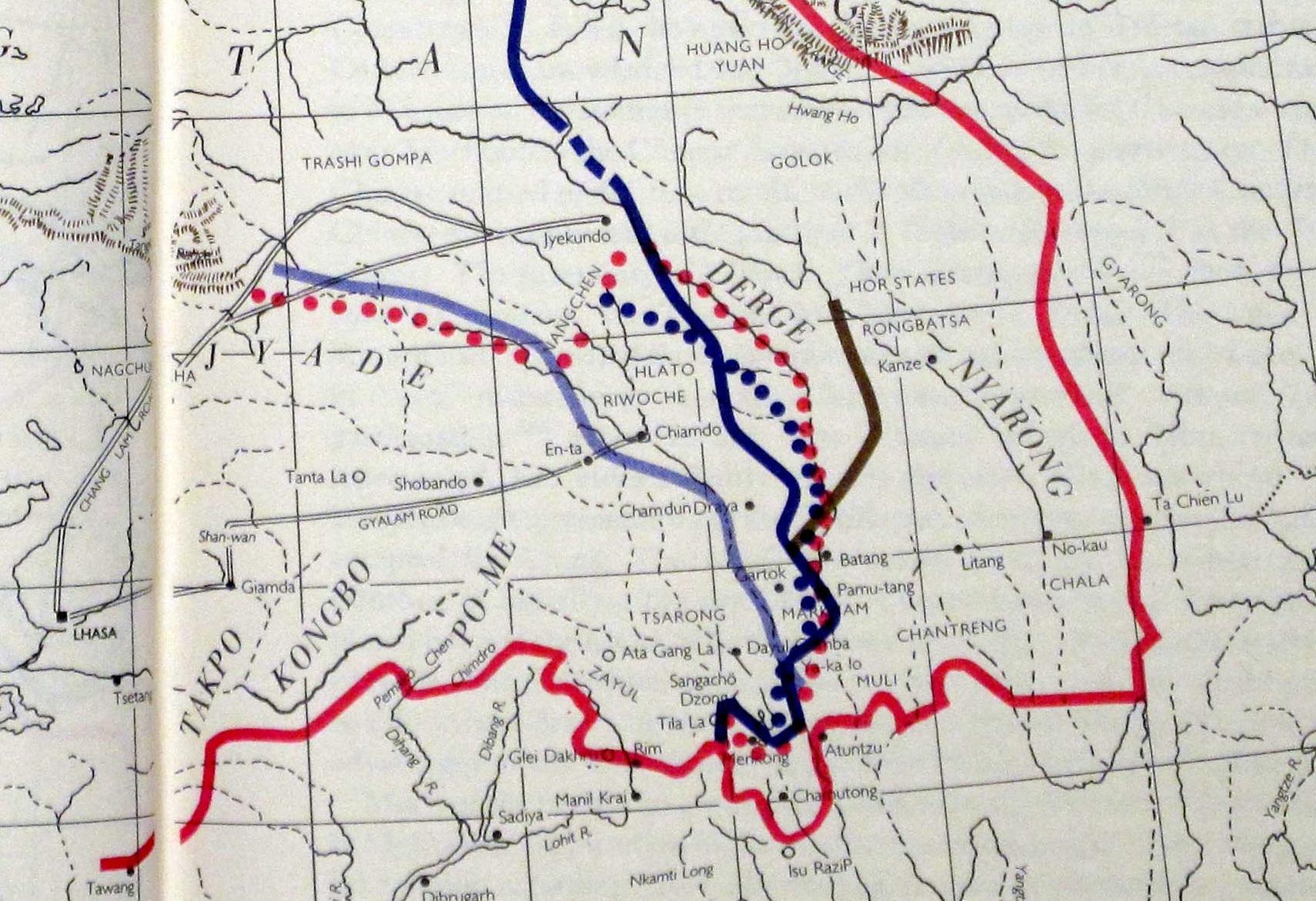
Golok Conflicts (1917–1949)
The Ma clique fought a series of military campaigns between 1917 and 1949 against unconquered Amchok and Ngolok (Golok) tribal Tibetan areas of Qinghai (Amdo), undertaken by two Hui commanders, Gen. Ma Qi and Gen. Ma Bufang, on behalf of the Beiyang and Kuomintang governments of the Republic of China. The campaigns lasted between 1917 and 1949. The conflict was spurred by multiple factors, notably for economic and socio-political reasons (including intertribal tensions) rather than by any racial or religious enmity. The war General Ma Qi was a Hui Chinese commander who joined the Kuomintang after the Northern Expedition in 1927–1928. His forces were composed entirely of Hui Chinese, organized in the Ninghai Army, which was then turned into a National Revolutionary Army division. Battles for Labrang Ma Qi occupied Labrang Monastery in 1917, the first time non-Tibetans had seized it. Ma Qi defeated the Tibetan forces with his Hui Chinese troops. His forces were praised by f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai
Qinghai is an inland Provinces of China, province in Northwestern China. It is the largest provinces of China, province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Hui people, Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese language, Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat language, Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibetans
Tibetans () are an East Asian ethnic group native to Tibet. Their current population is estimated to be around 7.7 million. In addition to the majority living in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, significant numbers of Tibetans live in the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Qinghai, Sichuan, and Yunnan, as well as in Bhutan, India, and Nepal. The Tibetic languages belong to the Tibeto-Burman language group. The traditional or mythological explanation of the Tibetan people's origin is that they are the descendants of the human Pha Trelgen Changchup Sempa and rock ogress Ma Drag Sinmo. It is thought that most of the Tibeto-Burman speakers in southwest China, including Tibetans, are direct descendants from the ancient Qiang people. Most Tibetans practice Tibetan Buddhism, although a significant minority observe the Indigenous Bon religion. There are also smaller communities of Tibetan Muslims and Christians. Tibetan Buddhism influences Tibetan art, drama and architecture, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai Province
Qinghai is an inland province in Northwestern China. It is the largest province of China (excluding autonomous regions) by area and has the third smallest population. Its capital and largest city is Xining. Qinghai borders Gansu on the northeast, Xinjiang on the northwest, Sichuan on the southeast and the Tibet Autonomous Region on the southwest. Qinghai province was established in 1928 during the period of the Republic of China, and until 1949 was ruled by Chinese Muslim warlords known as the Ma clique. The Chinese name "Qinghai" is after Qinghai Lake, the largest lake in China. The lake is known as Tso ngon in Tibetan, and as Kokonor Lake in English, derived from the Mongol Oirat name for Qinghai Lake. Both Tso ngon and Kokonor are names found in historic documents to describe the region.Gangchen Khishong, 2001. ''Tibet and Manchu: An Assessment of Tibet-Manchu Relations in Five Phases of Development''. Dharmasala: Narthang Press, p.1-70. Located mostly on the Tibetan P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yushu Batang Airport
Yushu Batang Airport is an airport serving Yushu City in Qinghai Province, China. It is located 18 kilometers to the south of the city center, Gyêgu, at the 3,890 meters elevation about the sea level, which makes it the highest civilian airport in Qinghai Province, and one of the highest in the world. The construction of the airport started in 2007. The first aircraft landed at the new airport on May 29, 2009, and the airport was officially opened on August 1, 2009. Yushu Batang Airport has a 3,800 meter-long runway, and can receive A319 aircraft. The passenger terminal is designed to serve up to 80,000 passengers per year. According to the CAAC statistics, the airport served 7,484 passengers during 2009, the first (incomplete) year of its operation. The airport played an important role in the delivery of rescue personnel and relief supplies to the area affected by the 2010 Yushu earthquake. The facility was re-opened at noon on the day of the earthquake (Wednesday, April ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xikang Province
Xikang (formerly romanized as Sikang or Hsikang, or 'Kham to the west f Sichuan) was a nominal province formed by the Republic of China (1912–1949)">Republic of China in 1939 on the initiative of prominent Sichuan warlord Liu Wenhui and retained by the early China, People's Republic of China. The former territory of Xikang is now divided between the Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) and Sichuan, Sichuan province. The idea behind Xikang province was to form a single unified province for the entire Kham region under direct Chinese administration, in effect annexing the western Kham region that was then under Tibetan control. Kham was entirely populated by Tibetan people called Khampas. The then-independent Tibet controlled the portion of Kham west of the Upper Yangtze River. The nominal Xikang province also included in the south the Assam Himalayan region (Arunachal Pradesh) that Tibet had recognised as a part of British India by the 1914 McMahon Line agreement. The eastern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture
Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture (, zh, s=玉树藏族自治州, p=Yùshù Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu, retranscribed into Tibetan as ), also transliterated as Yüxü or Yulshul, is an autonomous prefecture of Southwestern Qinghai Province, China. Largely inhabited by Tibetans, the prefecture has an area of and its seat is located in the town of Gyêgu in Yushu County, which is the place of the old Tibetan trade mart of Jyekundo. The official source of the Yellow River lies within the prefecture. Historically, the area belongs to the cultural realm of Kham in Eastern Tibet. On 14 April 2010, an earthquake struck the prefecture, registering a magnitude of 6.9 (USGS, EMSC) or 7.1About 400 dead, 10,000 injured in 7. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qinghai–Tibet War
The Qinghai–Tibet War or the Tsinghai–Tibet War was a conflict that took place during the Sino-Tibetan War. The 13th Dalai Lama wanted to expand the original conflict taking place between the Tibetan Army and Liu Wenhui (Sichuan clique) in Xikang, to attack Qinghai, a region northeast of Tibet. Using a dispute over a monastery in Yushu in Qinghai as an excuse in 1932, the Tibetan army attacked. Qinghai Muslim General Ma Bufang overran the Tibetan armies and recaptured several counties in Xikang province. Shiqu, Dege and other counties were seized from the Tibetans. The war against the Tibetan army was led by the Muslim General Ma Biao. The Tibetans were pushed back to the other side of the Jinsha river. The Qinghai army recaptured counties that had been controlled by the Tibetan army since 1919. The victory on the part of the Qinghai army threatened the supply lines to Tibetan forces in Garze and Xinlong. As a result, this part of the Tibetan army was forced to w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Golog
Golog (Golok or Guoluo) Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture ( zh, c=果洛藏族自治州 , p=Guǒluò Zàngzú Zìzhìzhōu; ) is an autonomous prefecture occupying the southeastern corner of Qinghai province, China. The prefecture has an area of and its seat is located in Maqên County. Due to its special geographical location and natural environment, the entire autonomous preference has been included in the Chinese largest natural environmental protection area — the Sanjiangyuan National Park. Geography Golog Prefecture is located in the southeastern part of Qinghai, in the upper basin of the Yellow River. Gyaring Lake and Ngoring Lake on the western edge of the prefecture are considered to be the source of the Yellow River. However, these lakes do receive water from rivers that flow from locations even further west, in Qumarleb County of the Yushu Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture. The lay of the land of the prefecture is largely determined by the Amne Machin mountain range ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet (1912–1951)
Tibet () was a Limited recognition, ''de facto'' independent state in East Asia that lasted from the collapse of the Qing dynasty in 1912 until its Annexation of Tibet by the People's Republic of China, annexation by the People's Republic of China in 1951.; The Tibetan Ganden Phodrang regime was a Tibet under Qing rule, protectorate under Qing rule until 1910 when the Qing dynasty decided to assert greater control over the region. In 1912 the Provisional Government of the Republic of China (1912), provisional government of the Republic of China (ROC) succeeded the Qing and received an Imperial Edict of the Abdication of the Qing Emperor, imperial edict inheriting the claims over all of its territories. However, the newly formed ROC was unable to assert any real authority in Tibet. The 13th Dalai Lama declared that Tibet's relationship with China ended with the fall of the Qing dynasty and proclaimed independence, although this was not formally recognized by other countries. Tibe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General
A general officer is an Officer (armed forces), officer of high rank in the army, armies, and in some nations' air force, air and space forces, marines or naval infantry. In some usages, the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED Online. March 2021. Oxford University Press. https://www.oed.com/view/Entry/77489?rskey=dCKrg4&result=1 (accessed May 11, 2021) The adjective ''general'' had been affixed to officer designations since the late medieval period to indicate relative superiority or an extended jurisdiction. French Revolutionary system Arab system Other variations Other nomenclatures for general officers include the titles and ranks: * Adjutant general * Commandant-General, Commandant-general * Inspector general * General-in-chief * General of the Air Force (USAF only) * General of the Armies, General of the Armies of the United States (of America), a title created for General John J. Pershing, and subsequently grante ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiahe
Xiahe County ( zh, s=夏河县; ) is a county in Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture, Gansu province, China, bordering Qinghai province to the west. The name (both Chinese and Tibetan), which literally means "Xia River", refers to the Daxia River which runs through the county. It is home to the famed Labrang Tibetan Buddhist monastery, one of the largest Tibetan Buddhist monasteries outside the Tibet Autonomous Region. The town is populated largely by ethnic Tibetans, as well as some Hui and Han Chinese. The area is highly rural and pastoral (including yak and other animal rearing). The geography is mountainous. In recent years it has become a tourist attraction. The county was named Xiahe in 1928, after the Daxia River that flows through its territory. History Xiahe (Sangqu) used to be part of Qinghai when it was under the control of Chinese Muslim General Ma Qi. It was the site of bloody battles between Muslim and Tibetan forces. In 1980, Xiahe mandible, a hominin fossil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Rock
Joseph Francis Charles Rock (1884 – 1962) was an Austrian-American botanist, List of explorers, explorer, geographer, linguistics, linguist, ethnographer and photographer. Life Josef Franz Karl Rock was born in Vienna, Austria, the son of a steward of a Polish count. As a result of a generally unhappy childhood and his father's determination that he become a priest, Rock set off on a wandering life in late adolescence. After a few precarious years traveling around Europe, he emigrated to the United States in 1905. He eventually ended up in Honolulu, Hawaii, in 1907, where he would remain for 13 years. Although Rock had no tertiary education, a fact about which he was sensitive and often dissembled, he had a remarkable capability for foreign languages; by the time he reached Hawaii he had a reasonable command of more than half a dozen, including Chinese. Hawaii (1907-1920) Initially Rock taught Latin and natural history at Mills College (now known as Mid-Pacific Institute). Wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |