|
Glass Harmonica
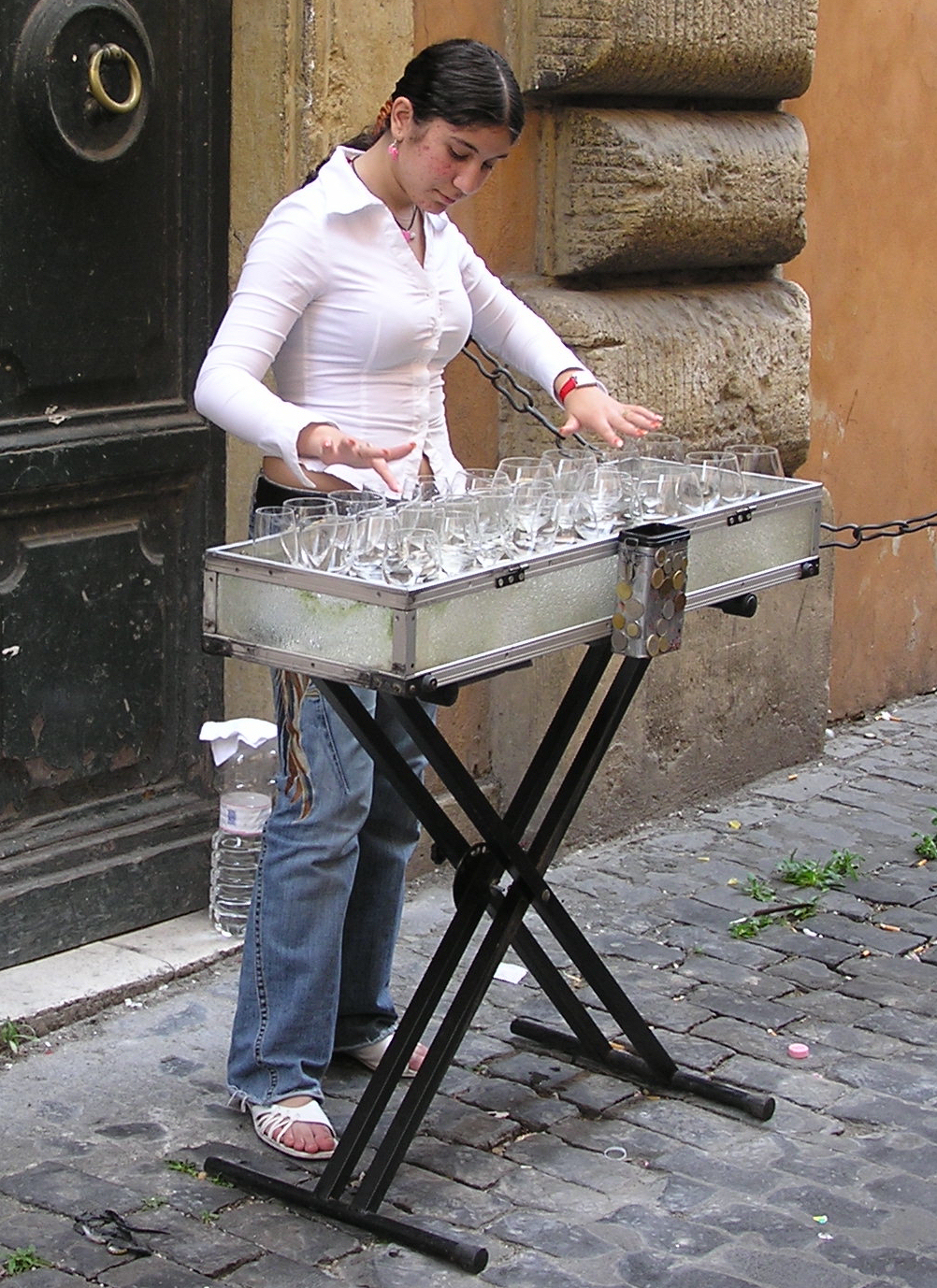
The glass harmonica, also known as the glass armonica, glass harmonium, bowl organ, hydrocrystalophone, or simply the armonica or harmonica (derived from , ''harmonia'', the Greek language, Greek word for harmony), is a type of musical instrument that uses a series of glass bowl (vessel), bowls or goblets graduated in size to produce musical pitch (music), tones by means of friction (instruments of this type are known as friction idiophones). It was invented in 1761 by Benjamin Franklin. Nomenclature The name "glass harmonica" (also "glass armonica", "glassharmonica"; ''harmonica de verre'', ''harmonica de Franklin'', ''armonica de verre'', or just ''harmonica'' in French; ''Glasharmonika'' in German; ''harmonica'' in Dutch) refers today to any instrument played by rubbing glass or crystal goblets or bowls. The alternative instrument consisting of a set of wine glasses (usually tuned with water) is generally known in English as "musical glasses" or the "glass harp". When Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Page 674 (A Dictionary Of Music And Musicians-Volume 1)
Page most commonly refers to: * Page (paper), one side of a leaf of paper, as in a book Page, PAGE, pages, or paging may also refer to: Roles * Page (assistance occupation), a professional occupation * Page (servant), traditionally a young male servant * Page (wedding attendant) People and fictional characters * Page (given name), a list of people * Page (surname), a list of people and fictional characters * Pages (surname) * H. A. Page, a pen name of Scottish author Alexander Hay Japp (1836–1905) Places Australia * Page, Australian Capital Territory, a suburb of Canberra * Division of Page, New South Wales * Pages River, a tributary of the Hunter River catchment in New South Wales, Australia * The Pages, South Australia, two islands and a reef **The Pages Conservation Park, a protected area in South Australia United States * Page, Arizona, a city * Page, Indiana * Page, Minneapolis, Minnesota, a neighborhood * Page, Nebraska, a village * Page, North Dakota, a city * Page, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) is a Periodization, period of history and a European cultural movement covering the 15th and 16th centuries. It marked the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and was characterized by an effort to revive and surpass the ideas and achievements of classical antiquity. Associated with great social change in most fields and disciplines, including Renaissance art, art, Renaissance architecture, architecture, politics, Renaissance literature, literature, Renaissance exploration, exploration and Science in the Renaissance, science, the Renaissance was first centered in the Republic of Florence, then spread to the Italian Renaissance, rest of Italy and later throughout Europe. The term ''rinascita'' ("rebirth") first appeared in ''Lives of the Artists'' () by Giorgio Vasari, while the corresponding French word was adopted into English as the term for this period during the 1830s. The Renaissance's intellectual basis was founded in its version of Renaiss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
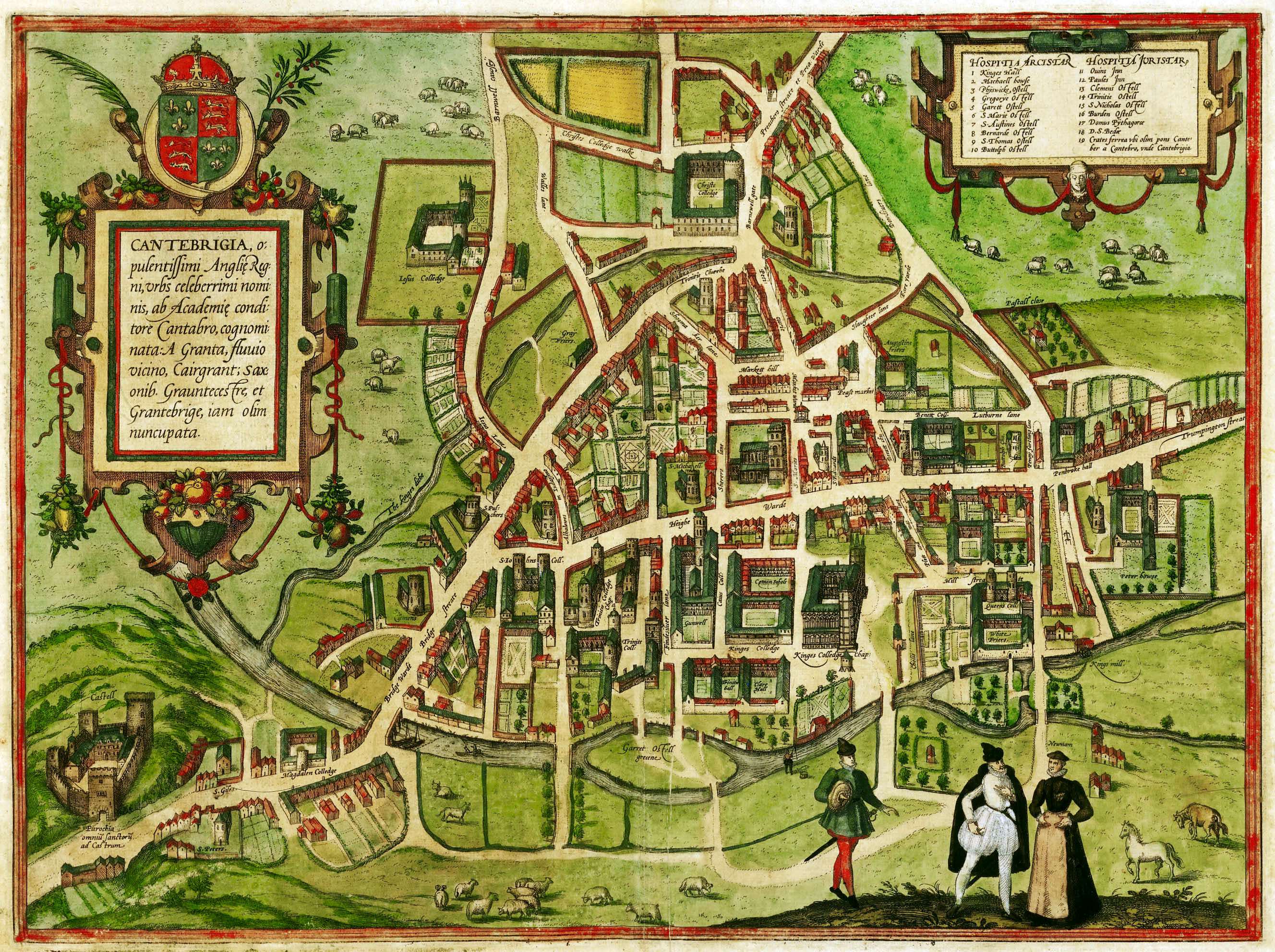
Cambridge
Cambridge ( ) is a List of cities in the United Kingdom, city and non-metropolitan district in the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It is the county town of Cambridgeshire and is located on the River Cam, north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of the City of Cambridge was 145,700; the population of the wider built-up area (which extends outside the city council area) was 181,137. (2021 census) There is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age, and Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman Britain, Roman and Viking eras. The first Town charter#Municipal charters, town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is well known as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wikimedia Commons
Wikimedia Commons, or simply Commons, is a wiki-based Digital library, media repository of Open content, free-to-use images, sounds, videos and other media. It is a project of the Wikimedia Foundation. Files from Wikimedia Commons can be used across all of the Wikimedia projects in all languages, including Wikipedia, Wikivoyage, Wikisource, Wikiquote, Wiktionary, Wikinews, Wikibooks and Wikispecies, and can also be downloaded for offsite use. As of April 2025, the repository contains over 120 million free-to-use media files, managed and editable by registered volunteers.commons:Special:Statistics, Statistics page on Wikimedia Commons History The idea for the project came from Erik Möller in March 2004 and Wikimedia Commons was started on September 7, 2004. In July 2013, the number of edits on Commons reached 100,000,000. In 2018, it became possible to upload 3D models to the site in STL (file format), STL format. One of the first models uploaded to Commons was a reconstruc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Bell & Sons
George Bell & Sons was an English book publishing house. It was based in London and existed from 1839 to 1986. History George Bell & Sons was founded by George Bell as an educational bookseller, with the intention of selling the output of London university presses; but became best known as an independent publisher of classics and children's books. One of Bell's first investments in publishing was a series of ''Railway Companions''; that is, booklets of timetables and tourist guides. Within a year Bell's publishing business had outstripped his retail business, and he elected to move from his original offices into Fleet Street. There G. Bell & Sons branched into the publication of books on art, architecture, and archaeology, in addition to the classics for which the company was already known. Bell's reputation was only improved by his association with Henry Cole. In the mid-1850s, Bell expanded again, printing the children's books of Margaret Gatty (''Parables from Nature' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pembroke College, Cambridge
Pembroke College is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge, England. The college is the third-oldest college of the university and has over 700 students and fellows. It is one of the university's larger colleges, with buildings from almost every century since its founding, as well as extensive gardens. Its members are termed "Valencians". The college's current master is Chris Smith, Baron Smith of Finsbury. Pembroke has a level of academic performance among the highest of all the Cambridge colleges; in 2013, 2014, 2016, and 2018 Pembroke was placed second in the Tompkins Table. Pembroke contains the first chapel designed by Sir Christopher Wren and is one of only six Cambridge colleges to have educated a British prime minister, in Pembroke's case William Pitt the Younger. The college library, with a Victorian neo-gothic clock tower, has an original copy of the first encyclopaedia to contain printed diagrams. History Marie de St Pol, Countess of Pembroke (1303� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Brown (academic)
James Brown (1709–1784) was an English cleric and academic. He was Master of Pembroke College, Cambridge from 1770 until his death. A close friend of Thomas Gray, he acted with William Mason as executor of Gray's will. Life His father was a London goldsmith. He was educated at Christ's Hospital, and matriculated at Pembroke College in 1726, graduating B.A. in 1730 and M.A. in 1733. He became a Fellow of Pembroke in 1735. Ordained as Anglican priest in 1736, he became vicar of Shepreth from 1737. He was Vice-Chancellor of the University of Cambridge in 1771-2. From 1771 he was vicar of Stretham Stretham Locally, the is a glottal stop: or even is a village and civil parish south-south-west of Ely, Cambridgeshire, Ely in Cambridgeshire, England, about by road from London. Its main attraction is Stretham Old Engine, a steam engine, .... References *Robert L. Mack, ''Thomas Gray: A Life'' Notes {{DEFAULTSORT:Brown, James 1709 births 1784 deaths 18th-century E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Gray
Thomas Gray (26 December 1716 – 30 July 1771) was an English poet, letter-writer, and classics, classical scholar at Cambridge University, being a fellow first of Peterhouse then of Pembroke College, Cambridge, Pembroke College. He is widely known for his ''Elegy Written in a Country Churchyard,'' published in 1751. Gray was a Self-criticism, self-critical writer who published only 13 poems in his lifetime, despite being very popular. He was even offered the position of Poet laureate, Poet Laureate in 1757 after the death of Colley Cibber, though he declined. Early life and education Thomas Gray was born in Cornhill, London. His father, Philip Gray, was a scrivener and his mother, Dorothy Antrobus, was a milliner. He was the fifth of twelve children, and the only one to survive infancy.John D. Baird, 'Gray, Thomas (1716–1771)', ''Oxford Dictionary of National Biography'' (Oxford University Press, 2004Accessed 21 February 2012/ref> An 1803 newspaper article including a biog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christoph Willibald Gluck
Christoph Willibald (Ritter von) Gluck (; ; 2 July 1714 – 15 November 1787) was a composer of Italian and French opera in the early classical period (music), classical period. Born in the Upper Palatinate and raised in Bohemia, both part of the Holy Roman Empire at the time, he gained prominence at the House of Habsburg, Habsburg court in Vienna. There he brought about the practical reform of opera's dramaturgical practices for which many intellectuals had been campaigning. With a series of radical new works in the 1760s, among them ''Orfeo ed Euridice'' and ''Alceste (Gluck), Alceste'', he broke the stranglehold that Metastasio, Metastasian ''opera seria'' had enjoyed for much of the century. Gluck introduced more drama by using orchestral recitative and cutting the usually long da capo aria. His later operas have half the length of a typical baroque opera. The strong influence of French opera encouraged Gluck to move to Paris in November 1773. Fusing the traditions of Italian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, recognising excellence in science, supporting outstanding science, providing scientific advice for policy, education and public engagement and fostering international and global co-operation. Founded on 28 November 1660, it was granted a royal charter by Charles II of England, King Charles II and is the oldest continuously existing scientific academy in the world. The society is governed by its Council, which is chaired by the society's president, according to a set of statutes and standing orders. The members of Council and the president are elected from and by its Fellows, the basic members of the society, who are themselves elected by existing Fellows. , there are about 1,700 fellows, allowed to use the postnominal title FRS (Fellow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward Delaval
Edward Hussey Delaval (born 1729; died 14 August 1814 in Westminster) was a British scholar and natural philosopher. Life He was the third son of Francis Blake Delaval and his wife Rhoda Apreece. He was educated at Pembroke College, Cambridge, admitted in 1747; he graduated B.A. in 1750, M.A. in 1754, and became a Fellow there in 1755. There also he knew the poet Thomas Gray. Delaval inherited both Seaton Delaval Hall in Northumberland and Doddington Hall in Lincolnshire, but preferred to live in London. He died at the age of 85 and was buried in Westminster Abbey. Works Delaval shared the 1766 Copley Medal where he was cited for his research on metals and glass. His interest in glass included its use in music. His performances on musical glasses became well-known, and may have inspired Benjamin Franklin Benjamin Franklin (April 17, 1790) was an American polymath: a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher and Political philosophy, politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |